高性能MCP服务器架构设计:并发、缓存与监控
🌟 Hello,我是摘星!🌈 在彩虹般绚烂的技术栈中,我是那个永不停歇的色彩收集者。
🦋 每一个优化都是我培育的花朵,每一个特性都是我放飞的蝴蝶。
🔬 每一次代码审查都是我的显微镜观察,每一次重构都是我的化学实验。
🎵 在编程的交响乐中,我既是指挥家也是演奏者。让我们一起,在技术的音乐厅里,奏响属于程序员的华美乐章。
摘要
作为一名深耕AI技术领域多年的博主摘星,我深刻认识到随着Model Context Protocol(MCP)在AI生态系统中的广泛应用,高性能服务器架构设计已成为确保系统稳定性和用户体验的关键因素。在当今AI应用爆发式增长的背景下,MCP服务器面临着前所未有的并发压力和性能挑战。从我多年的实践经验来看,一个优秀的MCP服务器架构不仅需要处理大量并发请求,还要保证数据的一致性、系统的可扩展性以及故障的快速恢复能力。本文将深入探讨高并发场景下的MCP服务器架构设计原则,包括连接池管理与资源复用策略、分布式缓存与数据一致性保障机制,以及全方位的性能监控与故障诊断体系。通过系统性的架构分析和实践案例分享,我希望能够为广大开发者提供一套完整的高性能MCP服务器构建方案,帮助大家在面对复杂的生产环境时能够游刃有余地设计出既稳定又高效的系统架构。1. 高并发场景下的架构设计
1.1 并发模型选择
在高并发MCP服务器设计中,选择合适的并发模型是架构成功的基础。import asyncioimport aiohttpfrom concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutorfrom typing import Dict, List, Optionalimport loggingclass MCPServerConcurrencyManager: """MCP服务器并发管理器""" def __init__(self, max_workers: int = 100, max_connections: int = 1000): self.max_workers = max_workers self.max_connections = max_connections self.thread_pool = ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=max_workers) self.semaphore = asyncio.Semaphore(max_connections) self.active_connections = 0 async def handle_request(self, request_handler, *args, **kwargs): """处理并发请求""" async with self.semaphore: self.active_connections += 1 try: # 异步处理请求 result = await request_handler(*args, **kwargs) return result except Exception as e: logging.error(f"Request handling error: {e}") raise finally: self.active_connections -= 1 async def cpu_intensive_task(self, task_func, *args, **kwargs): """处理CPU密集型任务""" loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() return await loop.run_in_executor( self.thread_pool, task_func, *args, **kwargs )1.2 负载均衡策略
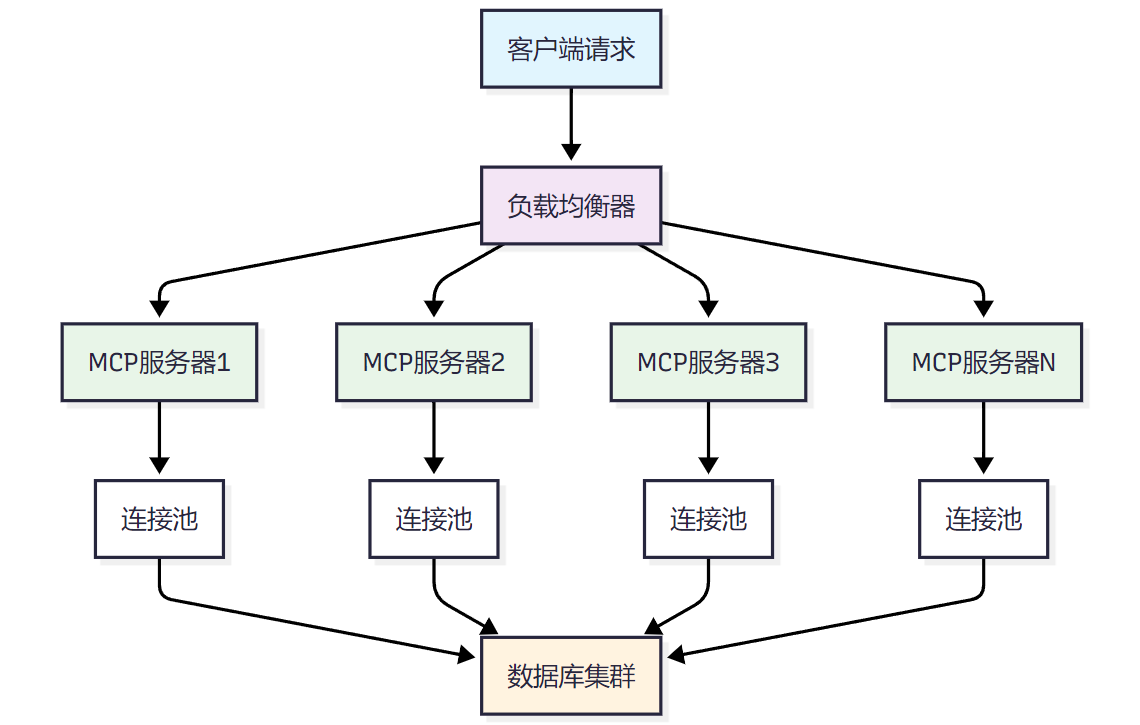图1 MCP服务器负载均衡架构图
1.3 异步处理架构
```pythonclass AsyncMCPServer: """异步MCP服务器实现"""def __init__(self, config: Dict): self.config = config self.request_queue = asyncio.Queue(maxsize=10000) self.worker_tasks = [] self.metrics = { 'requests_processed': 0, 'errors_count': 0, 'average_response_time': 0 }async def start_workers(self, num_workers: int = 10): """启动工作协程""" for i in range(num_workers): task = asyncio.create_task(self.worker(f"worker-{i}")) self.worker_tasks.append(task)async def worker(self, worker_id: str): """工作协程处理请求""" while True: try: request = await self.request_queue.get() start_time = asyncio.get_event_loop().time() # 处理请求 result = await self.process_request(request) # 更新指标 end_time = asyncio.get_event_loop().time() self.update_metrics(end_time - start_time) self.request_queue.task_done() except Exception as e: logging.error(f"Worker {worker_id} error: {e}") self.metrics['errors_count'] += 1async def process_request(self, request): """处理单个请求""" # 实现具体的请求处理逻辑 await asyncio.sleep(0.01) # 模拟处理时间 return {"status": "success", "data": "processed"}def update_metrics(self, response_time: float): """更新性能指标""" self.metrics['requests_processed'] += 1 current_avg = self.metrics['average_response_time'] count = self.metrics['requests_processed'] self.metrics['average_response_time'] = ( (current_avg * (count - 1) + response_time) / count )<h2 id="WhogI">2. 