Hands-on Rust Developer Workshop: Build and Optimize a Low-Latency Rust App (Sponsored)
Get practical tips for building high-performance Rust apps that scale.
During this free interactive workshop oriented for developers, engineers, and architects, you will learn how to:
Create and compile a real-world app with Rust
Connect the application to ScyllaDB (NoSQL data store)
Negotiate tradeoffs related to data modeling and querying
Manage and monitor the database for consistently low latencies
If you’re an application developer with an interest in Rust, Tokio, and event-driven architectures, this workshop is for you! This is a great way to discover the NoSQL strategies used by top teams and apply them in a guided, supportive environment.
This week’s system design refresher:
System Design: Why Is Docker Important? (Youtube video)
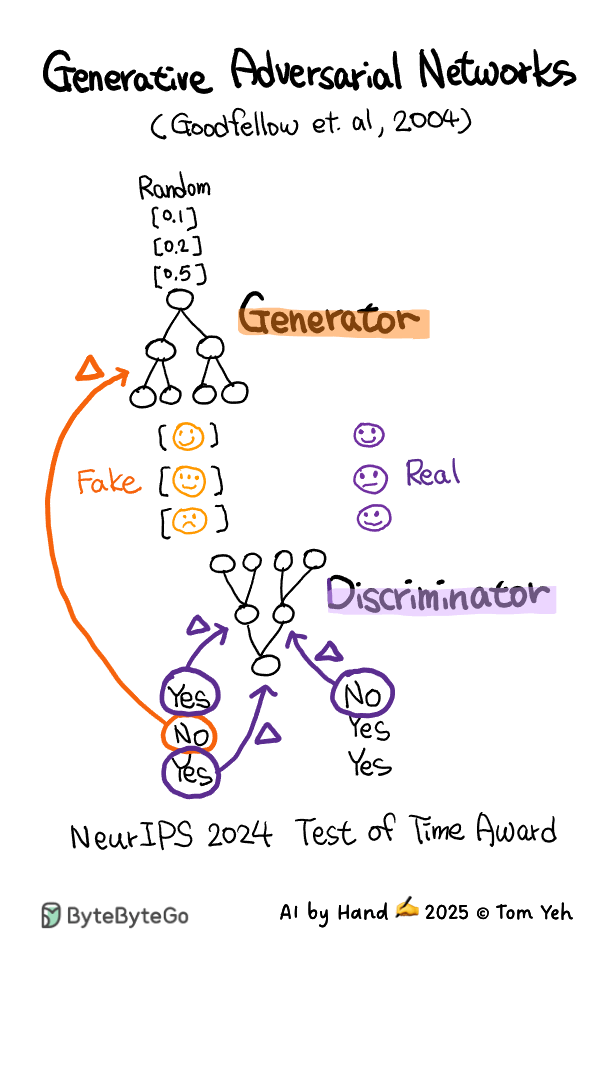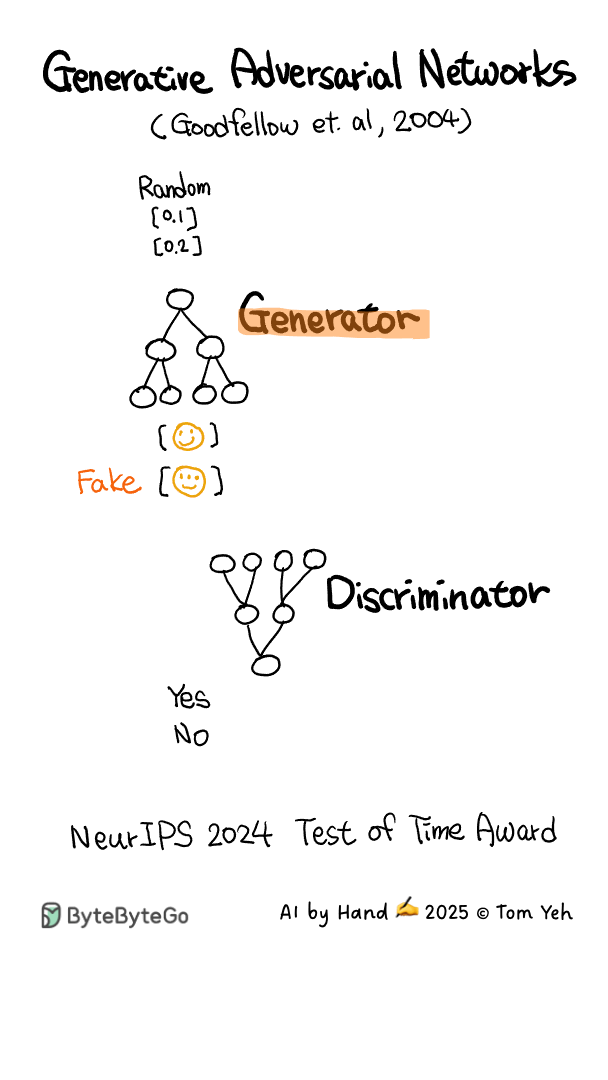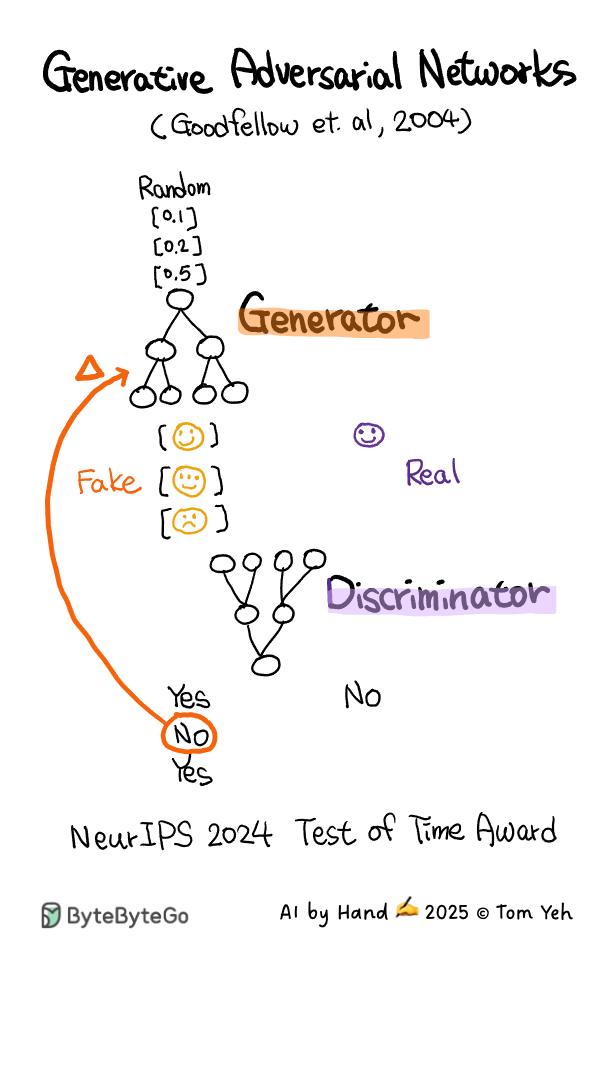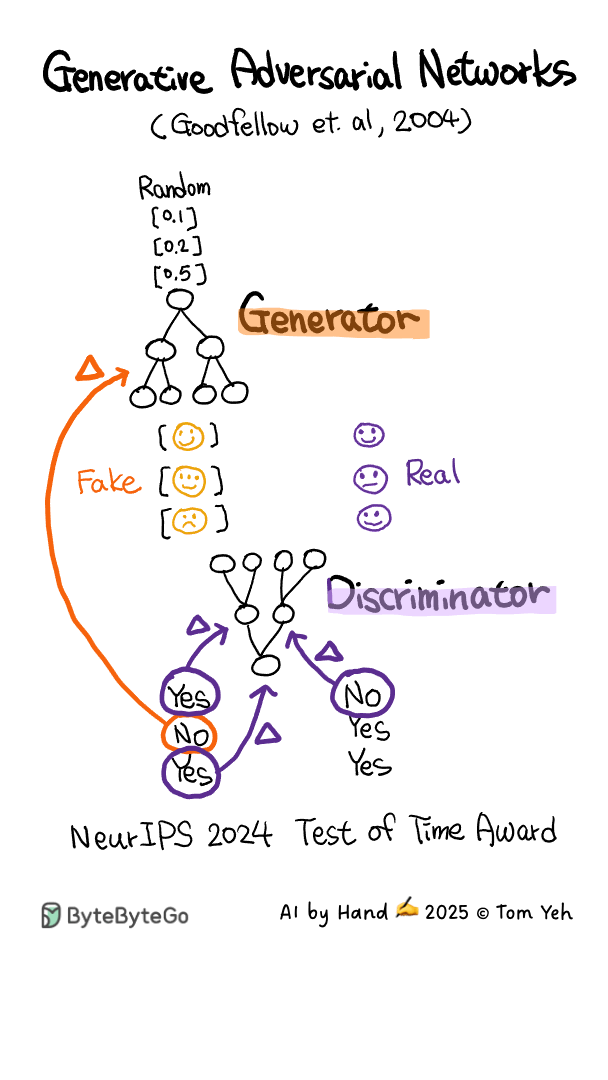
Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) - AI by Hand ✍️
