Modern databases don’t run on a single box anymore. They span regions, replicate data across nodes, and serve millions of queries in parallel.
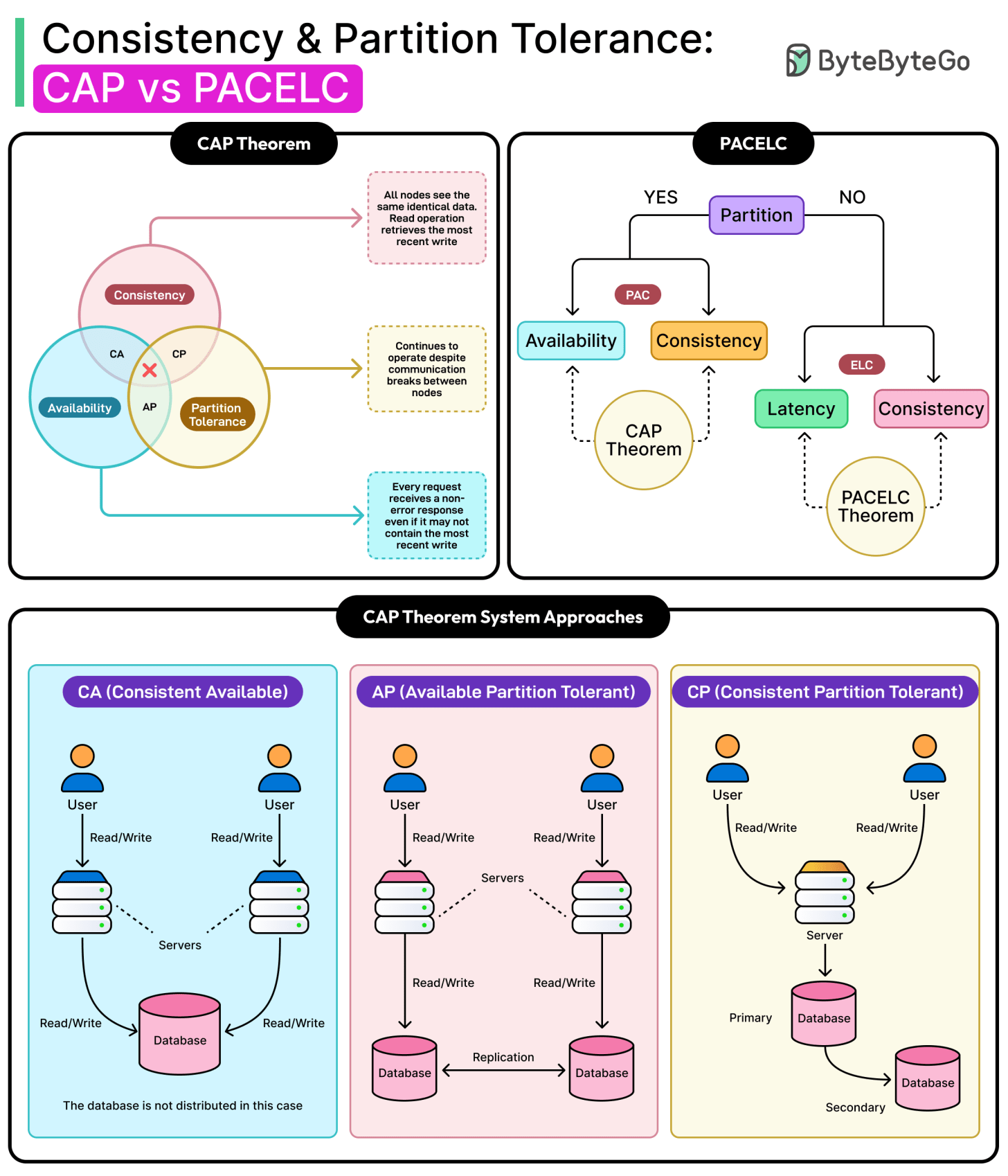
However, every time a database tries to be fast, available, and correct at once, something has to give. As systems scale, the promise of fault tolerance collides with the need for correctness. For example, a checkout service can’t afford to double-charge a user just because a node dropped off the network. But halting the system every time a replica lags can break the illusion of availability. Latency, replica lag, and network partitions are not edge cases.
Distributed databases have to manage these trade-offs constantly. For example,
A write request might succeed in one region but not another.
A read might return stale data unless explicitly told to wait.
Some systems optimize for uptime and accept inconsistencies. Others block until replicas agree, sacrificing speed to maintain correctness.
Two models help make sense of this: the CAP theorem and the PACELC theorem. CAP explains why databases must choose between staying available and staying consistent in the presence of network partitions. PACELC extends that reasoning to the normal case: even without failure, databases still trade latency for consistency.
In this article, we will look at these two models as they apply to real-world database design and understand the various trade-offs involved.