About 15% of the world’s population — over a billion people — are affected by neurological disorders, from commonly known diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s to hundreds of lesser-known, rare conditions.
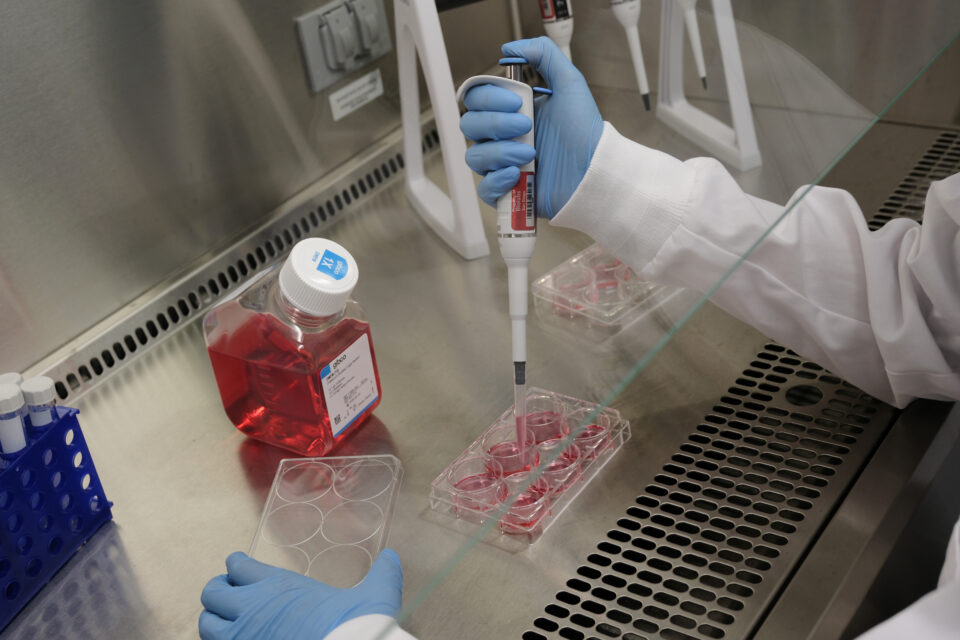
BrainStorm Therapeutics, a San Diego-based startup, is accelerating the development of cures for these conditions using AI-powered computational drug discovery paired with lab experiments using organoids: tiny, 3D bundles of brain cells created from patient-derived stem cells. This hybrid, iterative method, where clinical data and AI models inform one another to accelerate drug development, is known as lab in the loop.
“The brain is the last frontier in modern biology,” said BrainStorm’s founder and CEO Robert Fremeau, who was previously a scientific director in neuroscience at Amgen and a faculty member at Duke University and the University of California, San Francisco. “By combining our organoid disease models with the power of generative AI, we now have the ability to start to unravel the underlying complex biology of disease networks.”
The company aims to lower the failure rate of drug candidates for brain diseases during clinical trials — currently over 93% — and identify therapeutics that can be applied to multiple diseases. Achieving these goals would make it faster and more economically viable to develop treatments for rare and common conditions.
“This alarmingly high clinical trial failure rate is mainly due to the inability of traditional preclinical models with rodents or 2D cells to predict human efficacy,” said Jun Yin, cofounder and chief technology officer at BrainStorm. “By integrating human-derived brain organoids with AI-driven analysis, we’re building a platform that better reflects the complexity of human neurobiology and improves the likelihood of clinical success.”
Fremeau and Yin believe that BrainStorm’s platform has the potential to accelerate development timelines, reduce research and development costs, and significantly increase the probability of bringing effective therapies to patients.
BrainStorm Therapeutics’ AI models, which run on NVIDIA GPUs in the cloud, were developed using the NVIDIA BioNeMo Framework, a set of programming tools, libraries and models for computational drug discovery. The company is a member of NVIDIA Inception, a global network of cutting-edge startups.
Clinical Trial in a Dish
BrainStorm Therapeutics uses AI models to develop gene maps of brain diseases, which they can use to identify promising targets for potential drugs and clinical biomarkers. Organoids allow them to screen thousands of drug molecules per day directly on human brain cells, enabling them to test the effectiveness of potential therapies before starting clinical trials.
“Brains have brain waves that can be picked up in a scan like an EEG, or electroencephalogram, which measures the electrical activity of neurons,” said Maya Gosztyla, the company’s cofounder and chief operating officer. “Our organoids also have spontaneous brain waves, allowing us to model the complex activity that you would see in the human brain in this much smaller system. We treat it like a clinical trial in a dish for studying brain diseases.”
