Want to dive deeper? Explore security blog posts >
The GitHub Advisory Database (Advisory DB) is a vital resource for developers, providing a comprehensive list of known security vulnerabilities and malware affecting open source packages. This post analyzes trends in the Advisory DB, highlighting the growth in reviewed advisories, ecosystem coverage, and source contributions in 2024. We’ll delve into how GitHub provides actionable data to secure software projects.
Advisories
The GitHub Advisory Database contains a list of known security vulnerabilities and malware, grouped in three categories:
- GitHub-reviewed advisories: Manually reviewed advisories in software packages that GitHub supports.Unreviewed advisories: These are automatically pulled from the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) and are either in the process of being reviewed, do not affect a supported package, or do not discuss a valid vulnerability.Malware advisories: These are specific to malware threats identified by the npm security team.
Reviewed advisories
GitHub-reviewed advisories are security vulnerabilities that have been mapped to packages in ecosystems we support. We carefully review each advisory for validity and ensure that they have a full description, and contain both ecosystem and package information.
Every year, GitHub increases the number of advisories we publish. We have been able to do this due to the increase in advisories coming from our sources (see Sources section below), expanding our ecosystem coverage (also described below), and review campaigns of advisories published before we started the database.
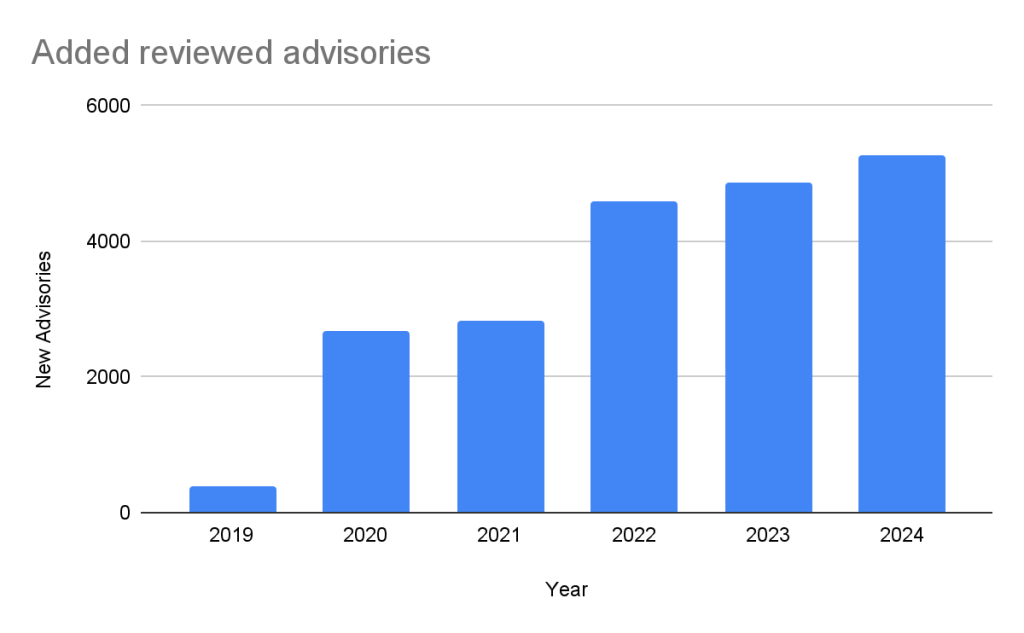
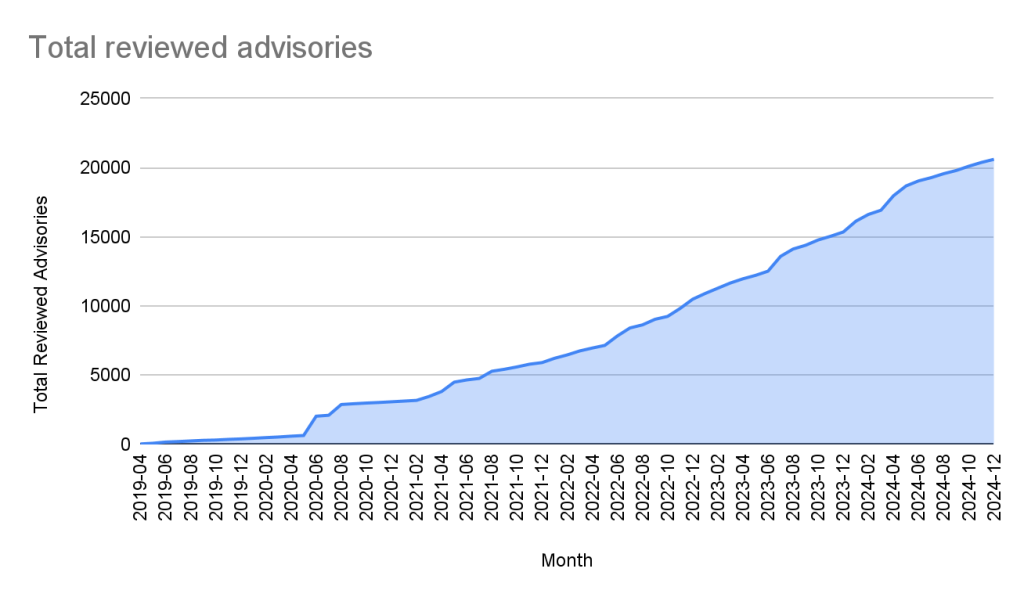
In the past five years, the database has gone from fewer than 400 reviewed advisories to over 20,000 reviewed advisories in October of 2024.