JWT 101: Key to Stateless Authentication
A handy cheat sheet for the most popular cloud services
How Digital Signatures Work?
0 to 1.5 Billion Guests: Airbnb’s Architectural Evolution
SPONSOR US
System Design: Why Is Docker Important?
Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) - AI by Hand ✍️
This animation is hand drawn by Prof. Tom Yeh exclusively for the readers of the ByteByteGo Newsletter..
If you want to learn more about GAN, check out Chapter 7 in the System Design Interview book.
JWT 101: Key to Stateless Authentication
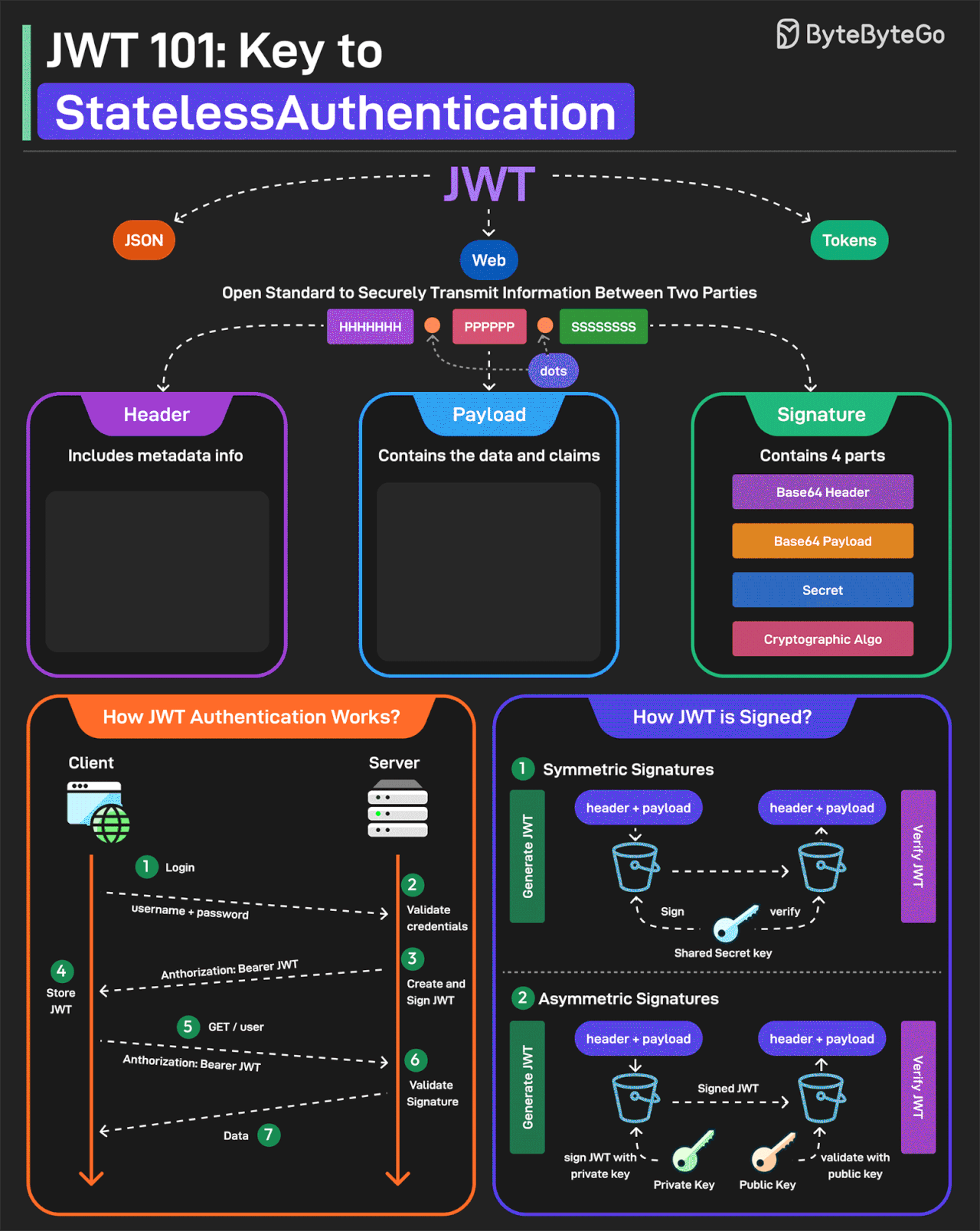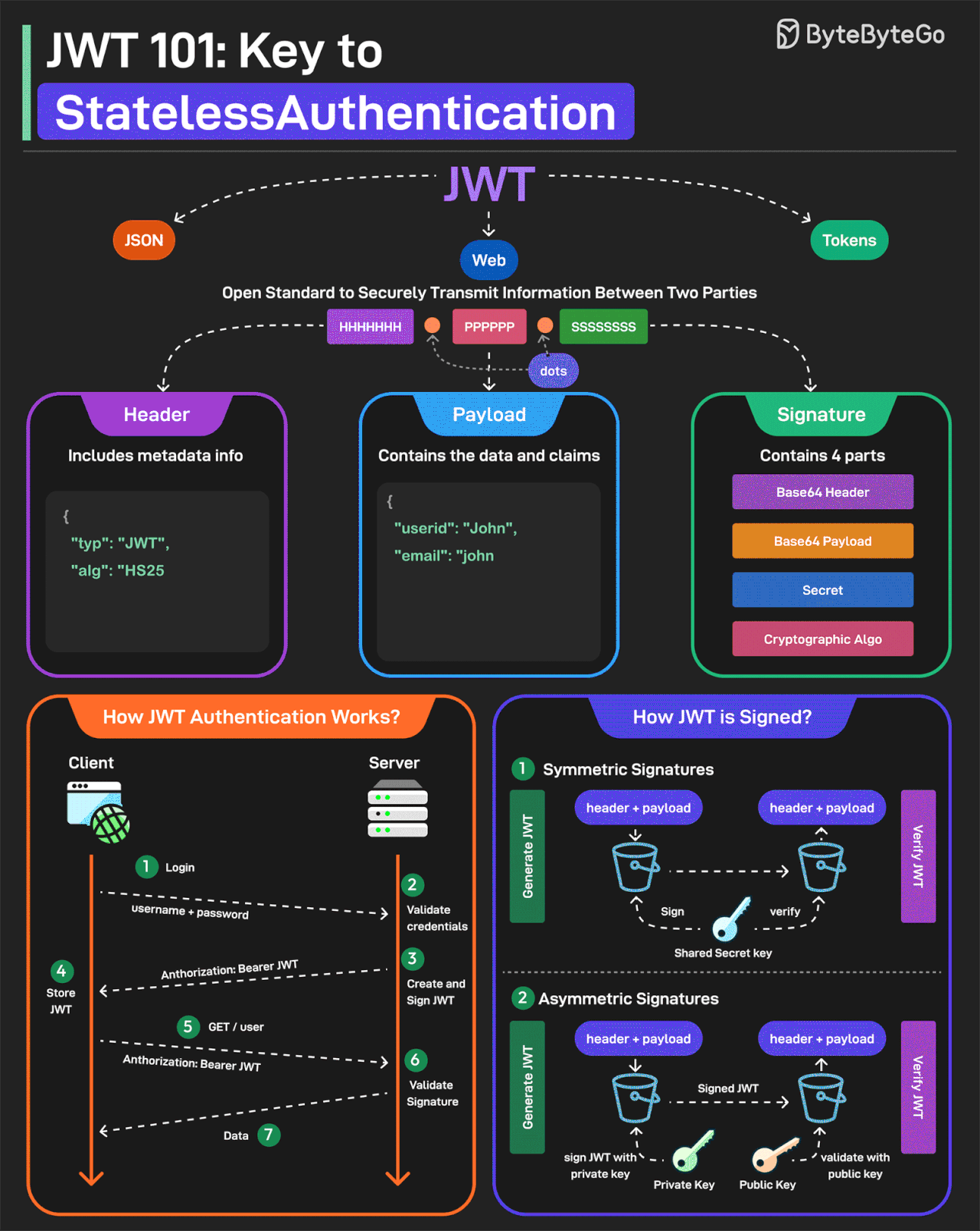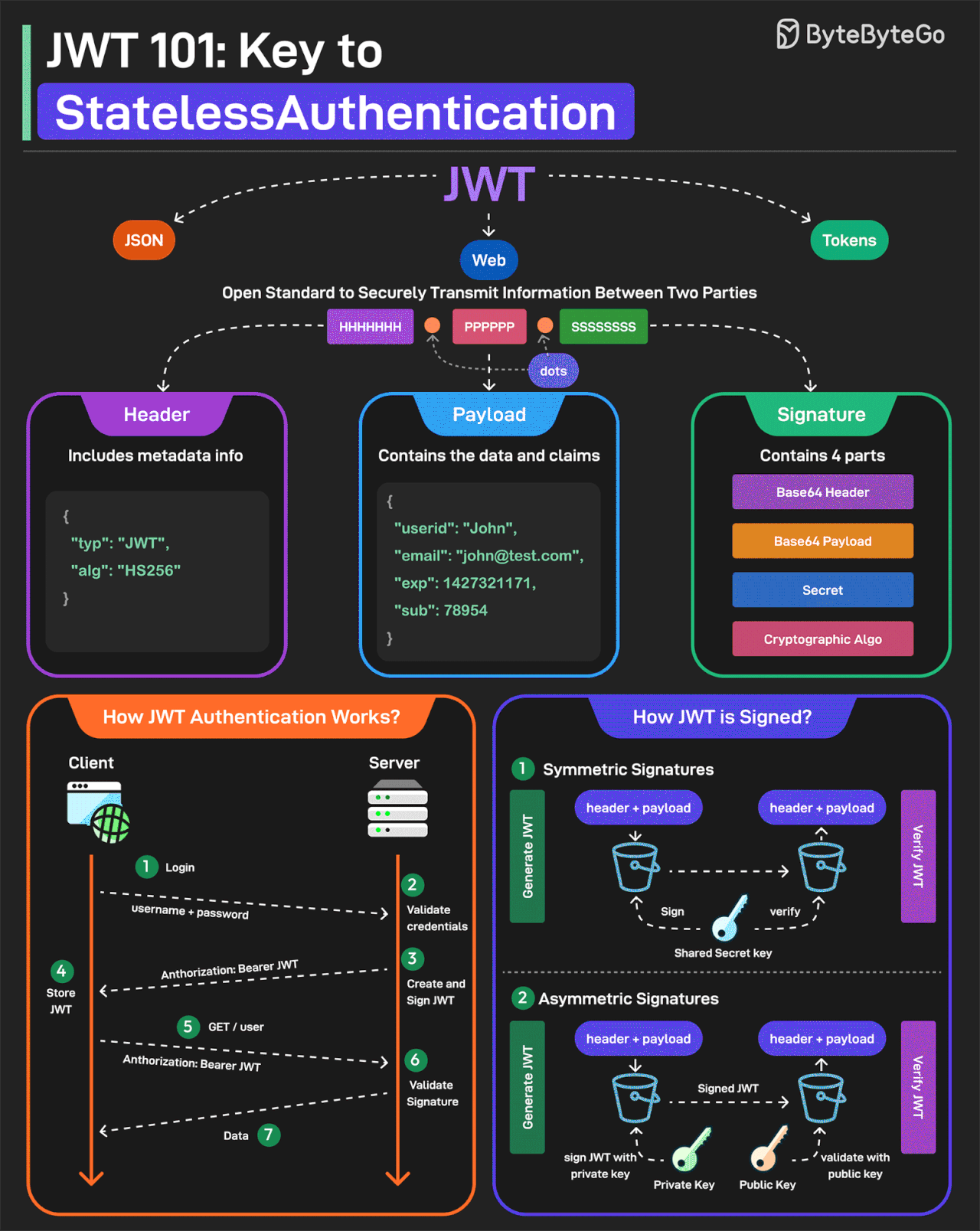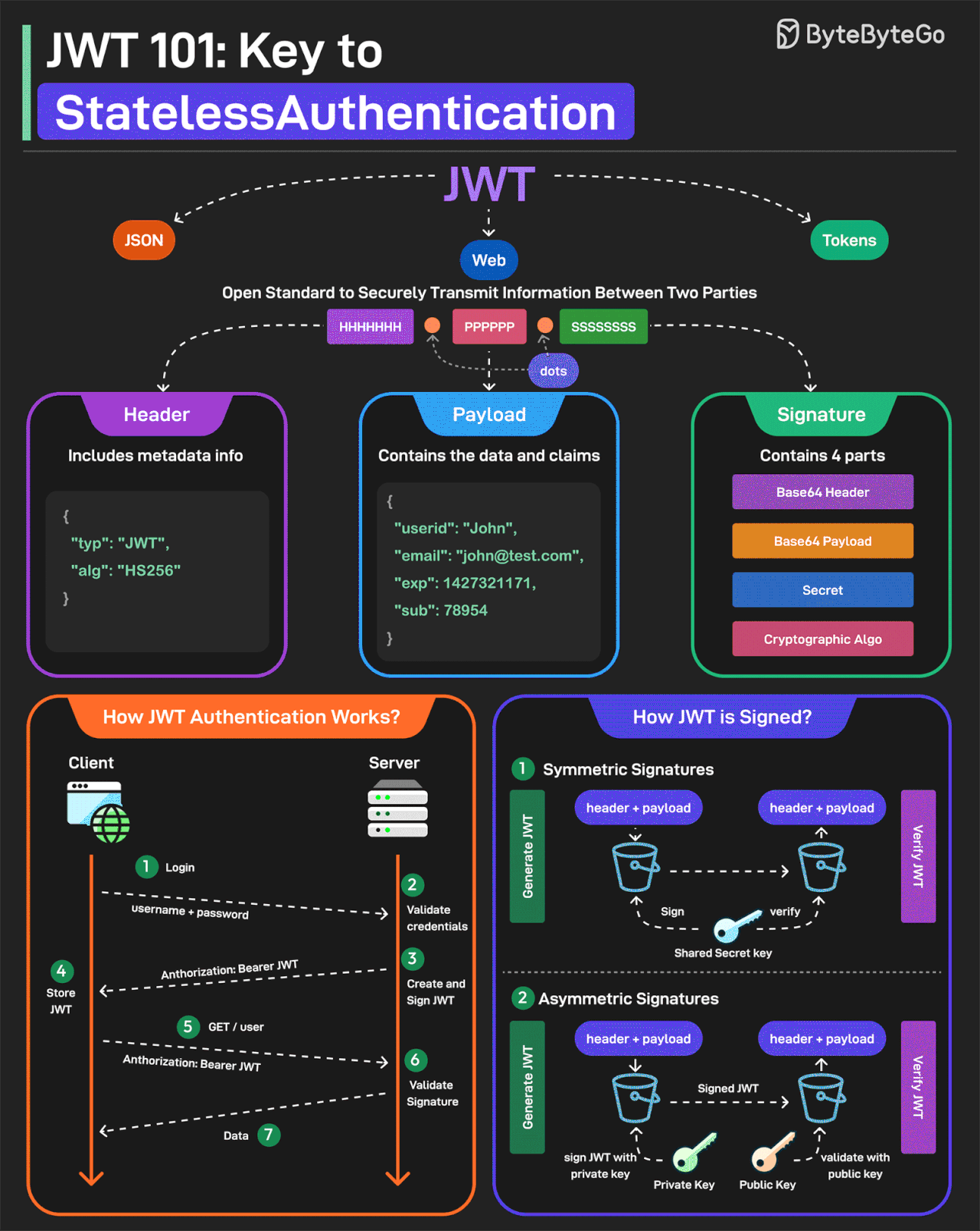
JWT or JSON Web Tokens is an open standard for securely transmitting information between two parties. They are widely used for authentication and authorization.
A JWT consists of three main components:
Header
Every JWT carries a header specifying the algorithms for signing the JWT. It’s written in JSON format.
Payload
The payload consists of the claims and the user data. There are different types of claims such as registered, public, and private claims.
