The discipline of epigraphy, focused on studying texts inscribed on durable materials like stone and metal, provides critical firsthand evidence for understanding the Roman world. The field faces numerous challenges including fragmentary inscriptions, uncertain dating, diverse geographical provenance, widespread use of abbreviations, and a large and rapidly growing corpus of over 176,000 Latin inscriptions, with approximately 1,500 new inscriptions added annually.
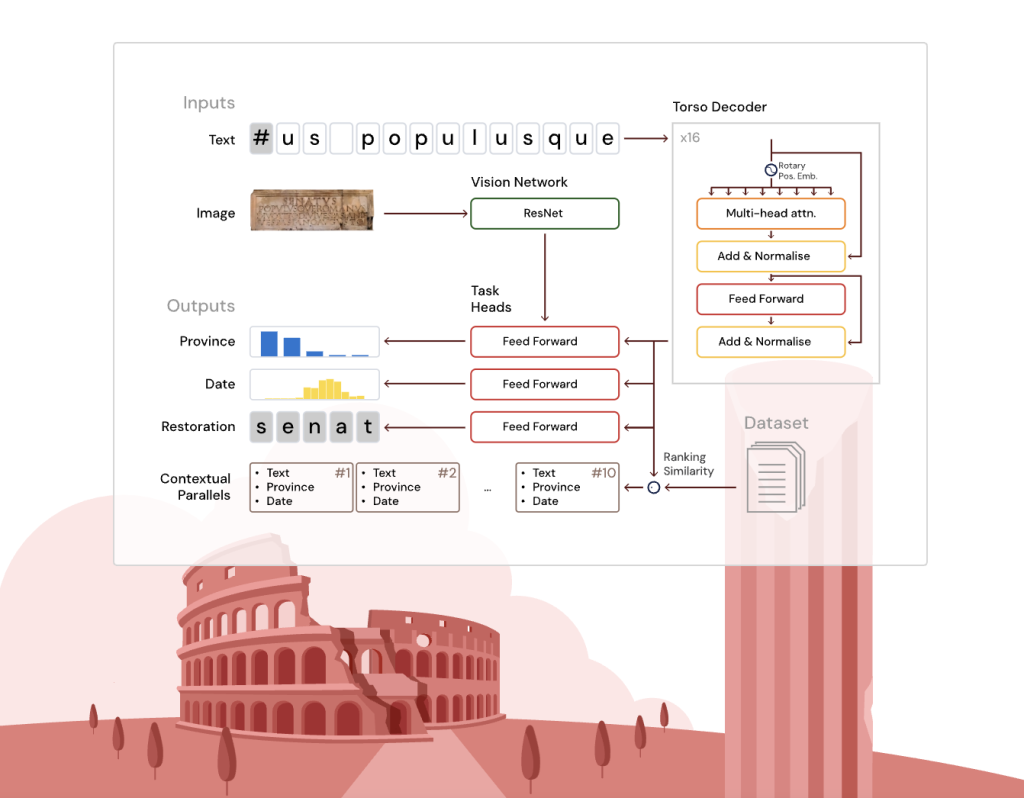
To address these challenges, Google DeepMind developed Aeneas: a transformer-based generative neural network that performs restoration of damaged text segments, chronological dating, geographic attribution, and contextualization through retrieval of relevant epigraphic parallels.
Challenges in Latin Epigraphy
Latin inscriptions span more than two millennia, from roughly the 7th century BCE to the 8th century CE, across the vast Roman Empire comprising over sixty provinces. These inscriptions vary from imperial decrees and legal documents to tombstones and votive altars. Epigraphers traditionally restore partially lost or illegible texts using detailed knowledge of language, formulae, and cultural context, and attribute inscriptions to certain timeframes and locations by comparing linguistic and material evidence.
However, many inscriptions suffer from physical damage with missing segments of uncertain lengths. The wide geographic dispersion and diachronic linguistic changes make dating and provenance attribution complex, especially when combined with the sheer corpus size. Manual identification of epigraphic parallels is labor-intensive and often limited by specialized expertise localized to certain regions or periods.

Latin Epigraphic Dataset (LED)
Aeneas is trained on the Latin Epigraphic Dataset (LED), an integrated and harmonized corpus of 176,861 Latin inscriptions aggregating records from three major databases. The dataset includes approximately 16 million characters covering inscriptions spanning seven centuries BCE to eight centuries CE. About 5% of these inscriptions have associated grayscale images.
The dataset uses character-level transcriptions employing special placeholder tokens: - marks missing text of a known length while # denotes missing segments of unknown length. Metadata includes province-level provenance over 62 Roman provinces and dating by decade.
Model Architecture and Input Modalities
Aeneas’s core is a deep, narrow transformer decoder based on the T5 architecture, adapted with rotary positional embeddings for effective local and contextual character processing. The textual input is processed alongside optional inscription images (when available) through a shallow convolutional network (ResNet-8), which feeds image embeddings to the geographical attribution head only.