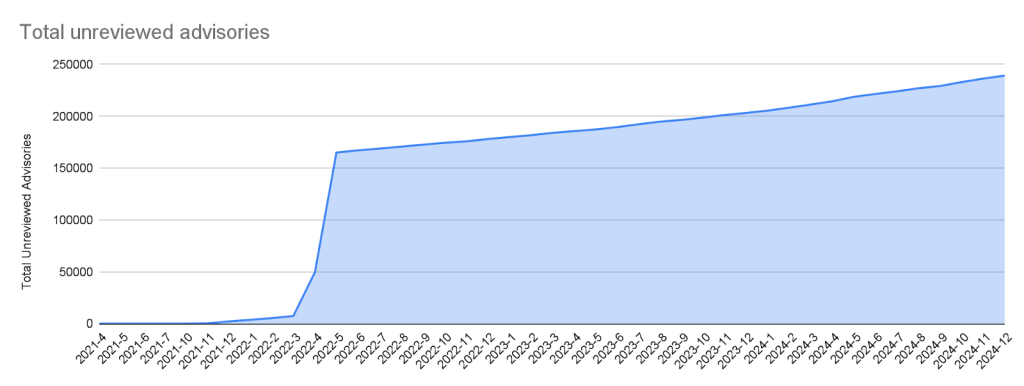
Unreviewed advisories
Unreviewed advisories are security vulnerabilities that we publish automatically into the GitHub Advisory Database directly from the National Vulnerability Database feed. The name is a bit of a misnomer as many of these advisories have actually been reviewed by a GitHub analyst. The reason why they fall into this category is because they are not found in a package in one of the supported ecosystems or are not discussing a valid vulnerability, and all have been reviewed by analysts other than someone from the GitHub Security Lab. Even though most of these advisories will never turn into a reviewed advisory, we still publish them so that you do not have to look in multiple databases at once.
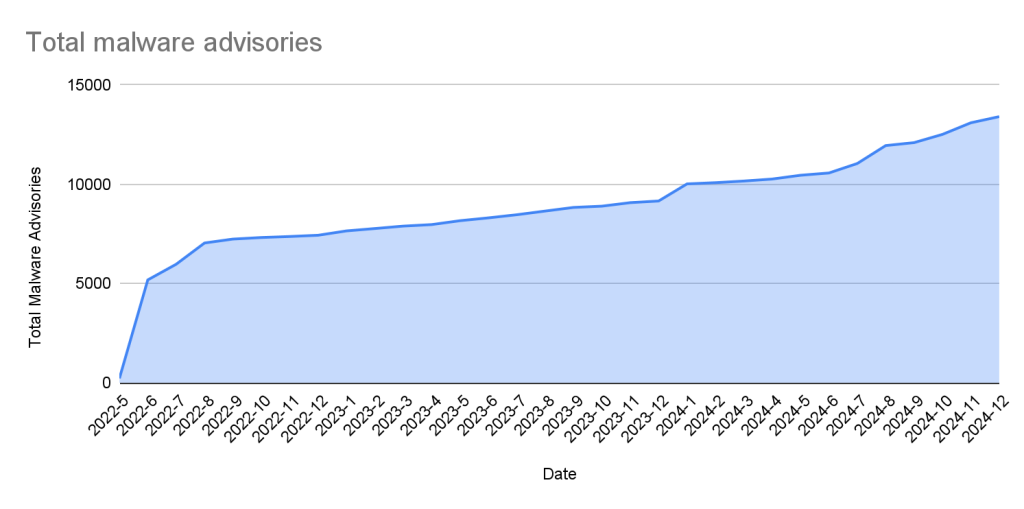
Malware
Malware advisories relate to vulnerabilities caused by malware, and are security advisories that GitHub publishes automatically into the GitHub Advisory Database directly from information provided by the npm security team. Malware advisories are currently exclusive to the npm ecosystem. GitHub doesn’t edit or accept community contributions on these advisories.
