😘 Kiss bugs goodbye with fully automated end-to-end test coverage (Sponsored)
Bugs sneak out when less than 80% of user flows are tested before shipping. However, getting that kind of coverage (and staying there) is hard and pricey for any team.
QA Wolf’s AI-native service provides high-volume, high-speed test coverage for web and mobile apps, reducing your organizations QA cycle to less than 15 minutes.
They can get you:
80% automated E2E test coverage in weeks
24-hour maintenance and on-demand test creation
Zero flakes, guaranteed
Engineering teams move faster, releases stay on track, and testing happens automatically—so developers can focus on building, not debugging.
The result? Drata achieved 4x more test cases and 86% faster QA cycles.
⭐ Rated 4.8/5 on G2
Disclaimer: The details in this post have been derived from the official documentation shared online by the Cursor (Anysphere) Engineering Team. All credit for the technical details goes to the Cursor (Anysphere) Engineering Team. The links to the original articles and sources are present in the references section at the end of the post. We’ve attempted to analyze the details and provide our input about them. If you find any inaccuracies or omissions, please leave a comment, and we will do our best to fix them.
Cursor is an AI-powered code editor (IDE) that has quickly become a standout tool for developers since its initial release in March 2023 by the startup Anysphere.
It has experienced remarkable growth and adoption, reaching a point where it is being used in a large number of Fortune 500 companies. This rapid rise in popularity is also evident in surveys, which identify Cursor as an extremely popular AI coding IDE among engineers.
The core reason for Cursor's success lies in its AI-first approach, which tightly integrates cutting-edge AI models into a familiar coding environment. Built as a fork of Visual Studio Code (VS Code), Cursor provides developers with a stable interface, familiar keybindings, and compatibility with the existing VS Code extension ecosystem. This minimizes friction for users while allowing Cursor’s engineering team to focus intensely on developing powerful AI capabilities rather than building an IDE from scratch.
Cursor's intelligence comes from its use of state-of-the-art large language models, including OpenAI's GPT-4 variants and Anthropic's Claude, and even its own fine-tuned models. Its backend is designed for immense scale, handling over 1 million transactions per second at peak and serving billions of AI code completions daily to ensure a responsive and seamless experience. Cursor also functions as an effective AI pair programmer that can understand entire codebases, recall project-wide details, suggest complex edits across multiple files, and even execute tasks on demand.