连接池管理与资源复用</h2><h3 id="xQ7iO">2.1 数据库连接池设计</h3>```pythonimport asyncpgfrom typing import Optionalimport timeclass DatabaseConnectionPool: """数据库连接池管理器""" def __init__(self, dsn: str, min_size: int = 10, max_size: int = 100): self.dsn = dsn self.min_size = min_size self.max_size = max_size self.pool: Optional[asyncpg.Pool] = None self.connection_stats = { 'active_connections': 0, 'total_connections': 0, 'connection_errors': 0 } async def initialize(self): """初始化连接池""" try: self.pool = await asyncpg.create_pool( self.dsn, min_size=self.min_size, max_size=self.max_size, command_timeout=60, server_settings={ 'jit': 'off', 'application_name': 'mcp_server' } ) logging.info(f"Database pool initialized: {self.min_size}-{self.max_size}") except Exception as e: logging.error(f"Failed to initialize database pool: {e}") raise async def execute_query(self, query: str, *args): """执行查询""" if not self.pool: raise RuntimeError("Connection pool not initialized") start_time = time.time() try: async with self.pool.acquire() as connection: self.connection_stats['active_connections'] += 1 result = await connection.fetch(query, *args) return result except Exception as e: self.connection_stats['connection_errors'] += 1 logging.error(f"Query execution error: {e}") raise finally: self.connection_stats['active_connections'] -= 1 execution_time = time.time() - start_time logging.debug(f"Query executed in {execution_time:.3f}s") async def get_pool_status(self) -> Dict: """获取连接池状态""" if not self.pool: return {"status": "not_initialized"} return { "size": self.pool.get_size(), "min_size": self.pool.get_min_size(), "max_size": self.pool.get_max_size(), "idle_connections": self.pool.get_idle_size(), "active_connections": self.connection_stats['active_connections'], "total_connections": self.connection_stats['total_connections'], "connection_errors": self.connection_stats['connection_errors'] }2.2 HTTP连接池优化
```pythonimport aiohttpfrom aiohttp import ClientTimeout, TCPConnectorclass HTTPConnectionManager:"""HTTP连接管理器"""
def __init__(self): self.connector = TCPConnector( limit=1000, # 总连接数限制 limit_per_host=100, # 每个主机连接数限制 ttl_dns_cache=300, # DNS缓存TTL use_dns_cache=True, keepalive_timeout=30, enable_cleanup_closed=True ) self.timeout = ClientTimeout( total=30, # 总超时时间 connect=10, # 连接超时时间 sock_read=10 # 读取超时时间 ) self.session = Noneasync def initialize(self): """初始化HTTP会话""" self.session = aiohttp.ClientSession( connector=self.connector, timeout=self.timeout, headers={'User-Agent': 'MCP-Server/1.0'} )async def make_request(self, method: str, url: str, **kwargs): """发起HTTP请求""" if not self.session: await self.initialize() try: async with self.session.request(method, url, **kwargs) as response: return await response.json() except aiohttp.ClientError as e: logging.error(f"HTTP request error: {e}") raiseasync def close(self): """关闭连接""" if self.session: await self.session.close()<h3 id="p7M7Y">2.3 资源复用策略对比</h3>| 资源类型 | 复用策略 | 优势 | 劣势 | 适用场景 || --- | --- | --- | --- | --- || 数据库连接 | 连接池 | 减少连接开销,提高并发性能 | 占用内存,需要管理连接状态 | 高频数据库访问 || HTTP连接 | Keep-Alive | 减少TCP握手开销 | 长时间占用连接 | 频繁API调用 || 线程池 | 线程复用 | 避免线程创建销毁开销 | 线程切换成本 | CPU密集型任务 || 内存缓存 | 对象池 | 减少GC压力 | 内存占用增加 | 频繁对象创建 |<h2 id="f0zPx">3. 分布式缓存与数据一致性</h2><h3 id="jMZiQ">3.1 Redis集群缓存架构</h3>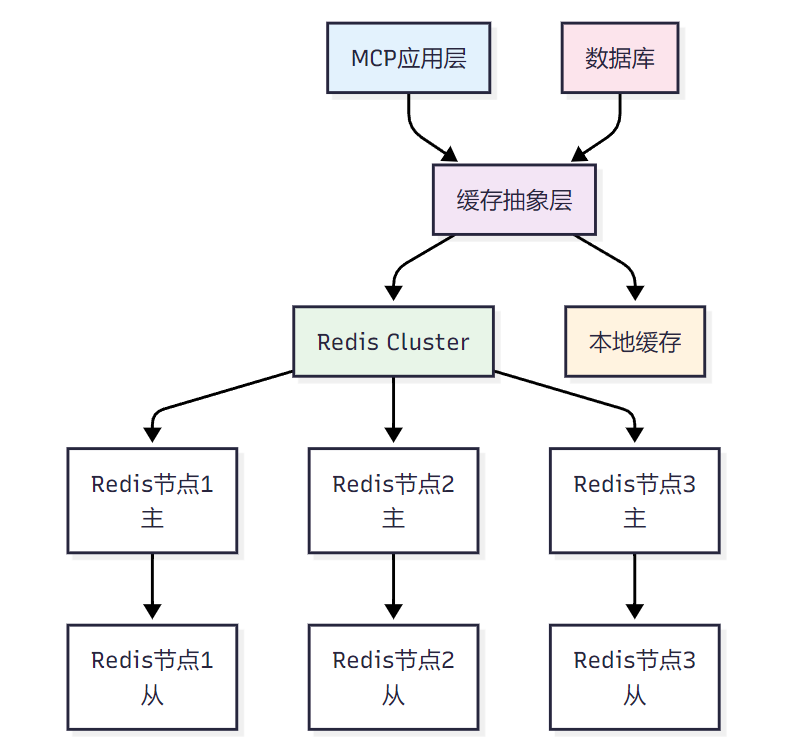**图2 分布式缓存架构图**<h3 id="Q85hN">3.2 缓存一致性实现</h3>```pythonimport redis.asyncio as redisimport jsonimport hashlibfrom typing import Any, Optional, Dictfrom enum import Enumclass CacheConsistencyStrategy(Enum): """缓存一致性策略""" WRITE_THROUGH = "write_through" # 写穿透 WRITE_BEHIND = "write_behind" # 写回 WRITE_AROUND = "write_around" # 写绕过class DistributedCacheManager: """分布式缓存管理器""" def __init__(self, redis_cluster_nodes: List[Dict], strategy: CacheConsistencyStrategy): self.redis_cluster = redis.RedisCluster( startup_nodes=redis_cluster_nodes, decode_responses=True, skip_full_coverage_check=True, health_check_interval=30 ) self.strategy = strategy self.local_cache = {} # 本地缓存 self.cache_stats = { 'hits': 0, 'misses': 0, 'writes': 0, 'errors': 0 } def _generate_cache_key(self, namespace: str, key: str) -> str: """生成缓存键""" return f"{namespace}:{hashlib.md5(key.encode()).hexdigest()}" async def get(self, namespace: str, key: str) -> Optional[Any]: """获取缓存数据""" cache_key = self._generate_cache_key(namespace, key) try: # 先检查本地缓存 if cache_key in self.local_cache: self.cache_stats['hits'] += 1 return self.local_cache[cache_key] # 检查Redis缓存 data = await self.redis_cluster.get(cache_key) if data: parsed_data = json.loads(data) # 更新本地缓存 self.local_cache[cache_key] = parsed_data self.cache_stats['hits'] += 1 return parsed_data self.cache_stats['misses'] += 1 return None except Exception as e: logging.error(f"Cache get error: {e}") self.cache_stats['errors'] += 1 return None async def set(self, namespace: str, key: str, value: Any, ttl: int = 3600): """设置缓存数据""" cache_key = self._generate_cache_key(namespace, key) try: serialized_value = json.dumps(value) if self.strategy == CacheConsistencyStrategy.WRITE_THROUGH: # 写穿透:同时写入缓存和数据库 await self.redis_cluster.setex(cache_key, ttl, serialized_value) self.local_cache[cache_key] = value elif self.strategy == CacheConsistencyStrategy.WRITE_BEHIND: # 写回:先写入缓存,异步写入数据库 self.local_cache[cache_key] = value asyncio.create_task( self.redis_cluster.setex(cache_key, ttl, serialized_value) ) self.cache_stats['writes'] += 1 except Exception as e: logging.error(f"Cache set error: {e}") self.cache_stats['errors'] += 1 async def invalidate(self, namespace: str, key: str): """失效缓存""" cache_key = self._generate_cache_key(namespace, key) try: # 删除本地缓存 self.local_cache.pop(cache_key, None) # 删除Redis缓存 await self.redis_cluster.delete(cache_key) except Exception as e: logging.error(f"Cache invalidation error: {e}") def get_cache_stats(self) -> Dict: """获取缓存统计信息""" total_requests = self.cache_stats['hits'] + self.cache_stats['misses'] hit_rate = (self.cache_stats['hits'] / total_requests * 100) if total_requests > 0 else 0 return { 'hit_rate': f"{hit_rate:.2f}%", 'total_requests': total_requests, **self.cache_stats }3.3 数据一致性保障机制
```pythonimport asynciofrom typing import Callable, Anyfrom dataclasses import dataclassfrom datetime import datetime, timedelta@dataclassclass ConsistencyEvent:"""一致性事件"""event_type: strnamespace: strkey: strtimestamp: datetimedata: Any = None
class EventualConsistencyManager:"""最终一致性管理器"""
def __init__(self, cache_manager: DistributedCacheManager): self.cache_manager = cache_manager self.event_queue = asyncio.Queue() self.subscribers = {} self.running = Falseasync def start(self): """启动一致性管理器""" self.running = True asyncio.create_task(self.process_events())async def stop(self): """停止一致性管理器""" self.running = Falsedef subscribe(self, event_type: str, callback: Callable): """订阅一致性事件""" if event_type not in self.subscribers: self.subscribers[event_type] = [] self.subscribers[event_type].append(callback)async def publish_event(self, event: ConsistencyEvent): """发布一致性事件""" await self.event_queue.put(event)async def process_events(self): """处理一致性事件""" while self.running: try: event = await asyncio.wait_for( self.event_queue.get(), timeout=1.0 ) # 通知订阅者 if event.event_type in self.subscribers: for callback in self.subscribers[event.event_type]: try: await callback(event) except Exception as e: logging.error(f"Event callback error: {e}") self.event_queue.task_done() except asyncio.TimeoutError: continue except Exception as e: logging.error(f"Event processing error: {e}")> "在分布式系统中,一致性、可用性和分区容错性不能同时满足,这就是著名的CAP定理。