Ecosystem coverage
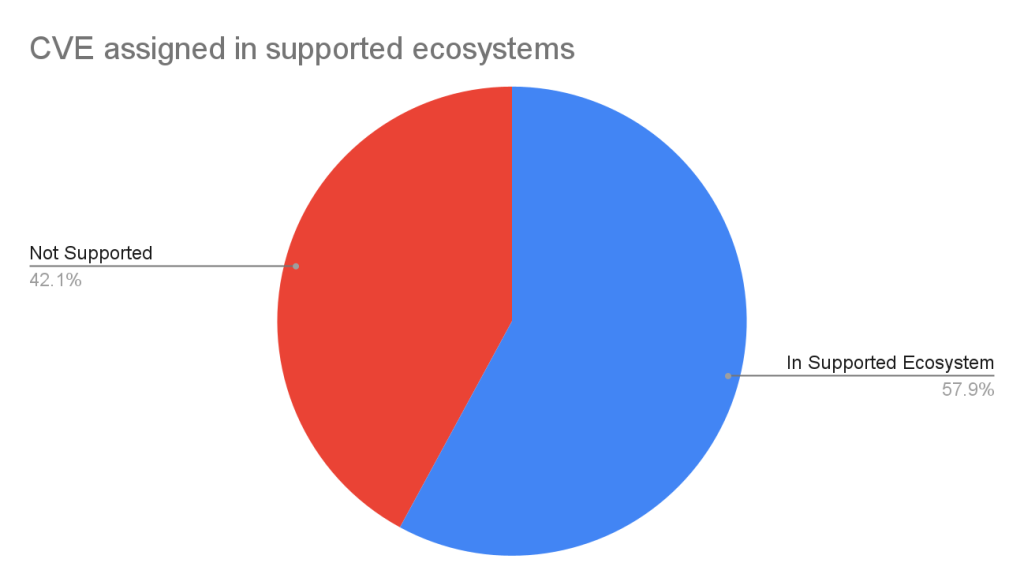
GitHub-reviewed advisories include security vulnerabilities that have been mapped to packages in ecosystems we support. Generally, we name our supported ecosystems after the software programming language’s associated package registry. We review advisories if they are for a vulnerability in a package that comes from a supported registry.
| Ecosystem | Total advisories | Vulnerable packages | First added |
|---|---|---|---|
| pip (registry: https://pypi.org/) | 3378 | 1044 | 2019-04-19 |
| Maven (registry: https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2) | 5171 | 955 | 2019-04-22 |
| Composer (registry: https://packagist.org/) | 4238 | 812 | 2019-04-26 |
| npm (registry: https://www.npmjs.com/) | 3653 | 2652 | 2019-04-26 |
| RubyGems (registry: https://rubygems.org/) | 840 | 371 | 2019-04-26 |
| NuGet (registry: https://www.nuget.org/) | 651 | 489 | 2019-04-26 |
| Go (registry: https://pkg.go.dev/) | 2011 | 865 | 2021-04-01 |
| Rust (registry: https://crates.io/) | 857 | 553 | 2021-05-25 |
| Erlang (registry: https://hex.pm/) | 31 | 26 | 2022-01-27 |
| GitHub Actions (https://github.com/marketplace?type=actions/) | 21 | 21 | 2022-07-29 |
| Pub (registry: https://pub.dev/packages/registry) | 10 | 9 | 2022-08-04 |
| Swift (registry: N/A) | 33 | 21 | 2023-05-10 |
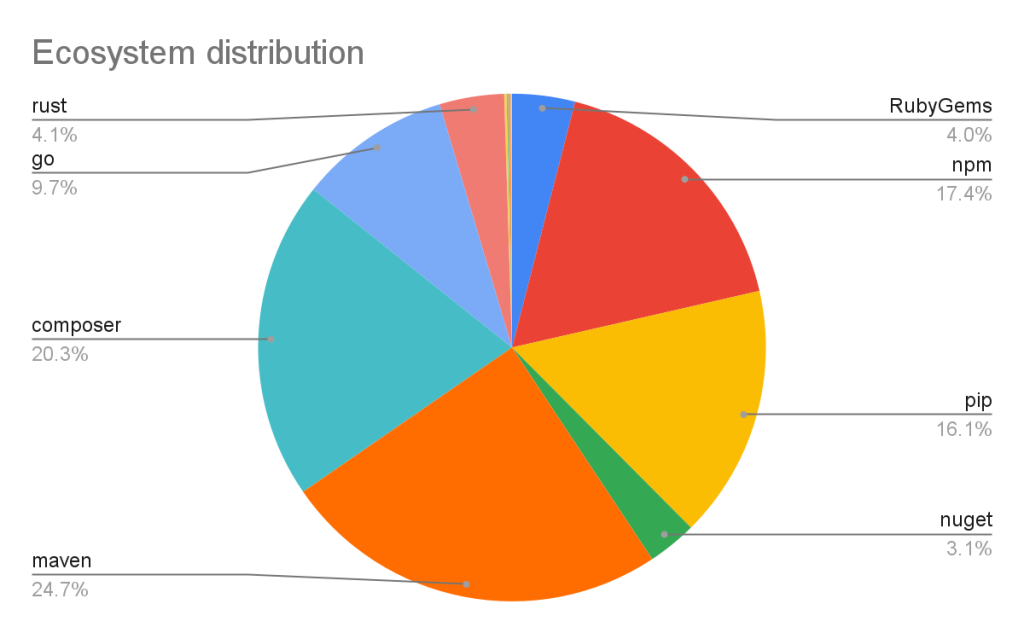
Vulnerabilities in Maven and Composer packages are nearly half of the advisories in the database. npm, pip, and Go make up much of the rest, while the other ecosystems have a much smaller footprint.