In this article, we will take a look at the key features of Cursor, how those features work, and the infrastructure stack that powers it.
Key Features of Cursor
The key features of Cursor, along with the technical details behind them, are as follows:
1 - AI Code Autocomplete
One of Cursor’s most important features is its AI-driven code completion, which significantly accelerates coding by suggesting code as the user types. Developers can accept these predictions, often displayed as light grey text, by pressing the Tab key. This capability extends beyond single lines, offering smarter suggestions for refactors and multi-file edits.
The responsiveness of Cursor’s autocomplete is a major engineering feat. Here’s how it works:
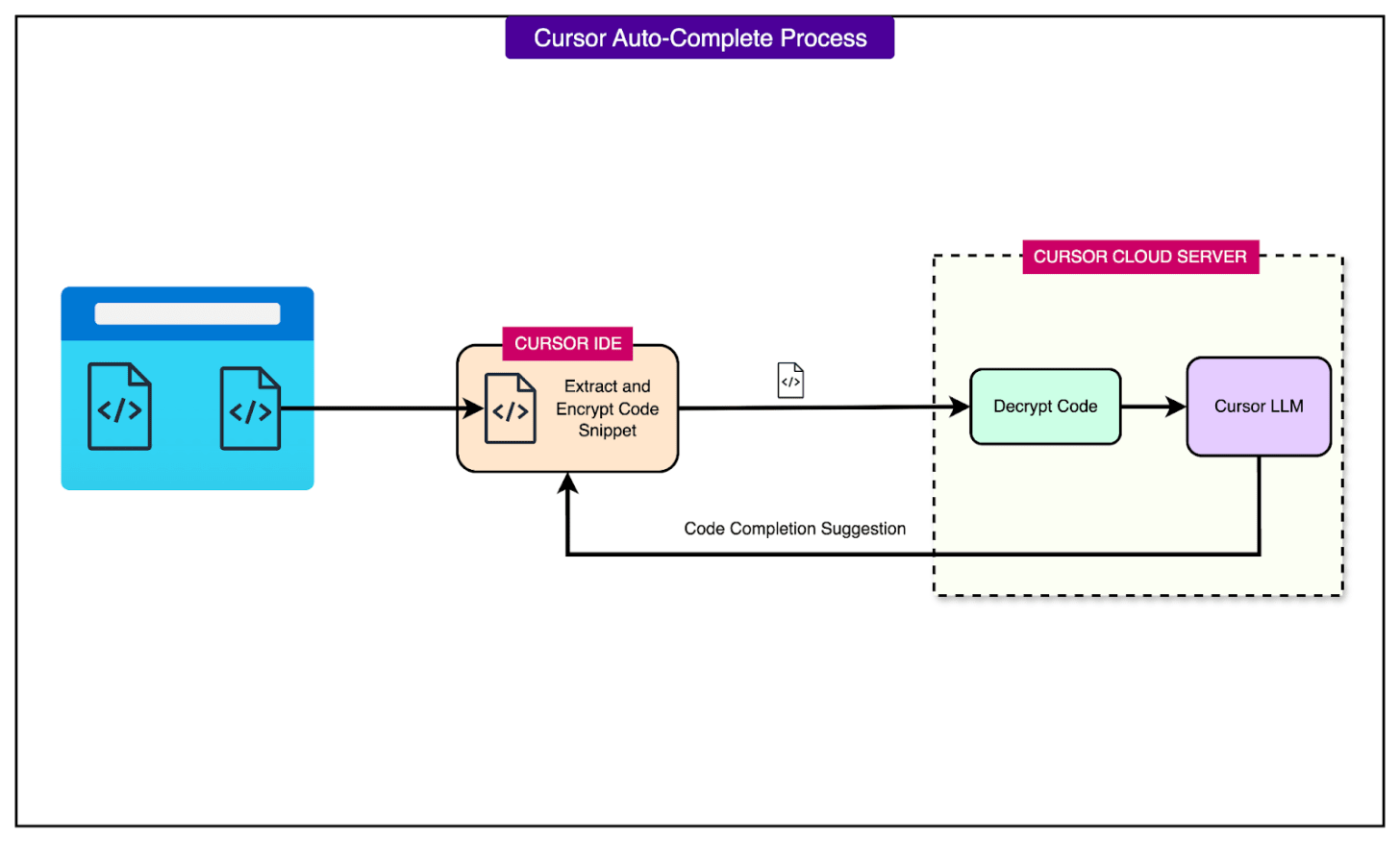
When a developer types, the Cursor client (the editor on the developer machine) collects a small snippet of the current code context, then encrypts this snippet locally before sending it over the network to Cursor’s cloud servers.
On the server, the snippet is securely decrypted, and Cursor’s in-house code Large Language Model (LLM) quickly generates a completion suggestion.
The predicted code is then returned to the client and displayed inline.
This entire process is engineered for ultra-low latency, ideally under a second, to feel instantaneous to the user. Crucially, Cursor does not persistently store the code from these autocomplete requests. The encrypted code is used on-the-fly for inference and then discarded, prioritizing user privacy.
The backend data layer sees over 1 million queries per second (QPS), primarily due to these tiny autocomplete requests.
2 - AI Chat Assistant
Beyond inline suggestions, Cursor provides a powerful AI chat assistant.
It operates as an "agentic" AI capable of handling larger, more complex tasks across an entire project. Users can interact with it through a dedicated chat panel within the IDE, providing instructions in natural language.
This feature leverages Cursor’s codebase indexing system to understand the entire project.
When asked to implement a feature, fix a bug, or refactor code, the chat agent can generate or modify code across multiple files, making coordinated edits based on higher-level instructions. This ability to operate on multiple file sets it apart from many other AI coding tools.
The chat agent can also access relevant context through special commands, such as @Web, which searches the web to gather up-to-date information, feeding the results into the conversation.
