DevOps Kit: Practical Tools for Engineering Teams (Sponsored)
The DevOps model can help you build software faster, ship applications with confidence, and break down silos across your engineering organizations. Gain instant access to hands-on resources from Datadog:
2 eBooks on scaling DevOps practices across development and operations
A solutions brief on gaining full-stack visibility from CI/CD to production
A tech talk on using observability data to automate and improve workflows
This week’s system design refresher:
How Does a URL Shortener Work? (Youtube video)
16 Coding Patterns That Make Interviews Easy
How to Learn Databases?
What happens when you type a URL into a browser?
How HTTPS Works?
The Evolution of Scaling at Netflix
Early teams hiring engineers
SPONSOR US
How Does a URL Shortener Work?
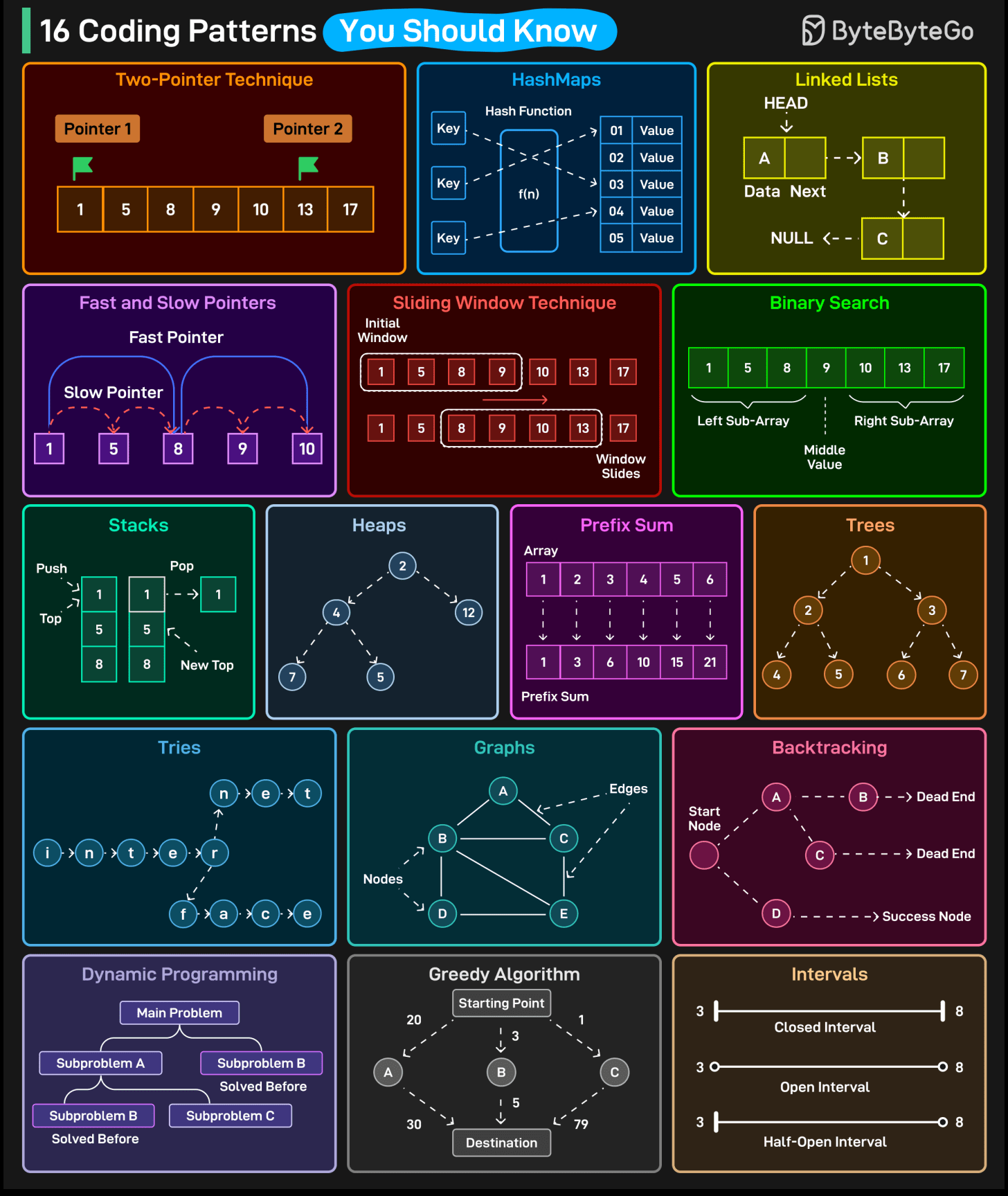
16 Coding Patterns That Make Interviews Easy
Two-Pointer Technique
HashMaps
Linked Lists
Fast and Slow Pointers
Sliding Window Technique
Binary Search
Stacks
Heaps
Prefix Sum
Trees
Tries
Graphs
Backtracking
Dynamic Programming
Greedy Algorithms
Intervals
Over to you: Which other coding pattern will you add to the list?
