Quantum repeaters are essential components of quantum networks, enabling long-distance entanglement distribution by temporarily storing quantum states. This temporary storage, facilitated by quantum memory, allows synchronization with other network operations and the implementation of error correction protocols, marking a significant advancement over classical repeaters, which merely amplify and retransmit signals.
Unlike classical systems, quantum repeaters mitigate photon loss, a major source of error in quantum communication. However, widely known quantum repeater designs often suffer from limitations such as the need for high phase stability and an inability to generate strongly entangled states.
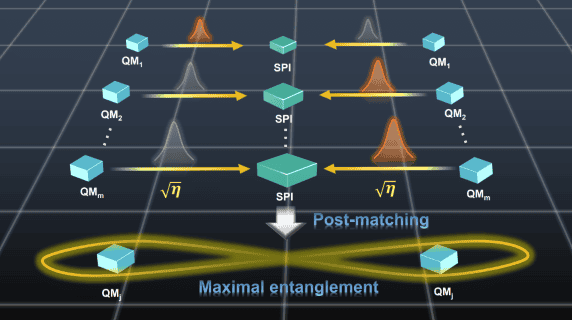
In this work, the authors propose a novel protocol based on post-matching, a technique originally developed in quantum cryptography to verify and secure transmitted information. Their theoretical framework offers new insights into both quantum communication and cryptographic systems, contributing to the advancement of quantum information theory and technology.
Read the full article
Asynchronous quantum repeater using multiple quantum memory
Chen-Long Li et al 2024 Rep. Prog. Phys. 87 127901
Do you want to learn more about this topic?
Explore our Focus on Quantum Entanglement: State of the Art and Open Questions
The post Quantum memory meets cryptography appeared first on Physics World.