This has not always been the case. When the database was initially launched, NPM advisories dominated the database, but as we have expanded our coverage and added support for new ecosystems, the distribution mix has changed.
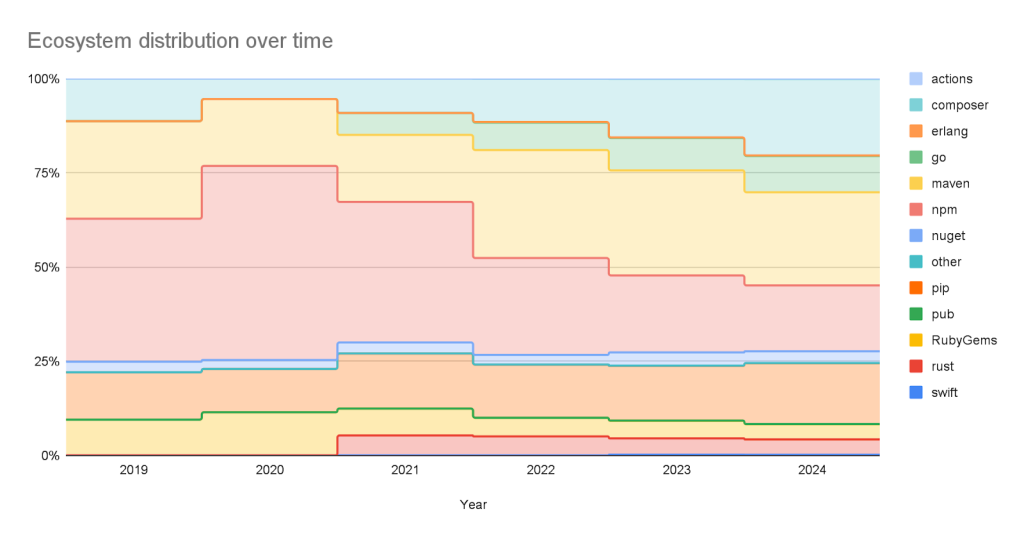
Sources: Where do the advisories come from?
We add advisories to the GitHub Advisory Database from the following sources:
| Source | Advisories | Reviewed advisories | Sole source | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NVD | 267429 | 18295 | 7450 | 6.84% |
| GitHub Repository Advisories | 12247 | 5311 | 564 | 43.37% |
| Community Contributions | 4512 | 4160 | 10 | 92.20% |
| PyPA Advisories | 3040 | 2739 | 14 | 90.10% |
| Go Vulncheck | 1581 | 1528 | 7 | 96.65% |
| NPM Advisories | 1411 | 1408 | 629 | 99.79% |
| FriendsOfPHP | 1406 | 1396 | 400 | 99.29% |
| RustSec | 943 | 849 | 171 | 90.03% |
| RubySec | 873 | 861 | 4 | 98.63% |
- NVD: This is a huge source of vulnerabilities covering all types of software. We publish all NVD advisories but only review those relevant to our supported ecosystems, which reduces noise for our users.GitHub Repository Advisories: The second largest source is made up of advisories published through GitHub’s repository security advisory feature. Similar to NVD, these aren’t restricted to our supported ecosystems. However, we provide better coverage of the repository advisories because they focus exclusively on open source software.Community Contributions: These are reports from the community that are almost exclusively requesting updates to existing advisories.Other Specialized Sources: Sources like PyPA Advisories (for Python) and Go Vulncheck (for Go) that focus on specific ecosystems. Because they only cover packages within our supported ecosystems, most of their advisories are relevant to us and get reviewed.