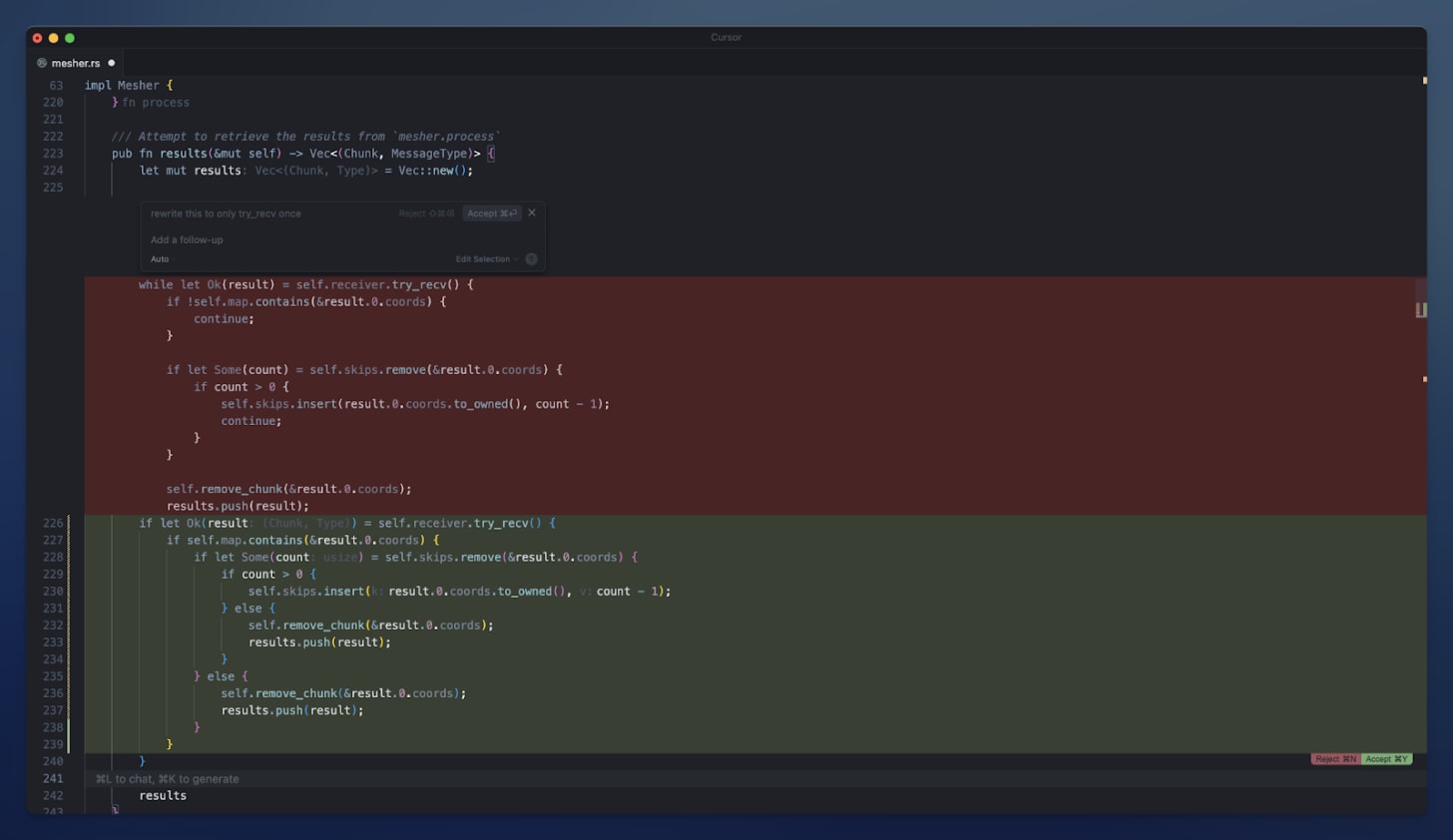
3 - Inline Edit Mode
For quick, targeted changes, Cursor offers an Inline Edit mode.
Developers can simply select a block of code within the editor, issue an instruction, and the Cursor AI will directly apply the requested changes within the selected area.