Shipping late? DevStats shows you why. (Sponsored)
Still pretending your delivery issues are a mystery? They’re not. You’re just not looking in the right place.
DevStats gives engineering leaders brutal clarity on where delivery breaks down, so you can fix the process instead of pointing fingers.
✅ Track DORA and flow metrics like a grown-up
✅ Spot stuck work, burnout risks, and aging issues
✅ Cut cycle time without cutting corners
✅ Ship faster. With fewer surprises.
More AI tools won’t fix your delivery. More Clarity will.
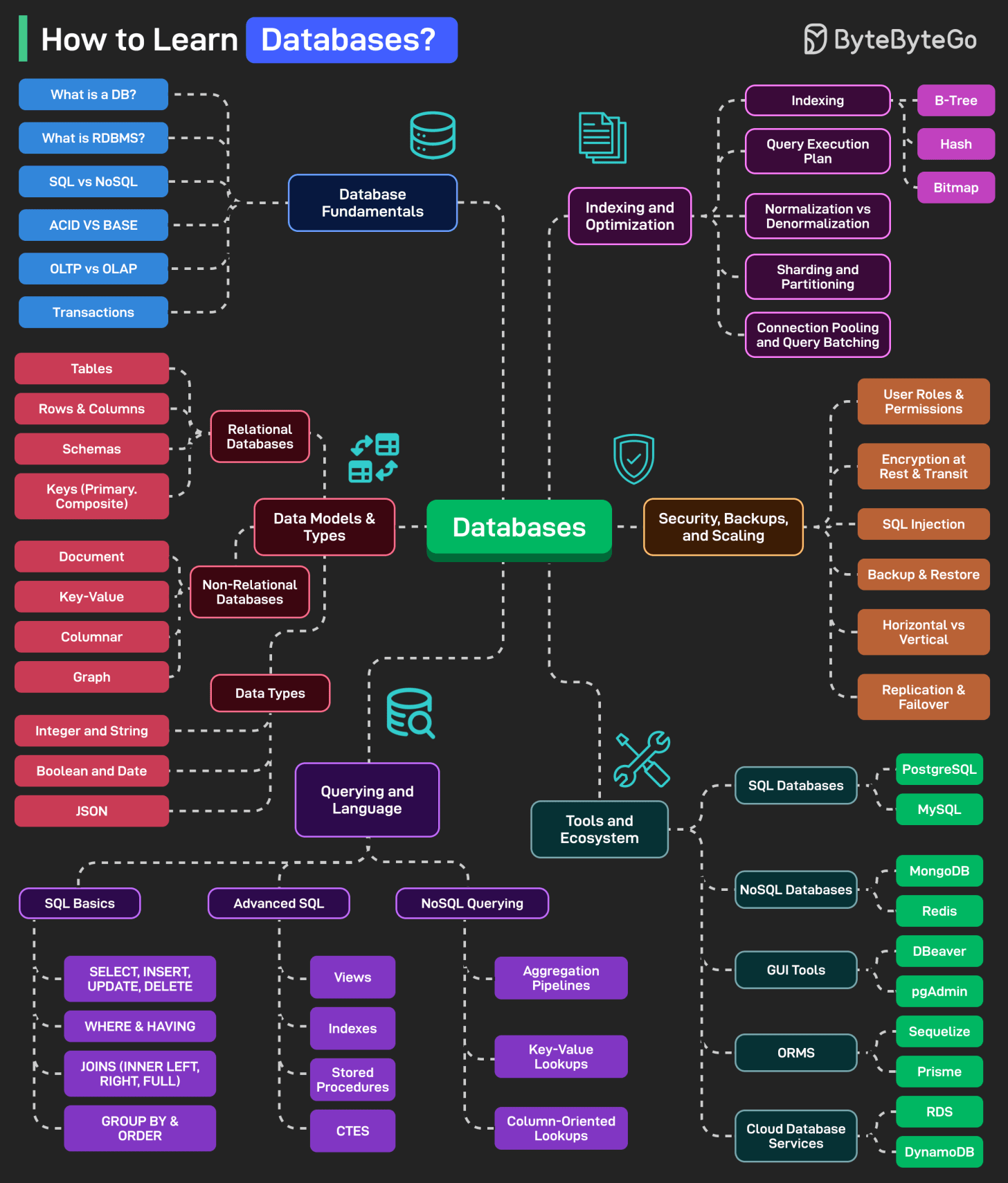
How to Learn Databases?