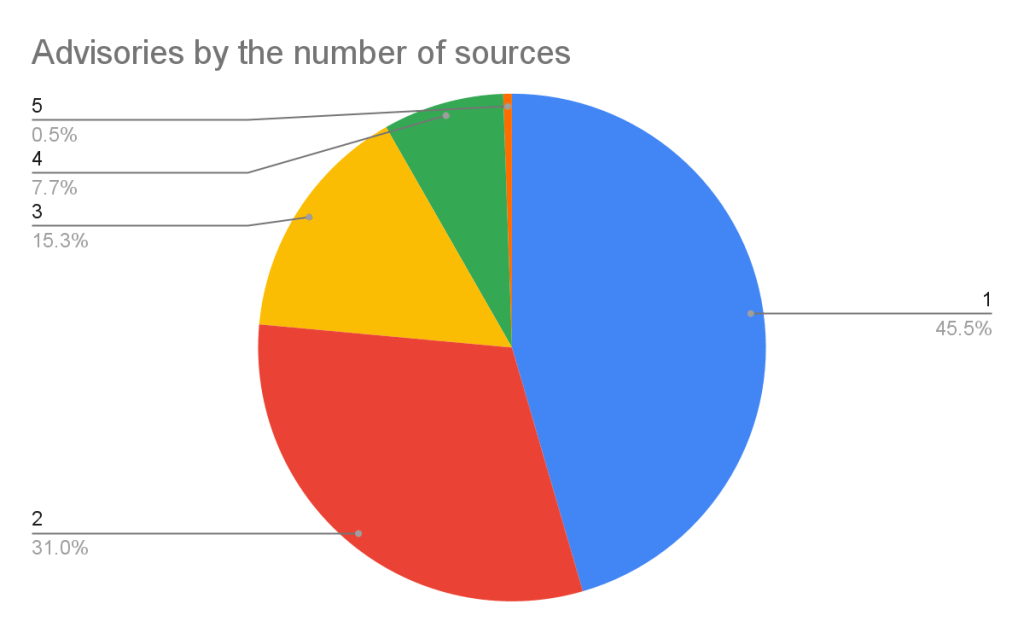
If you add up the number of reviewed advisories from each source, you will find that total is more than the total reviewed advisories. This is because each source can publish an advisory for the same vulnerability. In fact, over half of our advisories have more than one source.
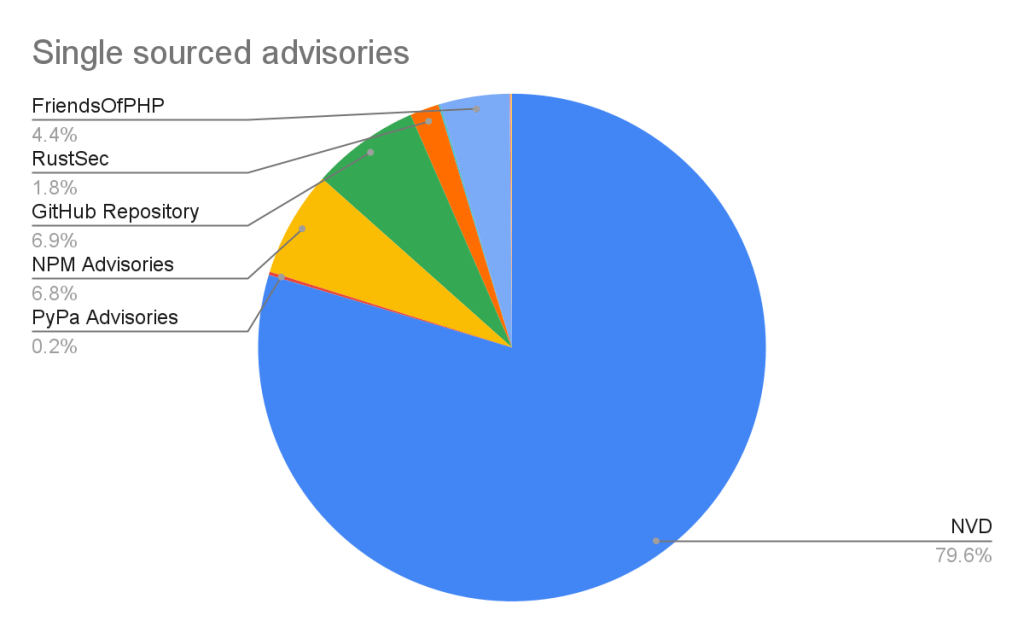
Of the advisories with a single source, nearly all of them come from NVD/CVE. This justifies NVD/CVE as a source, even though it is by far the noisiest.