在设计MCP服务器时,我们需要根据业务需求在这三者之间做出权衡。"><h2 id="v38cM">4. 性能监控与故障诊断</h2><h3 id="wupGj">4.1 全方位监控体系</h3>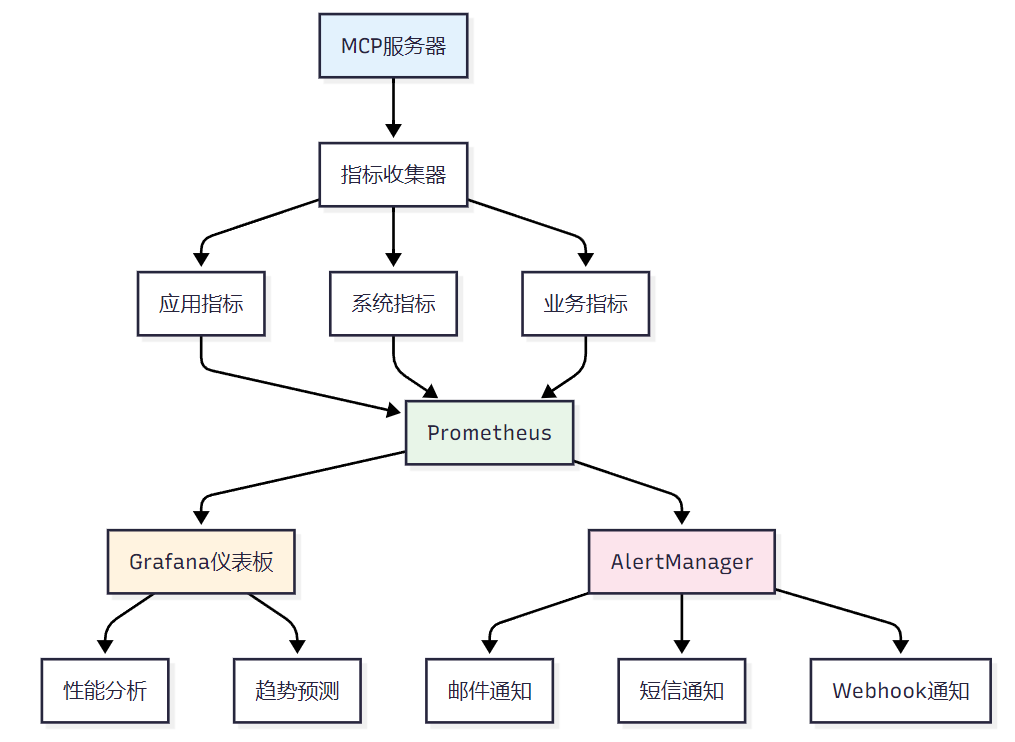**图3 性能监控体系架构图**<h3 id="zCC2n">4.2 监控指标实现</h3>```pythonimport timeimport psutilfrom prometheus_client import Counter, Histogram, Gauge, start_http_serverfrom typing import Dict, Listimport asyncioclass MCPServerMetrics: """MCP服务器指标收集器""" def __init__(self): # 请求指标 self.request_count = Counter( 'mcp_requests_total', 'Total number of requests', ['method', 'endpoint', 'status'] ) self.request_duration = Histogram( 'mcp_request_duration_seconds', 'Request duration in seconds', ['method', 'endpoint'] ) # 系统指标 self.cpu_usage = Gauge('mcp_cpu_usage_percent', 'CPU usage percentage') self.memory_usage = Gauge('mcp_memory_usage_bytes', 'Memory usage in bytes') self.active_connections = Gauge('mcp_active_connections', 'Active connections') # 缓存指标 self.cache_hits = Counter('mcp_cache_hits_total', 'Cache hits') self.cache_misses = Counter('mcp_cache_misses_total', 'Cache misses') # 错误指标 self.error_count = Counter( 'mcp_errors_total', 'Total number of errors', ['error_type'] ) def record_request(self, method: str, endpoint: str, status: str, duration: float): """记录请求指标""" self.request_count.labels(method=method, endpoint=endpoint, status=status).inc() self.request_duration.labels(method=method, endpoint=endpoint).observe(duration) def update_system_metrics(self): """更新系统指标""" self.cpu_usage.set(psutil.cpu_percent()) self.memory_usage.set(psutil.virtual_memory().used) def record_cache_hit(self): """记录缓存命中""" self.cache_hits.inc() def record_cache_miss(self): """记录缓存未命中""" self.cache_misses.inc() def record_error(self, error_type: str): """记录错误""" self.error_count.labels(error_type=error_type).inc()class PerformanceProfiler: """性能分析器""" def __init__(self): self.profiles = {} self.active_profiles = {} def start_profile(self, profile_name: str): """开始性能分析""" self.active_profiles[profile_name] = { 'start_time': time.time(), 'start_memory': psutil.Process().memory_info().rss } def end_profile(self, profile_name: str) -> Dict: """结束性能分析""" if profile_name not in self.active_profiles: return {} start_info = self.active_profiles.pop(profile_name) end_time = time.time() end_memory = psutil.Process().memory_info().rss profile_result = { 'duration': end_time - start_info['start_time'], 'memory_delta': end_memory - start_info['start_memory'], 'timestamp': end_time } if profile_name not in self.profiles: self.profiles[profile_name] = [] self.profiles[profile_name].append(profile_result) return profile_result def get_profile_summary(self, profile_name: str) -> Dict: """获取性能分析摘要""" if profile_name not in self.profiles: return {} profiles = self.profiles[profile_name] durations = [p['duration'] for p in profiles] memory_deltas = [p['memory_delta'] for p in profiles] return { 'count': len(profiles), 'avg_duration': sum(durations) / len(durations), 'max_duration': max(durations), 'min_duration': min(durations), 'avg_memory_delta': sum(memory_deltas) / len(memory_deltas), 'max_memory_delta': max(memory_deltas) }4.3 故障诊断系统