Databases power everything from websites and apps to enterprise systems. Here’s a learning map that can help you master databases:
Database Fundamentals
This includes topics like “What is a database”, RDBMS, SQL vs NoSQL, ACID vs BASE, OLTP vs OLAP, Transactions, and Isolation Levels.
Data Models and Types
Consists of topics like Relational Databases, Non-Relational Databases, and Data Types (Integer, String, Boolean, Date, JSON, etc).
Querying and Language
This includes topics like SQL Basics (SELECT, INSERT, etc), Advanced SQL (Views, Indexes, CTEs, etc), and NoSQL Querying (Aggregation and Key-Value Lookups).
Indexing and Optimization
Consists of topics like Indexing (B-Tree, Hash, and Bitmaps), Query Execution Plans, Denormalization vs Normalization, Sharding, Connecting Pooling, and Query Batching.
Security, Backups, and Scaling
This includes topics like User Roles, Permissions, Encryption, SQL Injection, High Availability (Replication and Failover), Horizontal vs Vertical Scaling.
Tools and Ecosystem
Consists of topics like Popular SQL Databases, NoSQL Database, GUI Tools, ORMs, Cloud DB services (RDS, DynamoDB, Google Cloud SQL, etc.)
Over to you: What else will you add to the list for learning databases?
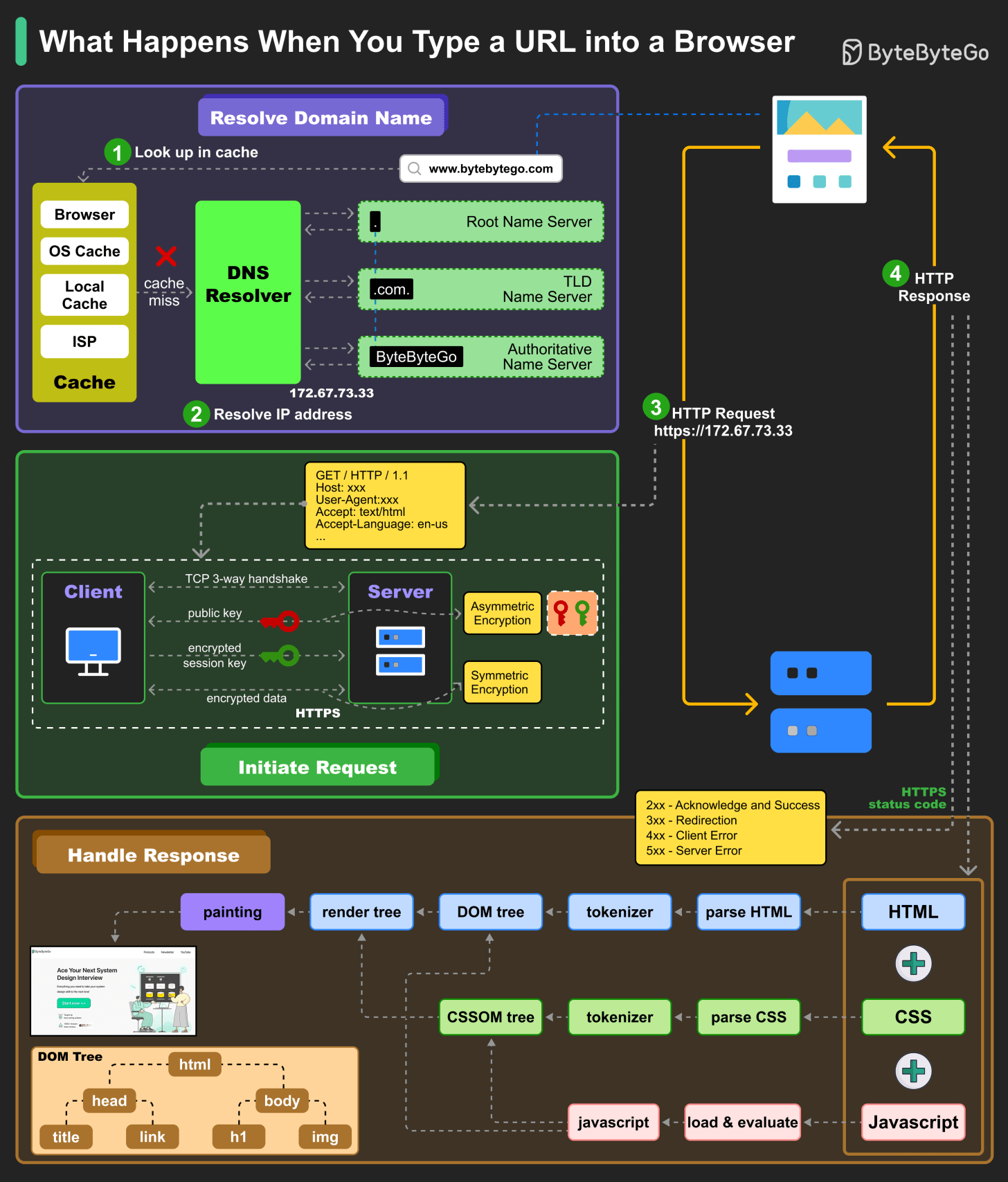
What happens when you type a URL into a browser?
Let’s look at the process step by step.
Step 1: The user enters a URL (bytebytego .com) into the browser and hits Enter. The first thing we need to do is to translate the URL to an IP address. The mapping is usually stored in a cache, so the browser looks for the IP address in multiple layers of cache: the browser cache, OS cache, local cache, and ISP cache. If the browser couldn’t find the mapping in the cache, it will ask the DNS (Domain Name System) resolver to resolve it.
Step 2: If the IP address cannot be found at any of the caches, the browser goes to DNS servers to do a recursive DNS lookup until the IP address is found.
Step 3: Now that we have the IP address of the server, the browser sends an HTTP request to the server. For secure access of server resources, we should always use HTTPS. It first establishes a TCP connection with the server via TCP 3-way handshake. Then it sends the public key to the client. The client uses the public key to encrypt the session key and sends to the server. The server uses the private key to decrypt the session key. The client and server can now exchange encrypted data using the session key.
Step 4: The server processes the request and sends back the response. For a successful response, the status code is 200. There are 3 parts in the response: HTML, CSS and Javascript. The browser parses HTML and generates DOM tree. It also parses CSS and generates CSSOM tree. It then combines DOM tree and CSSOM tree to render tree. The browser renders the content and display to the user.