See the screenshot below for reference:
4 - AI Code Review with Bugbot
Cursor 1.0 introduced BugBot, an AI-powered code review assistant specifically designed for GitHub pull requests (PRs). Setting up BugBot involves connecting Cursor to the GitHub repository via a GitHub App installation.
BugBot automatically analyzes code changes using the same powerful AI models that drive Cursor’s chat agent. It works by examining PRs to catch potential bugs, errors, or stylistic issues that human reviewers might overlook. It then leaves comments directly on the PR with detailed explanations and suggested fixes.
BugBot can operate in both automatic mode (re-running on every PR update) or be manually triggered by commenting "bugbot run" on a PR. Each comment includes a convenient "Fix in Cursor" link, allowing developers to jump directly into the Cursor editor with the relevant context loaded to apply the suggested fix instantaneously, tightening the iteration loop.
5 - Background Agents
A standout feature for handling complex or long-running coding tasks is Cursor’s Background Agents.
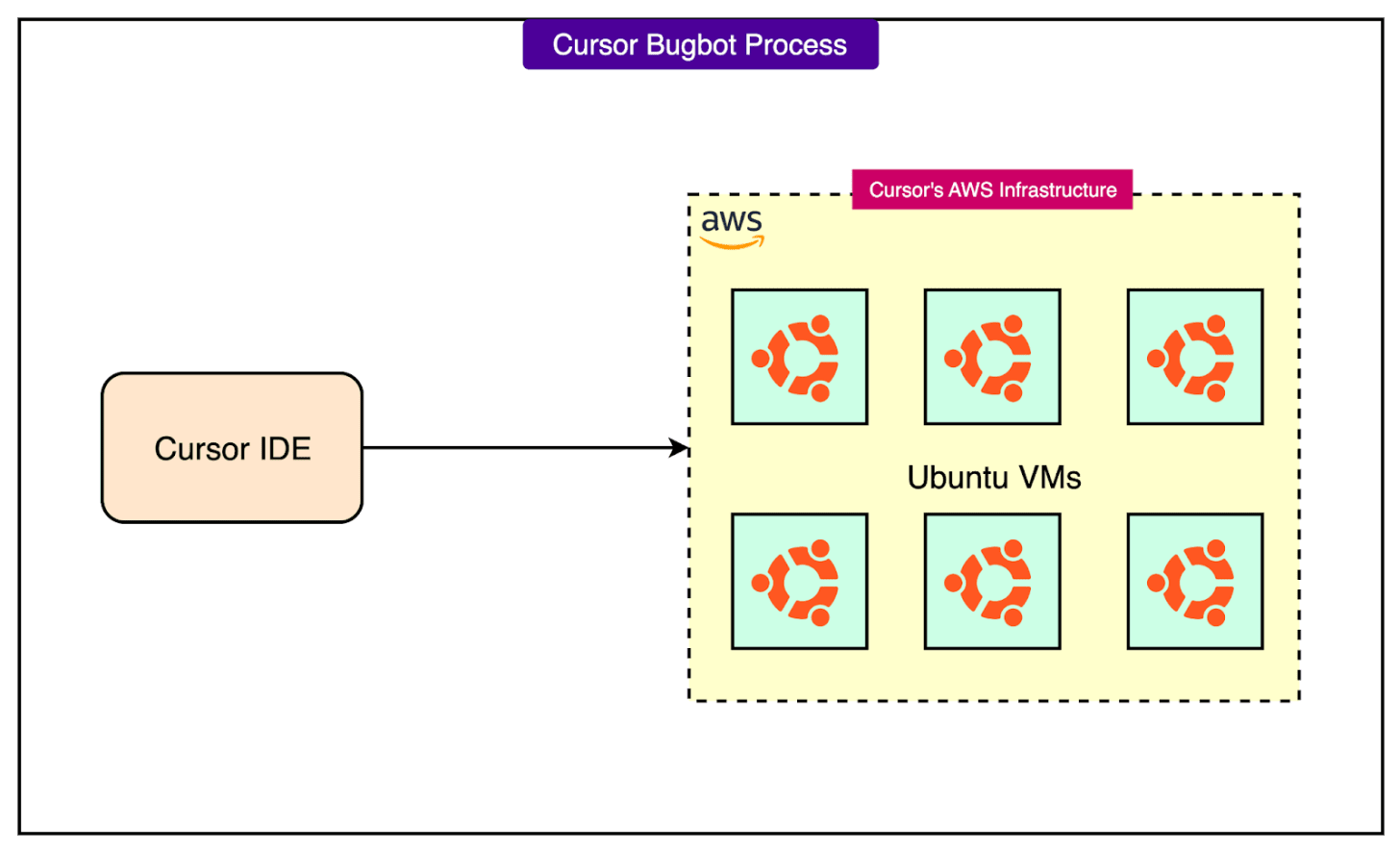
These are essentially "AI pair programmers in the cloud" that can work concurrently with a developer’s local editing session. They allow developers to offload tasks that might require executing code, running tests, or making broad changes, without tying up the local machine. Background agents typically utilize Cursor's more advanced "Max" models due to their extensive context needs.