BrainStorm Therapeutics is currently using patient-derived organoids for its work on drug discovery for Parkinson’s disease, a condition tied to the loss of neurons that produce dopamine, a neurotransmitter that helps with physical movement and cognition.
“In Parkinson’s disease, multiple genetic variants contribute to dysfunction across different cellular pathways, but they converge on a common outcome — the loss of dopamine neurons,” Fremeau said. “By using AI models to map and analyze the biological effects of these variants, we can discover disease-modifying treatments that have the potential to slow, halt or even reverse the progression of Parkinson’s.”
The BrainStorm team used single-cell sequencing data from brain organoids to fine-tune foundation models available through the BioNeMo Framework, including the Geneformer model for gene expression analysis. The organoids were derived from patients with mutations in the GBA1 gene, the most common genetic risk factor for Parkinson’s disease.
BrainStorm is also collaborating with the NVIDIA BioNeMo team to help optimize open-source access to the Geneformer model.
Accelerating Drug Discovery Research
With its proprietary platform, BrainStorm can mirror human brain biology and simulate how different treatments might work in a patient’s brain.
“This can be done thousands of times, much quicker and much cheaper than can be done in a wet lab — so we can narrow down therapeutic options very quickly,” Gosztyla said. “Then we can go in with organoids and test the subset of drugs the AI model thinks will be effective. Only after it gets through those steps will we actually test these drugs in humans.”
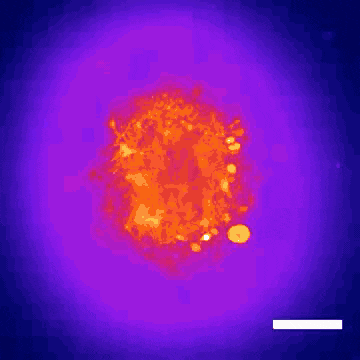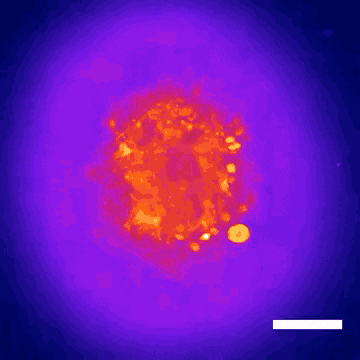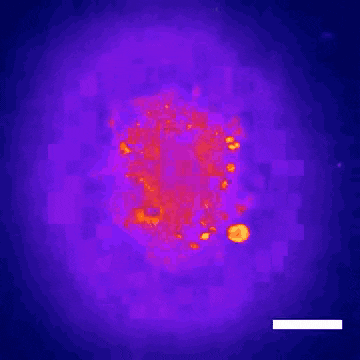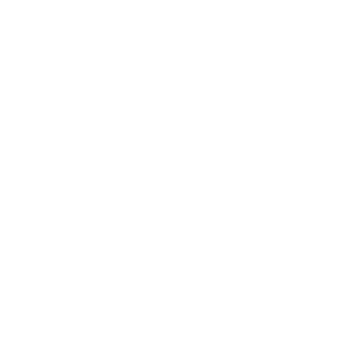
This technology led to the discovery that Donepezil, a drug prescribed for Alzheimer’s disease, could also be effective in treating Rett syndrome, a rare genetic neurodevelopmental disorder. Within nine months, the BrainStorm team was able to go from organoid screening to applying for a phase 2 clinical trial of the drug in Rett patients. This application was recently cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
BrainStorm also plans to develop multimodal AI models that integrate data from cell sequencing, cell imaging, EEG scans and more.
“You need high-quality, multimodal input data to design the right drugs,” said Yin. “AI models trained on this data will help us understand disease better, find more effective drug candidates and, eventually, find prognostic biomarkers for specific patients that enable the delivery of precision medicine.”
The company’s next project is an initiative with the CURE5 Foundation to conduct the most comprehensive repurposed drug screen to date for CDKL5 Deficiency Disorder, another rare genetic neurodevelopmental disorder.
“Rare disease research is transforming from a high-risk niche to a dynamic frontier,” said Fremeau. “The integration of BrainStorm’s AI-powered organoid technology with NVIDIA accelerated computing resources and the NVIDIA BioNeMo platform is dramatically accelerating the pace of innovation while reducing the cost — so what once required a decade and billions of dollars can now be investigated with significantly leaner resources in a matter of months.”
Get started with NVIDIA BioNeMo for AI-accelerated drug discovery.