```pythonfrom enum import Enumfrom dataclasses import dataclassfrom typing import List, Optionalimport asyncioimport loggingclass AlertLevel(Enum):"""告警级别"""INFO = "info"WARNING = "warning"ERROR = "error"CRITICAL = "critical"
@dataclassclass Alert:"""告警信息"""level: AlertLeveltitle: strmessage: strtimestamp: floatsource: strmetadata: Dict = None
class HealthChecker:"""健康检查器"""
def __init__(self, metrics: MCPServerMetrics): self.metrics = metrics self.checks = {} self.alerts = [] self.alert_callbacks = []def register_check(self, name: str, check_func: Callable, interval: int = 60): """注册健康检查""" self.checks[name] = { 'func': check_func, 'interval': interval, 'last_run': 0, 'status': 'unknown' }def add_alert_callback(self, callback: Callable): """添加告警回调""" self.alert_callbacks.append(callback)async def run_checks(self): """运行健康检查""" current_time = time.time() for name, check_info in self.checks.items(): if current_time - check_info['last_run'] >= check_info['interval']: try: result = await check_info['func']() check_info['status'] = 'healthy' if result else 'unhealthy' check_info['last_run'] = current_time if not result: alert = Alert( level=AlertLevel.ERROR, title=f"Health check failed: {name}", message=f"Health check {name} returned unhealthy status", timestamp=current_time, source="health_checker" ) await self.send_alert(alert) except Exception as e: logging.error(f"Health check {name} error: {e}") check_info['status'] = 'error'async def send_alert(self, alert: Alert): """发送告警""" self.alerts.append(alert) for callback in self.alert_callbacks: try: await callback(alert) except Exception as e: logging.error(f"Alert callback error: {e}")def get_health_status(self) -> Dict: """获取健康状态""" healthy_checks = sum(1 for check in self.checks.values() if check['status'] == 'healthy') total_checks = len(self.checks) return { 'overall_status': 'healthy' if healthy_checks == total_checks else 'unhealthy', 'healthy_checks': healthy_checks, 'total_checks': total_checks, 'checks': {name: info['status'] for name, info in self.checks.items()} }具体的健康检查实现
async def database_health_check(db_pool: DatabaseConnectionPool) -> bool:"""数据库健康检查"""try:result = await db_pool.execute_query("SELECT 1")return len(result) > 0except Exception:return False
async def cache_health_check(cache_manager: DistributedCacheManager) -> bool:"""缓存健康检查"""try:test_key = "health_check"await cache_manager.set("health", test_key, "test", ttl=60)result = await cache_manager.get("health", test_key)return result == "test"except Exception:return False
<h3 id="Irs6Y">4.4 性能测评体系</h3>| 指标类别 | 具体指标 | 评分标准 | 权重 | 监控方式 || --- | --- | --- | --- | --- || 响应性能 | 平均响应时间 | <100ms(10分), <500ms(8分), <1s(6分), >1s(4分) | 25% | 实时监控 || 并发能力 | QPS峰值 | >10000(10分), >5000(8分), >1000(6分), <1000(4分) | 20% | 压力测试 || 资源利用 | CPU使用率 | <70%(10分), <80%(8分), <90%(6分), >90%(4分) | 15% | 系统监控 || 内存效率 | 内存使用率 | <70%(10分), <80%(8分), <90%(6分), >90%(4分) | 15% | 系统监控 || 可用性 | 系统正常运行时间 | >99.9%(10分), >99%(8分), >95%(6分), <95%(4分) | 15% | 健康检查 || 错误率 | 请求错误率 | <0.1%(10分), <0.5%(8分), <1%(6分), >1%(4分) | 10% | 错误统计 |```python# 性能评估系统实现class PerformanceEvaluator: """性能评估器""" def __init__(self): self.metrics_history = [] self.evaluation_weights = { 'response_time': 0.25, 'qps': 0.20, 'cpu_usage': 0.15, 'memory_usage': 0.15, 'uptime': 0.15, 'error_rate': 0.10 } def evaluate_performance(self, metrics: Dict) -> Dict: """评估系统性能""" scores = {} # 响应时间评分 response_time = metrics.get('response_time', 0) if response_time < 100: scores['response_time'] = 10 elif response_time < 500: scores['response_time'] = 8 elif response_time < 1000: scores['response_time'] = 6 else: scores['response_time'] = 4 # QPS评分 qps = metrics.get('qps', 0) if qps > 10000: scores['qps'] = 10 elif qps > 5000: scores['qps'] = 8 elif qps > 1000: scores['qps'] = 6 else: scores['qps'] = 4 # CPU使用率评分 cpu_usage = metrics.get('cpu_usage', 0) if cpu_usage < 70: scores['cpu_usage'] = 10 elif cpu_usage < 80: scores['cpu_usage'] = 8 elif cpu_usage < 90: scores['cpu_usage'] = 6 else: scores['cpu_usage'] = 4 # 内存使用率评分 memory_usage = metrics.get('memory_usage', 0) if memory_usage < 70: scores['memory_usage'] = 10 elif memory_usage < 80: scores['memory_usage'] = 8 elif memory_usage < 90: scores['memory_usage'] = 6 else: scores['memory_usage'] = 4 # 可用性评分 uptime = metrics.get('uptime', 0) if uptime > 99.9: scores['uptime'] = 10 elif uptime > 99: scores['uptime'] = 8 elif uptime > 95: scores['uptime'] = 6 else: scores['uptime'] = 4 # 错误率评分 error_rate = metrics.get('error_rate', 0) if error_rate < 0.001: scores['error_rate'] = 10 elif error_rate < 0.005: scores['error_rate'] = 8 elif error_rate < 0.01: scores['error_rate'] = 6 else: scores['error_rate'] = 4 # 计算综合得分 total_score = sum( scores[metric] * weight for metric, weight in self.evaluation_weights.items() ) return { 'individual_scores': scores, 'total_score': total_score, 'grade': self.get_performance_grade(total_score), 'recommendations': self.generate_recommendations(scores) } def get_performance_grade(self, score: float) -> str: """获取性能等级""" if score >= 9: return 'A+' elif score >= 8: return 'A' elif score >= 7: return 'B+' elif score >= 6: return 'B' elif score >= 5: return 'C' else: return 'D' def generate_recommendations(self, scores: Dict) -> List[str]: """生成优化建议""" recommendations = [] if scores['response_time'] < 8: recommendations.append("优化响应时间:考虑使用缓存、异步处理或负载均衡") if scores['qps'] < 8: recommendations.append("提升并发能力:增加服务器实例或优化数据库查询") if scores['cpu_usage'] < 8: recommendations.append("降低CPU使用率:优化算法复杂度或增加计算资源") if scores['memory_usage'] < 8: recommendations.append("优化内存使用:检查内存泄漏或增加内存容量") if scores['uptime'] < 8: recommendations.append("提高系统可用性:实施故障转移和健康检查机制") if scores['error_rate'] < 8: recommendations.append("降低错误率:加强输入验证和异常处理") return recommendations5. 实际案例分析
5.1 电商平台MCP服务器架构
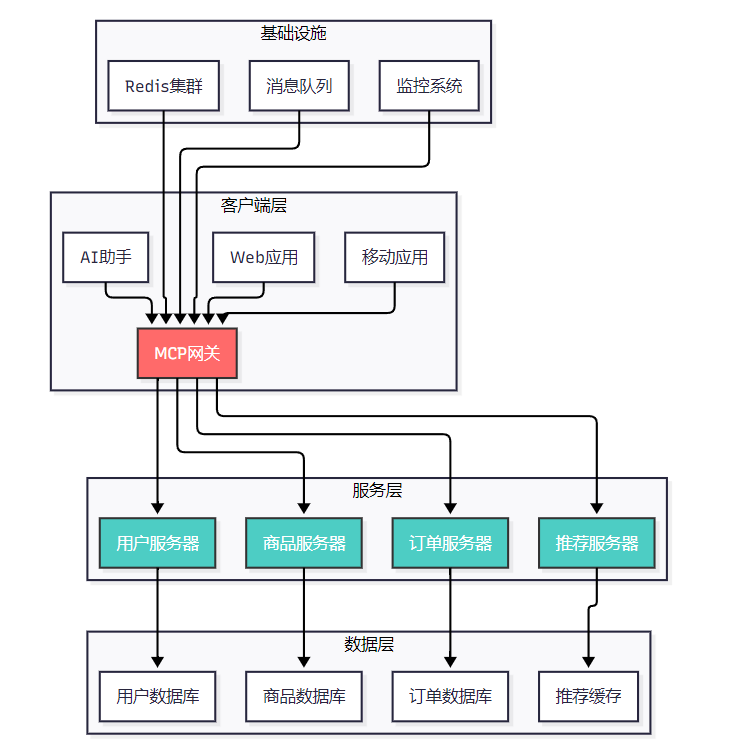图4 电商平台MCP架构案例
5.2 性能优化实施案例
```python# 电商MCP服务器优化实现class EcommerceMCPServer: """电商MCP服务器"""def __init__(self): self.connection_pool = DatabaseConnectionPool( dsn="postgresql://user:pass@localhost/ecommerce", min_size=20, max_size=100 ) self.cache_manager = DistributedCacheManager( redis_cluster_nodes=[ {"host": "redis1", "port": 6379}, {"host": "redis2", "port": 6379}, {"host": "redis3", "port": 6379} ], strategy=CacheConsistencyStrategy.WRITE_THROUGH ) self.metrics = MCPServerMetrics() self.rate_limiter = RateLimiter(max_requests=1000, window_seconds=60)async def get_product_info(self, product_id: str) -> Dict: """获取商品信息(带缓存优化)""" # 性能监控开始 timer = self.metrics.request_duration.labels( method="GET", endpoint="product_info" ).time() try: # 先检查缓存 cache_key = f"product:{product_id}" cached_data = await self.cache_manager.get("products", cache_key) if cached_data: self.metrics.record_cache_hit() return cached_data # 缓存未命中,查询数据库 self.metrics.record_cache_miss() query = """ SELECT p.