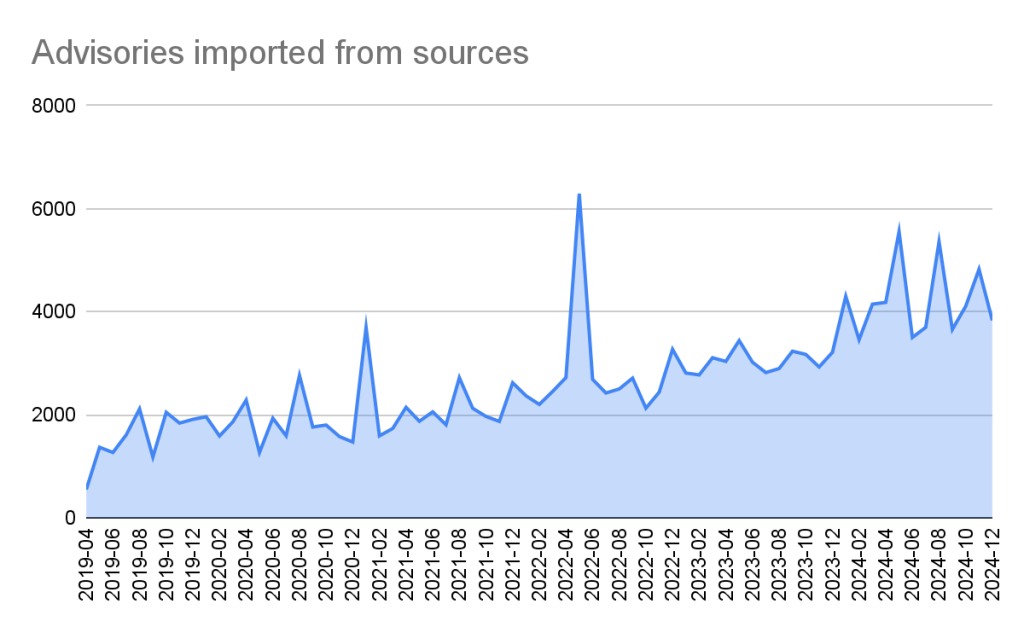
2024 saw a significant increase (39%) in the number of advisories imported from our sources. This is for the most part caused by an increase in the number of CVE records published.
CVE Numbering Authority
In addition to publishing advisories in the GitHub Advisory Database, we are also a CVE Numbering Authority (CNA) for any repository on GitHub. This means that we issue CVE IDs for vulnerabilities reported to us by maintainers, and we publish the vulnerabilities to the CVE database once the corresponding repository advisory is published.
GitHub published over 2,000 CVE records in 2024, making us the fifth-largest CNA in the CVE Program.
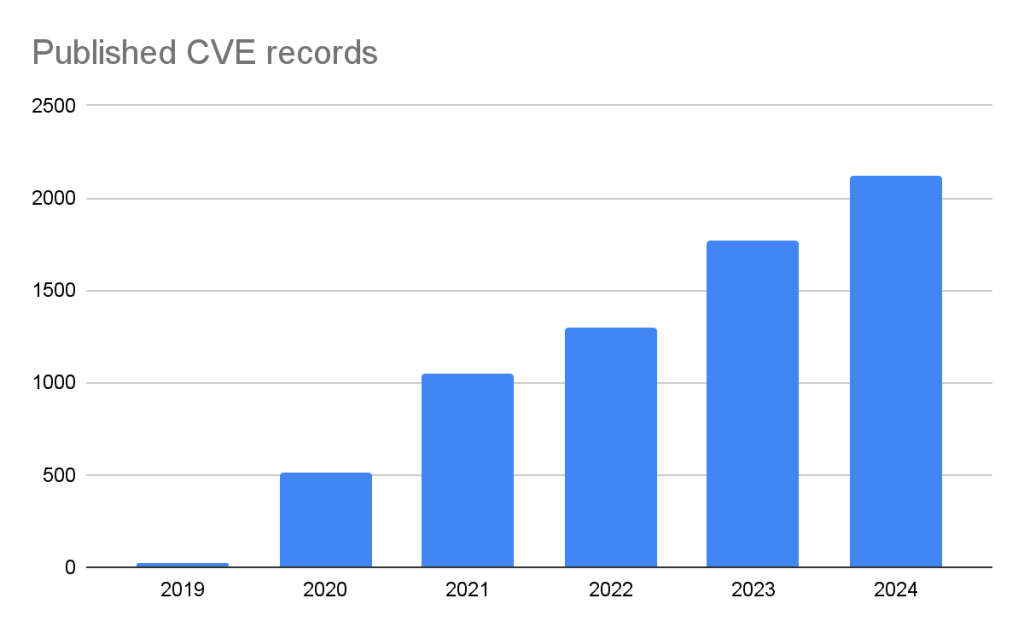
The GitHub CNA is open to all repositories on GitHub, not just ones in a supported ecosystem.