When we launch a Background Agent, the code is executed on a remote machine in Cursor’s cloud infrastructure. Specifically, Background Agents run on isolated Ubuntu-based virtual machines (VMs) in Cursor’s AWS infrastructure. This ensures the agent’s operations (like running tests or making code changes) are sandboxed away from the user’s local environment.
6 - Persistent Project Knowledge: Rules and Memories
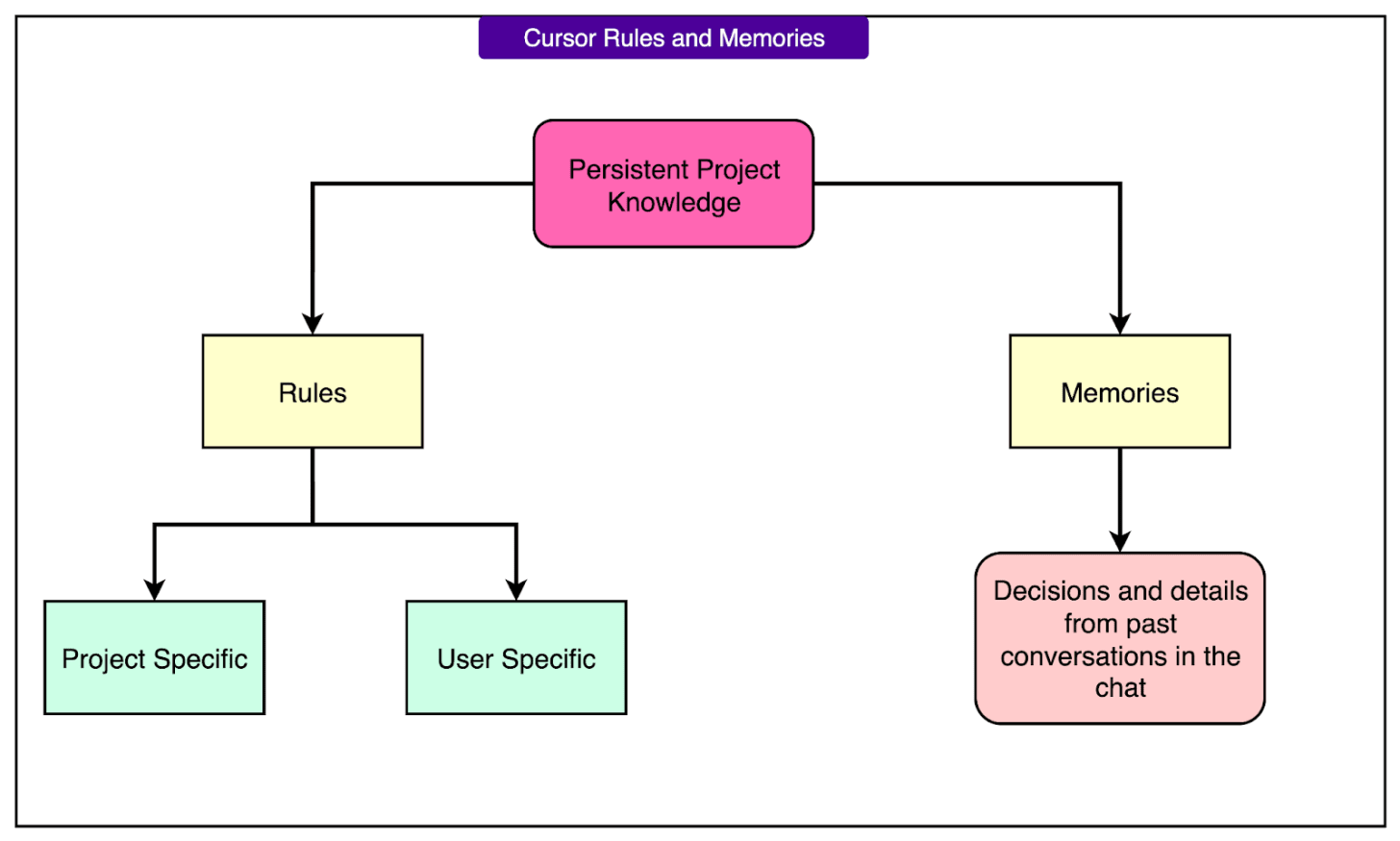
To overcome the limitation of AI models losing context between sessions, Cursor implements two features for persistent project knowledge: Rules and Memories. These enable the AI to maintain a long-term understanding of the project and adhere to specific guidelines.
Rules are explicit, system-level instructions that developers can create in special markdown files (often stored in a “.cursor/rules directory” in the repository) or in global settings. They can dictate coding style, architectural conventions, or any custom instruction that the AI should consistently follow when generating or editing code. When active, these rule contents are injected into the AI's context for every operation, ensuring consistent behavior. Rules can be project-specific (version-controlled) or user-specific (global). They allow teams to encode best practices that the AI "knows" without repeated prompting.
Memories have been launched in beta with Cursor 1.0. They allow the AI to automatically remember key details and decisions from past conversations in the chat, carrying that knowledge across sessions.
A "sidecar model" observes the chat and suggests potential memories to save, which developers can approve or reject. This means if a developer explains a tricky function or a design choice in one session, the AI can recall that context later, avoiding redundant explanations and acting as if it knows the project's nuances over time. Memories essentially become auto-generated rules managed in the settings.