*, c.name as category_name, AVG(r.rating) as avg_rating, COUNT(r.id) as review_count FROM products p LEFT JOIN categories c ON p.category_id = c.id LEFT JOIN reviews r ON p.id = r.product_id WHERE p.id = $1 AND p.status = 'active' GROUP BY p.id, c.name """ result = await self.connection_pool.execute_query(query, product_id) if not result: raise ValueError(f"Product {product_id} not found") product_data = dict(result[0]) # 异步更新缓存 asyncio.create_task( self.cache_manager.set("products", cache_key, product_data, ttl=3600) ) return product_data except Exception as e: self.metrics.record_error("database_error") raise finally: timer.stop()async def search_products(self, query: str, filters: Dict) -> Dict: """商品搜索(带分页和过滤)""" # 构建搜索缓存键 cache_key = hashlib.md5( f"{query}:{json.dumps(filters, sort_keys=True)}".encode() ).hexdigest() # 检查搜索缓存 cached_results = await self.cache_manager.get("search", cache_key) if cached_results: return cached_results # 构建动态查询 base_query = """ SELECT p.*, c.name as category_name, ts_rank(to_tsvector('english', p.name || ' ' || p.description), plainto_tsquery('english', $1)) as relevance FROM products p LEFT JOIN categories c ON p.category_id = c.id WHERE p.status = 'active' """ params = [query] conditions = [] if query: conditions.append("to_tsvector('english', p.name || ' ' || p.description) @@ plainto_tsquery('english', $1)") if filters.get('category_id'): params.append(filters['category_id']) conditions.append(f"p.category_id = ${len(params)}") if filters.get('min_price'): params.append(filters['min_price']) conditions.append(f"p.price >= ${len(params)}") if filters.get('max_price'): params.append(filters['max_price']) conditions.append(f"p.price <= ${len(params)}") if conditions: base_query += " AND " + " AND ".join(conditions) # 添加排序和分页 page = filters.get('page', 1) page_size = min(filters.get('page_size', 20), 100) # 限制最大页面大小 offset = (page - 1) * page_size base_query += f""" ORDER BY relevance DESC, p.created_at DESC LIMIT {page_size} OFFSET {offset} """ # 执行查询 results = await self.connection_pool.execute_query(base_query, *params) # 获取总数 count_query = base_query.replace( "SELECT p.*, c.name as category_name, ts_rank(...) as relevance", "SELECT COUNT(*)" ).split("ORDER BY")[0] total_count = await self.connection_pool.execute_query(count_query, *params) search_results = { 'products': [dict(row) for row in results], 'pagination': { 'page': page, 'page_size': page_size, 'total_count': total_count[0]['count'], 'total_pages': (total_count[0]['count'] + page_size - 1) // page_size } } # 缓存搜索结果 await self.cache_manager.set("search", cache_key, search_results, ttl=300) return search_results<h3 id="Yi3rQ">5.3 监控仪表板配置</h3>```yaml# grafana-dashboard.ymlapiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata: name: mcp-dashboarddata: dashboard.json: | { "dashboard": { "title": "MCP服务器性能监控", "panels": [ { "title": "请求响应时间", "type": "graph", "targets": [ { "expr": "histogram_quantile(0.95, mcp_request_duration_seconds_bucket)", "legendFormat": "95th percentile" }, { "expr": "histogram_quantile(0.50, mcp_request_duration_seconds_bucket)", "legendFormat": "50th percentile" } ] }, { "title": "请求吞吐量", "type": "graph", "targets": [ { "expr": "rate(mcp_requests_total[5m])", "legendFormat": "RPS" } ] }, { "title": "错误率", "type": "singlestat", "targets": [ { "expr": "rate(mcp_errors_total[5m]) / rate(mcp_requests_total[5m]) * 100", "legendFormat": "Error Rate %" } ] }, { "title": "缓存命中率", "type": "singlestat", "targets": [ { "expr": "mcp_cache_hits_total / (mcp_cache_hits_total + mcp_cache_misses_total) * 100", "legendFormat": "Cache Hit Rate %" } ] } ] } }6. 最佳实践总结