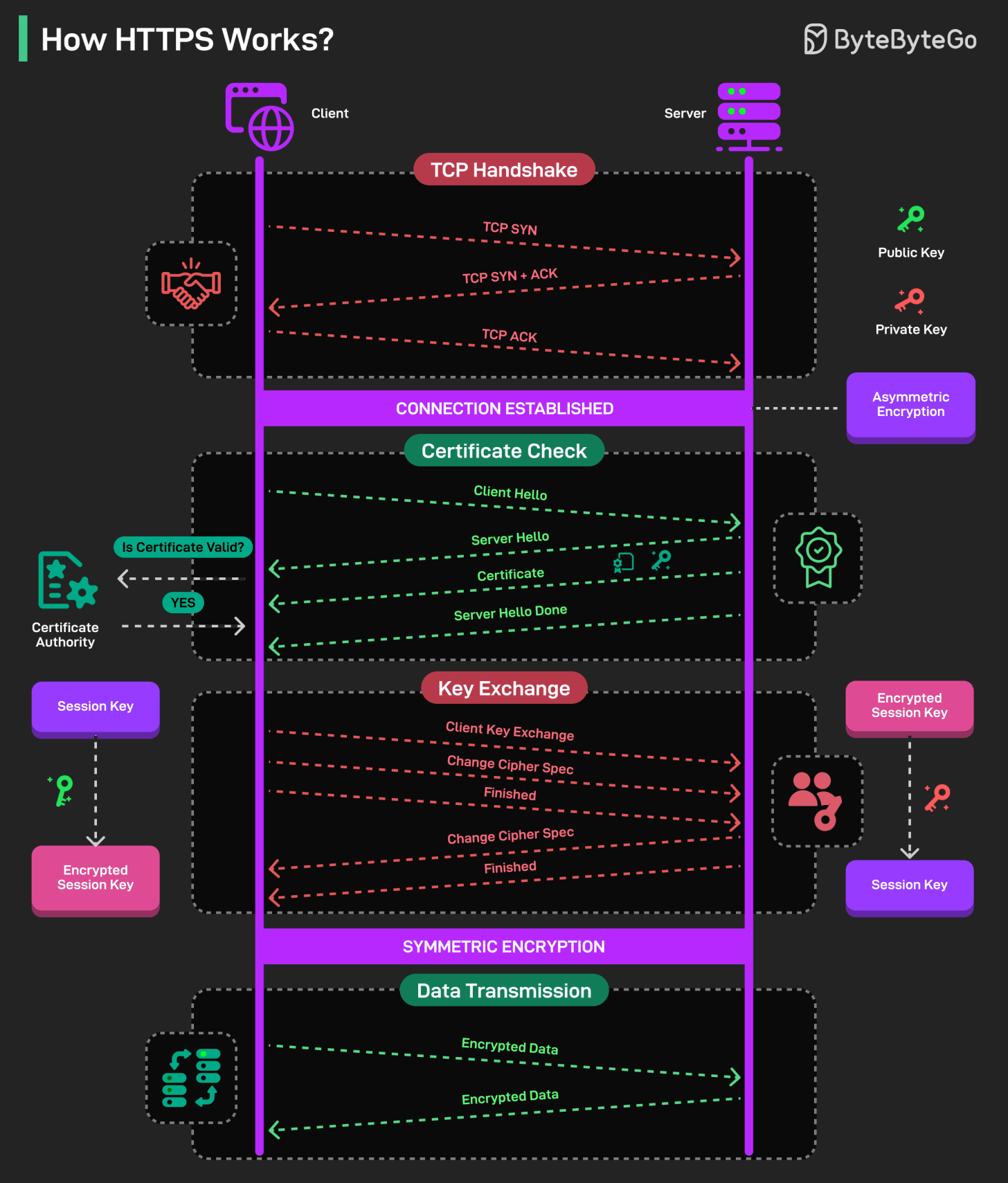
How HTTPS Works?
HTTPS ensures secure communication between your browser (client) and a website’s server using encryption.
TCP Handshake: Before any secure communication occurs, the client and server first establish a basic connection using the TCP handshake process. At this point, the data is not encrypted.
Certificate Check: This stage is meant to verify the server’s identity. The client starts the TLS handshake with a “hello” message that offers supported encryption algorithms. The server replies, choosing algorithms and sending its digital certificate, which contains the public key. The client verifies the certificate to ensure it’s from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
Key Exchange: Once the client validates the certificate, it starts the key exchange process. The client uses the server’s public key (from the certificate) to encrypt the session key. The encrypted session key is sent to the server, and the server can decrypt it using its private key. The change cipher spec message signifies that from this point onward, all messages will be encrypted using the agreed-upon session key and cipher. This step uses asymmetric encryption to securely exchange the session key.
Data Transmission: Now, both sides switch to symmetric encryption (faster) using the shared session key. Messages are encrypted and decrypted with the same key. All data exchanged is now secure and private.