7 - Codebase Indexing and Semantic Search
To effectively assist with large projects, Cursor performs codebase indexing in the background, enabling its AI to "understand" and answer questions about the entire codebase.
Here’s how it works:
Initial Indexing: When we open a project, Cursor analyzes the files, splitting them into smaller chunks (like functions). These chunks are then encrypted locally and sent to Cursor’s server with obfuscated file identifiers (even file names are not sent in plaintext). The server decrypts each chunk, computes a numerical "embedding" (a vector representation capturing the code's meaning) using an AI model (such as OpenAI's embedding model), and immediately discards the actual file content and names. Only these embedding vectors are stored in a specialized vector database (Turbopuffer). This means that the server has no human-readable code stored persistently.
Semantic Search: When the developer asks a question in Chat (or uses Cmd+K), Cursor turns the query into a vector and performs a vector similarity search against the stored embeddings. This finds relevant code sections based on meaning, not just exact keywords, without the server initially seeing the actual code.
Fetching Relevant Code: If actual code content is needed to answer a question, the server requests those specific chunks (identified by obfuscated IDs) from the Cursor client. The client then sends the corresponding source code, presumably still encrypted, which the server decrypts on the fly for the immediate query, then discards. This design prioritizes privacy, as embeddings are generally one-way, meaning original code cannot be reconstructed from them. Cursor also respects .gitignore and a dedicated .cursorignore file to prevent indexing sensitive files, and heuristically scans for secrets before sending chunks.