Advisory prioritization
Given the constant deluge of reported vulnerabilities, you’ll want tools that can help you prioritize your remediation efforts. To that end, GitHub provides additional data in the advisory to allow readers to prioritize their vulnerabilities. In particular, there are:
- Severity Rating/CVSS: A low to critical rating for how severe the vulnerability is likely to be, along with a corresponding CVSS score and vector.CWE: CWE identifiers provide a programmatic method for determining the type of vulnerability.EPSS: The Exploit Prediction Scoring System, or EPSS, is a system devised by the global Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST) for quantifying the likelihood a vulnerability will be attacked in the next 30 days.
GitHub adds a severity rating to every advisory. The severity level is one of four possible levels defined in the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), Section 5.
- LowMedium/ModerateHighCritical
Using these ratings, half of all vulnerabilities (15% are Critical and 35% are High) warrant immediate or near-term attention. By focusing remediation efforts on these, you can significantly reduce risk exposure while managing workload more efficiently.
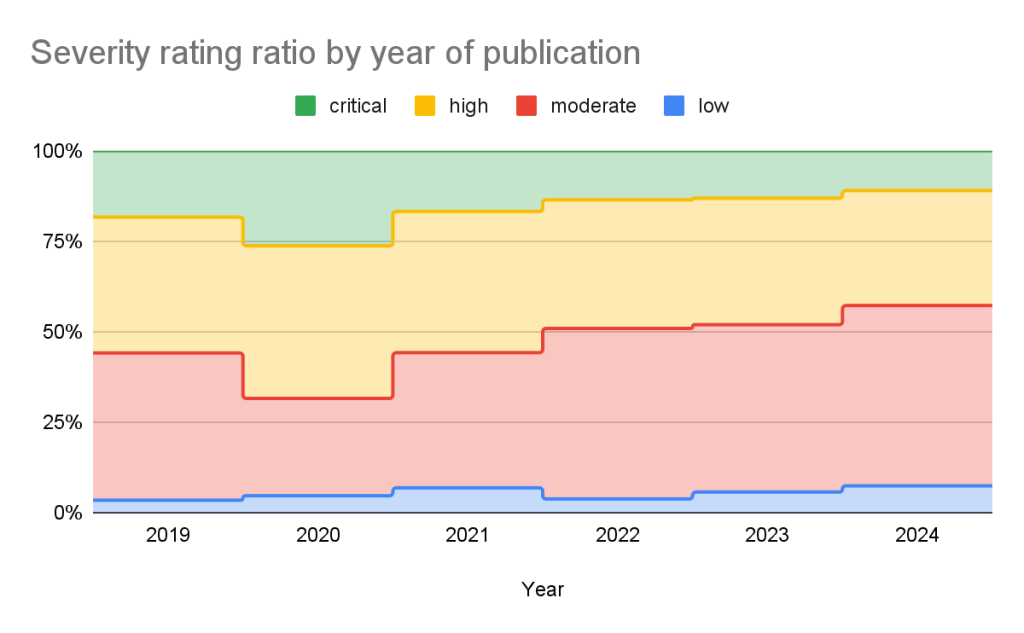
The CVSS specification says the base score we provide, “reflects the severity of a vulnerability according to its intrinsic characteristics which are constant over time and assumes the reasonable worst-case impact across different deployed environments.” However, the worst-case scenario for your deployment may not be the same as CVSS’s. After all, a crash in a word processor is not as severe as a crash in a server. In order to give more context to your prioritization, GitHub allows you to filter alerts based on the type of vulnerability or weakness using CWE identifiers. So you have the capability to never see another regular expression denial of service (CWE-1333) vulnerability again or always see SQL injection (CWE-89) vulnerabilities.
| Rank | CWE ID | CWE name | Number of advisories in 2024 | Change in rank from 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CWE-79 | Improper Neutralization of Input During Web Page Generation (‘Cross-site Scripting’) | 936 | +0 |
| 2 | CWE-200 | Exposure of Sensitive Information to an Unauthorized Actor | 320 | +0 |
| 3 | CWE-22 | Improper Limitation of a Pathname to a Restricted Directory (‘Path Traversal’) | 259 | +2 |
| 4 | CWE-20 | Improper Input Validation | 202 | +0 |
| 5 | CWE-94 | Improper Control of Generation of Code (‘Code Injection’) | 188 | +2 |
| 6 | CWE-89 | Improper Neutralization of Special Elements used in an SQL Command (‘SQL Injection’) | 181 | +3 |
| 7 | CWE-352 | Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) | 161 | -4 |
| 8 | CWE-284 | Improper Access Control | 153 | +4 |
| 9 | CWE-400 | Uncontrolled Resource Consumption | 149 | -3 |
| 10 | CWE-287 | Improper Authentication | 124 | +11 |
Still drowning in vulnerabilities? Try using EPSS to focus on vulnerabilities likely to be attacked in the next 30 days. EPSS uses data from a variety of sources to create a probability of whether exploitation attempts will be seen in the next 30 days for a given vulnerability. As you can see from the chart below, if you focus on vulnerabilities with EPSS scores of 10% or higher (approx. 7% of all vulnerabilities in the Advisory DB), you can cover nearly all of the vulnerabilities that are likely to see exploit activity.