Over to you: Will you add anything more to explain the HTTPS process?
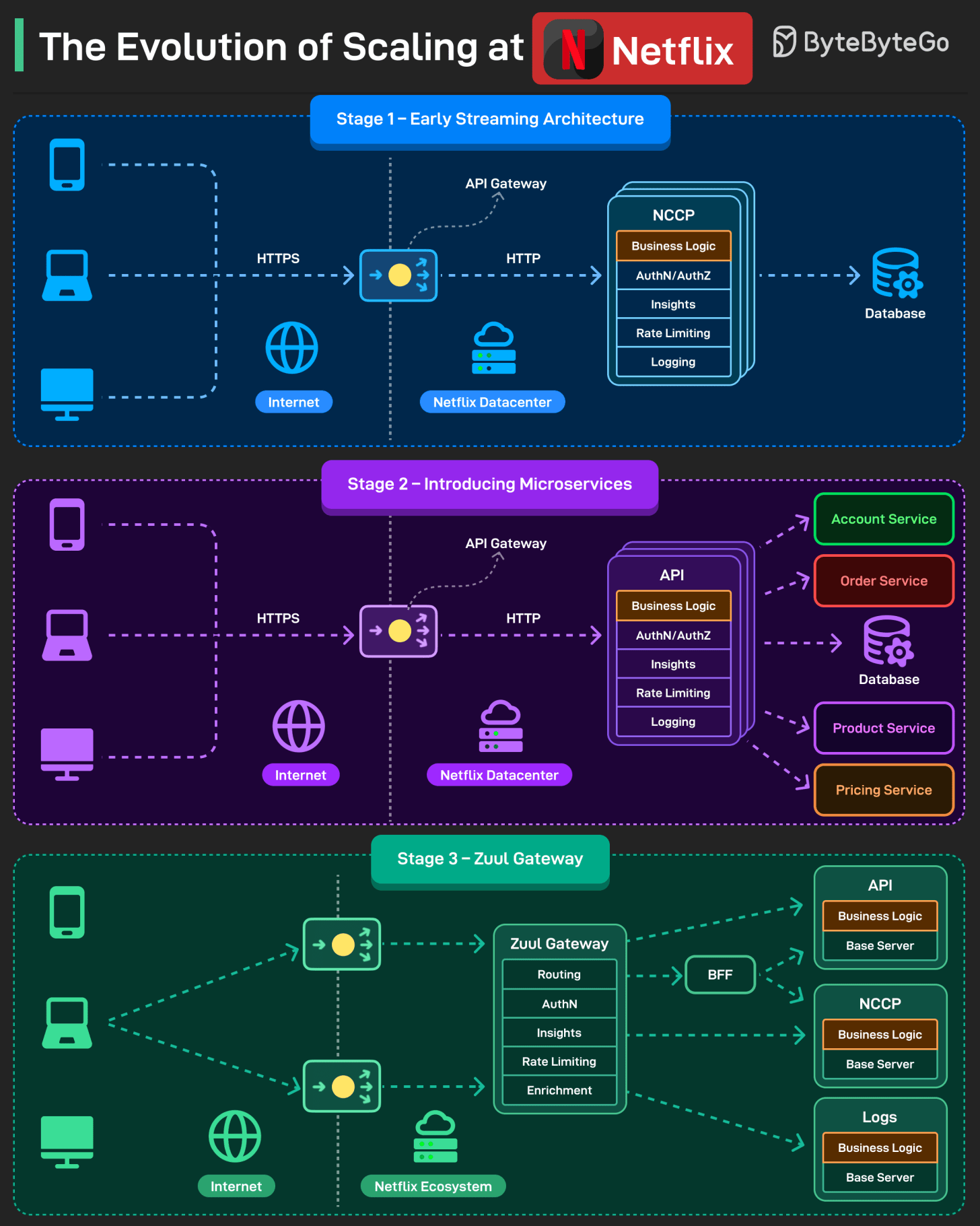
The Evolution of Scaling at Netflix
Over the years, Netflix went through several growth stages. With each stage, they had to evolve the scaling approach.