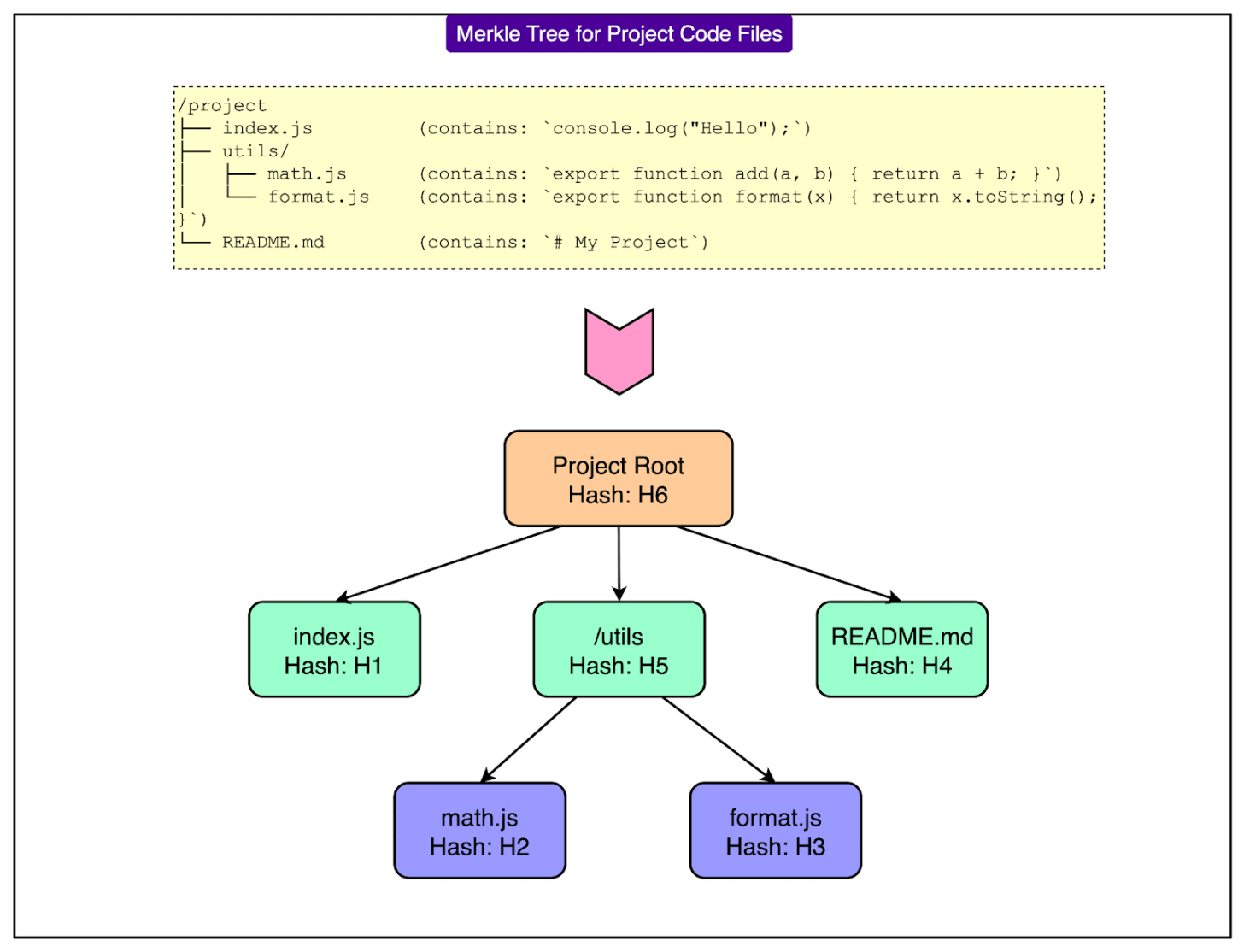
Index Synchronization: To keep the index up-to-date as developers edit code, Cursor uses a Merkle tree synchronization mechanism. A Merkle tree is a hash-based data structure that allows for efficient detection of changes in large datasets. The client computes a Merkle tree of the project's files, and the server maintains its own. By comparing these trees every few minutes, Cursor can pinpoint exactly which files have been modified and only send those changed parts for re-indexing, minimizing bandwidth and latency.
See the diagram below for a sample Merkle Tree for visualizing the project code files.