6.1 架构设计原则
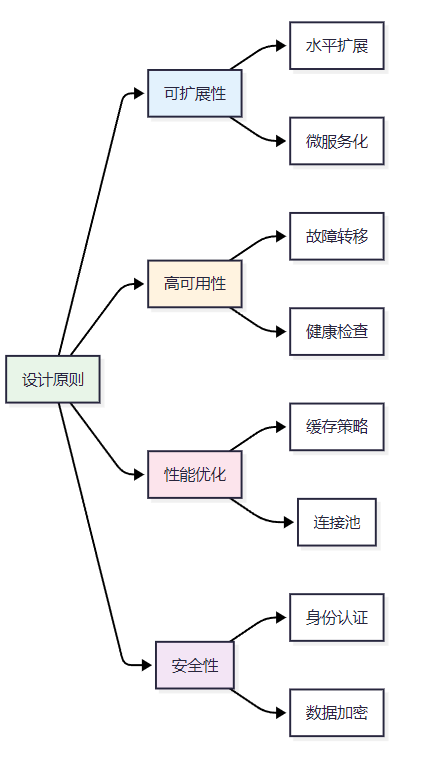图5 MCP服务器设计原则图
6.2 性能优化检查清单
- [ ] **连接池配置**:合理设置最小/最大连接数- [ ] **缓存策略**:实施多级缓存和一致性保证- [ ] **异步处理**:使用异步I/O和事件驱动架构- [ ] **负载均衡**:配置合适的负载均衡算法- [ ] **监控告警**:建立完善的监控和告警体系- [ ] **资源限制**:设置合理的资源使用限制- [ ] **错误处理**:实现优雅的错误处理和恢复机制- [ ] **安全防护**:加强身份认证和访问控制6.3 运维管理建议
```python# 运维自动化脚本示例class MCPServerOperations: """MCP服务器运维管理"""def __init__(self, config_path: str): self.config = self.load_config(config_path) self.health_checker = HealthChecker() self.backup_manager = BackupManager()async def daily_maintenance(self): """日常维护任务""" tasks = [ self.check_system_health(), self.cleanup_old_logs(), self.backup_critical_data(), self.update_performance_reports(), self.check_security_alerts() ] results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks, return_exceptions=True) # 生成维护报告 report = self.generate_maintenance_report(results) await self.send_maintenance_report(report)async def emergency_response(self, alert: Alert): """紧急响应处理""" if alert.level == AlertLevel.CRITICAL: # 立即通知运维团队 await self.notify_ops_team(alert) # 尝试自动恢复 if alert.source == "database": await self.restart_database_connections() elif alert.source == "memory": await self.trigger_garbage_collection() elif alert.source == "disk": await self.cleanup_temporary_files()async def performance_tuning(self): """性能调优""" current_metrics = await self.collect_performance_metrics() # 基于指标自动调整配置 if current_metrics['cpu_usage'] > 80: await self.scale_out_instances() if current_metrics['memory_usage'] > 85: await self.adjust_cache_size() if current_metrics['response_time'] > 500: await self.optimize_database_queries()> "高性能的MCP服务器不是一蹴而就的,而是通过持续的监控、优化和改进逐步实现的。每一个性能瓶颈的解决,都是向更好用户体验迈进的一步。"><h2 id="ll36V">总结</h2>作为博主摘星,通过深入研究和实践高性能MCP服务器架构设计,我深刻认识到这不仅是一个技术挑战,更是一个系统工程。在当今AI应用快速发展的时代,MCP服务器作为连接AI模型与外部世界的关键基础设施,其性能表现直接影响着用户体验和业务成功。从我的实践经验来看,构建高性能MCP服务器需要在多个维度上精心设计:首先是架构层面的合理规划,包括并发模型选择、负载均衡策略和微服务拆分;其次是技术实现的精细优化,涵盖连接池管理、缓存策略设计和异步处理机制;再次是运维监控的全面覆盖,确保系统的稳定性和可观测性。通过本文详细介绍的分布式缓存、数据一致性保障、性能监控体系等核心技术,我们可以看到现代高性能系统设计的复杂性和精妙之处。特别值得强调的是,性能优化不是一次性的工作,而是需要持续的监控、分析和改进。在实际项目中,我建议开发团队建立完善的性能基准测试体系,定期进行性能评估,并根据业务发展需要及时调整架构策略。同时,安全性和可靠性同样重要,不能为了追求极致性能而忽视系统的稳定性和数据安全。展望未来,随着AI技术的不断演进和应用场景的日益丰富,MCP服务器的性能要求将会更加严苛,这也为我们技术人员提供了更多的挑战和机遇。我相信,通过不断的技术创新和实践积累,我们能够构建出更加高效、稳定、安全的MCP服务器系统,为AI应用的蓬勃发展提供坚实的技术支撑。<h2 id="YZdXA">参考资料</h2>1. [Model Context Protocol官方文档](https://modelcontextprotocol.io/)2. [高性能系统设计模式](https://martinfowler.com/articles/patterns-of-distributed-systems/)3. [Redis集群架构最佳实践](https://redis.io/topics/cluster-tutorial)4. [PostgreSQL连接池优化指南](https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/runtime-config-connection.html)5. [Prometheus监控系统设计](https://prometheus.io/docs/introduction/overview/)6. [分布式系统CAP定理深度解析](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAP_theorem)7. [微服务架构性能优化策略](https://microservices.io/patterns/performance.html)8. [云原生应用监控最佳实践](https://www.cncf.io/blog/2021/12/21/monitoring-best-practices/)---_本文由博主摘星原创,专注于AI技术与系统架构的深度分析。如有技术问题或合作需求,欢迎通过评论区或私信联系。_🌈_ 我是摘星!如果这篇文章在你的技术成长路上留下了印记:___👁️_ 【关注】与我一起探索技术的无限可能,见证每一次突破_👍_ 【点赞】为优质技术内容点亮明灯,传递知识的力量_🔖_ 【收藏】将精华内容珍藏,随时回顾技术要点_💬_ 【评论】分享你的独特见解,让思维碰撞出智慧火花_🗳️_【投票】用你的选择为技术社区贡献一份力量____技术路漫漫,让我们携手前行,在代码的世界里摘取属于程序员的那片星辰大海!_