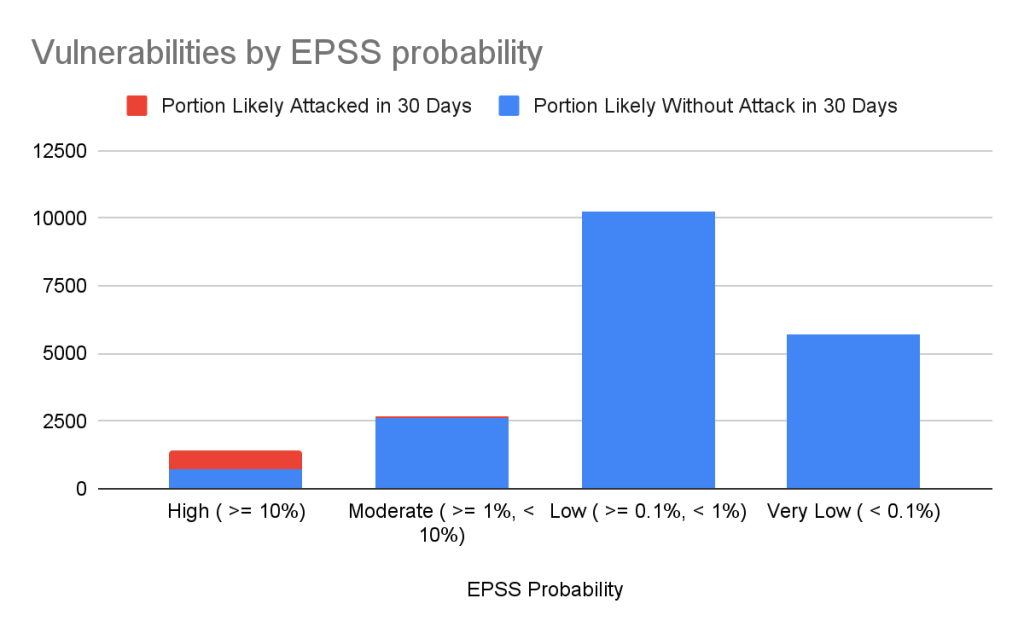
| EPSS probability | Vulnerabilities in range | Percentage of overall vulnerabilities | Expected vulnerabilities in range attacked within the next 30 days | Percentage of total attacked vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High ( >= 10%) | 1440 | 7.17% | 741 | 85.96% |
| Moderate ( >= 1%, < 10%) | 2687 | 13.37% | 84 | 9.74% |
| Low ( >= 0.1%, < 1%) | 10264 | 51.09% | 35 | 4.06% |
| Very Low ( < 0.1%) | 5701 | 28.37% | 2 | 0.23% |
Important caveats to remember when using EPSS:
- Low probability events occur.EPSS does not tell you whether a vulnerability is exploited; it only claims how likely it is.EPSS scores are updated daily and will change as new information comes in, so a low-probability vulnerability today may become high probability tomorrow.
For more details on how to use CVSS and EPSS for prioritization, see our blog on prioritizing Dependabot alerts.
Actionable data
The GitHub Advisory DB isn’t just a repository of vulnerabilities. It powers tools that help developers secure their projects. Services like Dependabot use the Advisory DB to:
- Identify vulnerabilities: It checks if your projects use any software packages with known vulnerabilities.Suggest fixes: It recommends updated versions of packages that fix those vulnerabilities when available.Reduce noise: You’ll only get notified about vulnerabilities that affect the version of the package you are using.
Take this with you
The GitHub Advisory Database is a powerful resource for tracking open source software vulnerabilities, with over 22,000 reviewed advisories to date. By focusing on popular package registries, GitHub allows you to definitively connect vulnerabilities to the packages you are using. Additional data such as CVSS and EPSS scores help you properly prioritize your mitigation efforts.
GitHub’s role as a CVE Numbering Authority extends beyond the Advisory Database, ensuring that thousands of vulnerabilities each year reach the broader CVE community. Want to ensure your vulnerability fix reaches your users? Create a GitHub security advisory in your repository to take advantage of both the GitHub Advisory Database and GitHub’s CNA services.
The post GitHub Advisory Database by the numbers: Known security vulnerabilities and what you can do about them appeared first on The GitHub Blog.