Infrastructure and Subprocessor Overview
Cursor’s AI-powered features rely on a combination of cloud infrastructure providers, model hosts, indexing engines, and analytics tools. These services are integrated with careful attention to privacy, latency, and security.
Below is a breakdown of how each provider fits into Cursor’s stack:
AWS is the backbone of Cursor’s infrastructure. The majority of backend services, including API servers, job queues, and real-time components, are hosted in AWS data centers. Most servers are located in the United States, with additional latency-optimized deployments in Tokyo and London to improve response times globally.
Cloudflare serves as a reverse proxy in front of many Cursor services. It improves network performance, handles TLS termination, and offers an additional layer of DDoS protection.
Microsoft Azure hosts parts of Cursor’s secondary infrastructure. These services also reside in the United States and participate in processing AI-related requests.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is used for a smaller set of backend systems, also hosted in U.S. regions.
Fireworks hosts Cursor’s fine-tuned, proprietary AI models. These are the models used for low-latency code completion and other real-time features. Fireworks operates across regions including the U.S., Europe, and Asia.
OpenAI provides Cursor with access to GPT-based models for various tasks, including chat responses, summarization, and completions. Even if a user selects another model (like Claude or Gemini), some requests (particularly for background summarization) may still be routed to OpenAI.
Anthropic supplies Claude models, which Cursor uses for general-purpose chat and code reasoning. Similar to OpenAI, Anthropic may receive code data for inference even when not explicitly selected, depending on task routing.
Google Cloud Vertex AI is used to access Gemini models. These models may be selected explicitly by the user or invoked for specific tasks like large-context summarization.
xAI offers Grok models, which are integrated into Cursor’s model-switching infrastructure.
Turbopuffer is Cursor’s embedding engine and vector index store. It stores obfuscated representations of the codebase, specifically numerical embeddings generated from code chunks and metadata like file hashes.
Exa and SerpApi are used to power Cursor’s @web feature, which lets the AI assistant query the internet to supplement answers.
MongoDB is used for analytics and feature usage tracking. It stores aggregate usage information, such as frequency of feature use or session metrics.
Datadog handles performance monitoring and log aggregation. Logs related to AI requests from Privacy Mode users are stripped of any code content.
Databricks (MosaicML), Foundry, and Voltage Park are used in the training and fine-tuning of Cursor’s proprietary models.
Slack and Google Workspace are used for internal team collaboration and debugging.
Sentry is used for error tracking. While traces may include user context, code content is never explicitly logged.
Mistral is used only to parse public documents, such as internet-accessible PDFs.
Pinecone stores vector embeddings of public documentation and is used by Cursor’s AI to understand common libraries and APIs when assisting with coding tasks.
Amplitude supports high-level analytics, such as tracking how often a feature is used or how long sessions last.
HashiCorp Terraform is used to manage Cursor’s cloud infrastructure via infrastructure-as-code.
Stripe handles billing and payment infrastructure.
Vercel hosts Cursor’s public-facing website.
WorkOS provides single sign-on (SSO) and authentication infrastructure.
Conclusion
Cursor stands out as a pioneering AI-first code editor that seamlessly blends a familiar development environment with cutting-edge artificial intelligence. By forking Visual Studio Code, Cursor provides developers with a stable and intuitive interface while enabling a rapid focus on deep AI integration.
At its core, Cursor's architecture is designed to deliver intelligent assistance without compromising speed or privacy. Many of its features, like its real-time AI code autocomplete, are powered by in-house models running on cloud servers, sending only encrypted code snippets to ensure low latency and data security.
This sophisticated cloud-backed system, handling billions of AI completions daily, redefines the coding experience by deeply embedding AI into every workflow, boosting developer productivity and changing how code is written and managed.
References:
SPONSOR US
Get your product in front of more than 1,000,000 tech professionals.
Our newsletter puts your products and services directly in front of an audience that matters - hundreds of thousands of engineering leaders and senior engineers - who have influence over significant tech decisions and big purchases.
Space Fills Up Fast - Reserve Today
Ad spots typically sell out about 4 weeks in advance. To ensure your ad reaches this influential audience, reserve your space now by emailing sponsorship@bytebytego.com.