Stage 1 (Early Streaming Architecture)
It was a typical 3-tier consisting of a client, an API, and a database.
The API application was named NCCP (Netflix Content Control Protocol). It was a monolithic application that contained all functionalities.
Stage 2 (Introducing Microservices)
As more features were added, maintaining the engineering velocity became critical. To support this, the monolithic application was broken up into microservices.
Features were extracted from the NCCP application and developed as separate applications, but the orchestration logic remained in the NCCP application.
Stage 3 (Zuul Gateway)
Next, Netflix split the application. The NCCP stayed there for the playback experience while other APIs started to handle other features.
A Zuul API Gateway was introduced to reduce the coupling between the client and the services.
Reference: Netflix TechBlog
Over to you: Have you come across any other nuance of how Netflix scaled to its current level?
Early teams hiring engineers
If you’d like to find interesting job opportunities at startups or meet like-minded peers (like co-founders or collaborators), check out Next Play on Substack
Jake previously founded the therapist platform Headway and is now building Marble Health. They are hiring software engineers. They are building a therapy platform for students. Apply here. (NYC)
Brian from a37 is building an ai-powered DevOps platform. They are hiring a founding software engineer. They say they will match or exceed any offer you get. Apply here. (SF)
Sarah from Retail Ready is building a supply chain compliance platform for brands and 3PLs. They have signed ten enterprise contracts. They are hiring a full-stack engineer. Apply here. (SF)
Ben from Tilde is hiring engineers. They recently raised from Khosla to build an AI interpretability platform. Apply here. (SF)
Alon previously founded Better Help and is now working on Strawberry, a career and personal coaching platform. They have scaled from 10,000 to 20,000 user sessions in just the past 10 weeks. They are hiring engineers. Apply here. (Remote, SF)
Connor from Miter is building an all-in-one contractor management platform. They are hiring software engineers. Apply here. (SF, NYC).
Mike from Extend grew revenue 50%+ last month. They recently raised $17m to scale their document processing cloud. They are hiring engineers. Apply here. (NYC)
Nominal is hiring software engineers. They are building a unified platform for building hardware and infrastructure. Apply here. (LA, NYC, Austin)
Justin from Phoebe previously started and sold a company to Airtable. They are now building an AI assistant for home health work, and are hiring an early full stack engineer. Apply here. (NYC)
Stedman and Harry from Neon Health are building AI agents that accelerate patient access to life-saving drugs. They are already profitable. They are hiring founding engineers. Apply here. (SF)
AnhPhu from Halo is building “wearable intelligence” that’s already gone viral (80m+ views). They are hiring a founding engineer. Apply here. (SF)
Elliot from Chalk is building a data platform for inference. They recently raised $50m, and are hiring software engineers. Apply here. (SF, NYC)
Hakob from Synthflow just raised a $20m series A and is hiring for engineering. They are building a voice agent platform. Apply here. (NYC, Berlin, Remote)
Austin from Clarify is hiring engineers. They are building an ai-powered CRM, and just raised $22.5m. Apply here. (Remote)
Dani from Jam is hiring senior engineers. They are building a platform to make engineering more productive. Apply here. (SF, Remote)
Nicholas from Proto is building a stealth healthcare ai company that’s already signed revenue generating deals and closed a pre-seed round. They are hiring AI and fullstack engineers. Reach out: nicholas@theproto.ai. (NYC)
John from Campfire is hiring full stack engineers. They are building a platform to empower accounting and finance departments. Apply here. (SF)
Mackenzie from Ambrook just raised a new round led by the founder of Figma. They are building a financial operating system for the agriculture industry. They are hiring software engineers. Apply here. (NYC, Denver, Remote, SF)
Mitchell from Basis is hiring software engineers. They are building AI agents for accountants. Apply here. (NYC)
SPONSOR US
Get your product in front of more than 1,000,000 tech professionals.
Our newsletter puts your products and services directly in front of an audience that matters - hundreds of thousands of engineering leaders and senior engineers - who have influence over significant tech decisions and big purchases.
Space Fills Up Fast - Reserve Today
Ad spots typically sell out about 4 weeks in advance. To ensure your ad reaches this influential audience, reserve your space now by emailing sponsorship@bytebytego.com.