Get started with GitHub Copilot >
Since I joined GitHub as a software engineer on the billing team almost three years ago, I’ve had a front row seat to the evolution of AI coding tools including Github Copilot. What started out as code completions has evolved into so much more including agentic workflows and refactoring suggestions. When I first started using Copilot, I was mainly using it in VSCode. As Copilot has grown and expanded, I’ve extended my use cases beyond my code editor and into all parts of my day-to-day work, including pull requests, code reviews, and more.
GitHub Copilot is now available in all parts of the software development life cycle and one place where it can be extremely useful is when you’re creating pull requests and doing code reviews. During my time at GitHub, I’ve discovered some practical ways Copilot can make a difference during the pull request and code review processes. Here are a few things I’ve started doing that have made my workflow smoother and more efficient.
Using Copilot suggestions when reviewing code
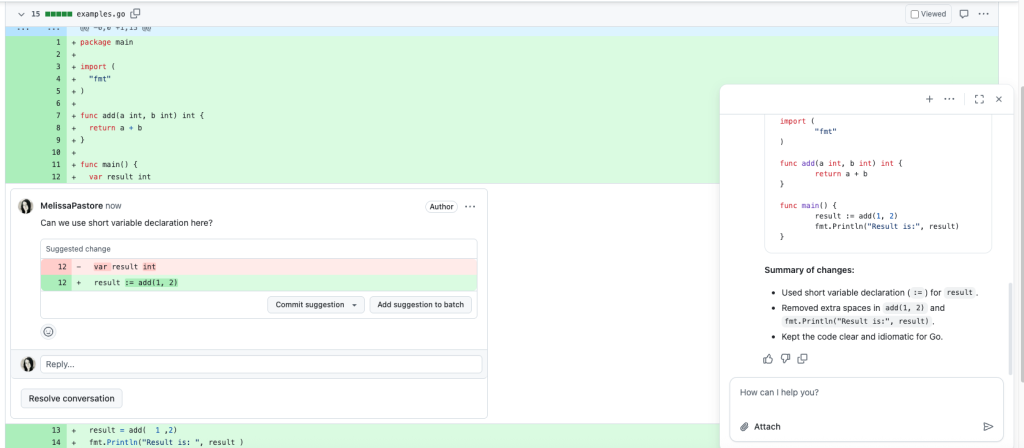
Often, when I’m reviewing a teammate’s pull request, I’ll have an idea for how their code could be improved, or I’ll want to confirm the code is following best practices. However, I don’t always have time to write the suggested refactored code myself. In these cases, I’ll usually click the Copilot icon next to the file I’m reviewing and ask Copilot to suggest a specific improvement about the lines of code I’m currently reviewing. Then I’ll add that suggestion in my review comment along with some explanation of why I think the suggestion would improve the code.
Recently while reviewing a teammate’s code, I noticed some repetitive code in a Ruby file. I clicked the Copilot icon next to the relevant code and prompted it with:
> “Can you refactor this Ruby on Rails code to reduce repetition?”Copilot’s suggestion matched what I would have written and saved me several minutes, which allowed me to focus on higher-level feedback.
Since I frequently switch context and review code in different languages like Ruby, TypeScript and Go, sometimes I’ll need a reminder on best practices for each language. I recently used this prompt to help me review some Go code:
> “Is this code addition following Go best practices for variable assignment? If not, can you suggest improvements?”Copilot quickly generated a suggestion that I reviewed and used as part of my code review comment. It saved me time and made my feedback more actionable.
Formatting tables and data for pull requests
I like to add images, screen recordings, and occasionally spreadsheets to my pull request descriptions to add context to help reviewers understand my changes. Adding this type of information in Markdown can be tedious! In these cases, I ask Copilot to do the formatting for me.
Recently, I was working on some improvements to help decrease the load time of a React page, and I wanted to show the improvements that my changes were making. I had been keeping a spreadsheet detailing the the page load times before and after my changes, and I wanted to include it in my pull request description, so I gave Copilot this prompt:
Format this data into a GitHub flavored markdown table that I can paste into a GitHub pull request description: Load Time Before (in seconds) Load Time After Updates (in seconds) 1.3 1.2 1.2 1.1 1.1 0.885 1.3 1.3 1.2 0.918 Average 1.22 1.0806And Copilot gave this response:
Here’s your data formatted as a GitHub-flavored markdown table, ready to paste into a pull request description:Markdown| Test Run | Load Time Before (seconds) | Load Time After Updates (seconds) ||----------|---------------------------|-----------------------------------|| 1 | 1.3 | 1.2 || 2 | 1.2 | 1.1 || 3 | 1.1 | 0.885 || 4 | 1.3 | 1.3 || 5 | 1.2 | 0.918 || **Average** | **1.22** | **1.0806** Let me know if you’d like any adjustments!This simple trick has made it much easier for me to clearly share data in my pull request descriptions and comments.
Letting Copilot help write pull request summaries
I often use Copilot to help me write pull request summaries. We’ve all been there: you finally open your pull request after fixing a bug or introducing a new feature and the last hurdle is writing the pull request description. Copilot can help kickstart this process for you by using the Copilot icon in the pull request description editor bar. Even if I end up editing the text, having a starting point makes it less daunting.
Using Copilot for code reviews and understanding unfamiliar code
Copilot is very good at reviewing and explaining code and two ways I leverage this in my day-to-day work are requesting initial code reviews from Copilot and asking questions about unfamiliar code.
Before I mark a pull request as ready for review, I’ll use Copilot to do a quick pass over my changes by requesting a code review from Copilot. It often catches things I might have missed or suggests a better way to write something. And don’t forget to add some notes in the custom instructions in your repository on what you want Copilot to focus on when reviewing pull requests.
If I’m reviewing someone else’s code and I don’t understand a change, I’ll ask Copilot to explain it. This helps me get context quickly, especially when I’m less familiar with that part of the codebase. This better understanding of the code allows me to provide more thoughtful and thorough code reviews for my teammates and ensures that I fully understand the potential impact of any pull request that I’m approving.
Copilot’s impact on code reviews and pull requests
While Copilot isn’t a replacement for thoughtful, engaged code reviews, it has become an indispensable tool in my daily workflow as a software engineer. From generating smart suggestions and code refactors, to quick Markdown formatting and drafting pull request summaries, Copilot helps streamline the work that surrounds writing code by making feedback more actionable and the code review process faster and more thorough. By integrating Copilot into every stage of the software development life cycle, I’m able to focus on higher-level engineering problems and collaboration. As Copilot continues to evolve, I’m excited to see how it will further transform not just my workflow, but the way developers everywhere build software together.
The post How to use GitHub Copilot to level up your code reviews and pull requests appeared first on The GitHub Blog.