The model includes multiple specialized task heads to perform:
- Restoration: Predict missing characters, supporting arbitrary-length unknown gaps using an auxiliary neural classifier.Geographical Attribution: Classify inscriptions among 62 provinces by combining text and visual embeddings.Chronological Attribution: Estimate text date by decade using a predictive probabilistic distribution aligned with historical date ranges.
Additionally, the model generates a unified historically enriched embedding by combining outputs from the core and task heads. This embedding enables retrieval of ranked epigraphic parallels using cosine similarity, incorporating linguistic, epigraphic, and broader cultural analogies beyond exact textual matches.
Training Setup and Data Augmentation
Training occurs on TPU v5e hardware with batch sizes up to 1024 text-image pairs. Losses for each task are combined with optimized weighting. The data is augmented by random text masking (up to 75% characters), text clipping, word deletions, punctuation dropping, image augmentations (zoom, rotation, brightness/contrast adjustments), dropout, and label smoothing to improve generalization.
Prediction uses beam search with specialized non-sequential logic for unknown-length text restoration, ensuring multiple restoration candidates ranked by joint probability and length.
Performance and Evaluation
Evaluated on the LED test set and through a human-AI collaboration study with 23 epigraphers, Aeneas demonstrates marked improvements:
- Restoration: Character error rate (CER) reduced to approximately 21% when Aeneas support is provided, compared to 39% for unaided human experts. The model itself achieves around 23% CER on the test set.Geographical Attribution: Achieves around 72% accuracy in correctly classifying the province among 62 options. With Aeneas assistance, historians improve accuracy up to 68%, outperforming either alone.Chronological Attribution: Average error in date estimation is approximately 13 years for Aeneas, with historians aided by Aeneas reducing error from about 31 years to 14 years.Contextual Parallels: Epigraphic parallels retrieved are accepted as useful starting points for historical research in approximately 90% of cases and increase historians’ confidence by an average of 44%.
These improvements are statistically significant and highlight the model’s utility as an augmentation to expert scholarship.
Case Studies
Res Gestae Divi Augusti:
Aeneas’s analysis of this monumental inscription reveals bimodal dating distributions reflecting scholarly debates about its compositional layers and stages (late first century BCE and early first century CE). Saliency maps highlight date-sensitive linguistic forms, archaic orthography, institutional titles, and personal names, mirroring expert epigraphic knowledge. Parallels retrieved predominantly include imperial legal decrees and official senatorial texts sharing formulaic and ideological features.
Votive Altar from Mainz (CIL XIII, 6665):
Dedicated in 211 CE by a military official, this inscription was accurately dated and geographically attributed to Germania Superior and related provinces. Saliency maps identify key consular dating formulas and cultic references. Aeneas retrieved highly related parallels including a 197 CE altar sharing rare textual formulas and iconography, revealing historically meaningful connections beyond direct text overlap or spatial metadata.
Integration in Research Workflows and Education
Aeneas operates as a cooperative tool, not a replacement for historians. It accelerates searching for epigraphic parallels, aids restoration, and refines attribution, freeing scholars to focus on higher-level interpretation. The tool and dataset are openly available via the Predicting the Past platform under permissive licenses. An educational curriculum has been co-developed targeting high school students and educators, promoting interdisciplinary digital literacy by bridging AI and classical studies.
FAQ 1: What is Aeneas and what tasks does it perform?
Aeneas is a generative multimodal neural network developed by Google DeepMind for Latin epigraphy. It assists historians by restoring damaged or missing text in ancient Latin inscriptions, estimating their date within about 13 years, attributing their geographical origin with around 72% accuracy, and retrieving historically relevant parallel inscriptions for contextual analysis.
FAQ 2: How does Aeneas handle incomplete or damaged inscriptions?
Aeneas can predict missing text segments even when the length of the gap is unknown, a capability known as arbitrary-length restoration. It uses a transformer-based architecture and specialized neural network heads to generate multiple plausible restoration hypotheses, ranked by likelihood, facilitating expert evaluation and further research.
FAQ 3: How is Aeneas integrated into historian workflows?
Aeneas provides historians with ranked lists of epigraphic parallels and predictive hypotheses for restoration, dating, and provenance. These outputs boost historians’ confidence and accuracy, reduce research time by quickly suggesting relevant texts, and support collaborative human-AI analysis. The model and datasets are openly accessible via the Predicting the Past platform.
Check out the Paper, Project and Google DeepMind Blog. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. SUBSCRIBE NOW to our AI Newsletter
The post Google DeepMind Introduces Aeneas: AI-Powered Contextualization and Restoration of Ancient Latin Inscriptions appeared first on MarkTechPost.