Signature
The signature is what makes the JWT secure. It is created by taking the encoded header, encoded payload, secret key, and the algorithm and signing it.
JWTs can be signed in two different ways:
Symmetric Signatures
It uses a single secret key for both signing the token and verifying it. The same key must be shared between the server that signs the JWT and the system that verifies it.
Asymmetric Signatures
In this case, a private key is used to sign the token, and a public key to verify it. The private key is kept secure on the server, while the public key can be distributed to anyone who needs to verify the token.
Over to you: Do you use JWTs for authentication?
How I use 20+ AI models in one app
(PRESENTED BY YOU.COM)
I routinely have ChatGPT, Claude, and DeepSeek open side-by-side because each model excels at tasks that the others don't.
That’s why I like using You.com, the tool that combines the most popular AI models in one app:
Toggle 20+ AI models in the same chat thread
Compare answers to find the best one
Eliminates tab switching/prompt pasting
Ends soon: Access 12 months of Pro at no cost ($180 value). Just visit the offer page to redeem your special offer as a ByteByteGo newsletter subscriber.
A handy cheat sheet for the most popular cloud services
What’s included?
AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Oracle Cloud, Alibaba Cloud
Cloud servers
Databases
Message queues and streaming platforms
Load balancing, DNS routing software
Security
Monitoring
Over to you - which company is the best at naming things?
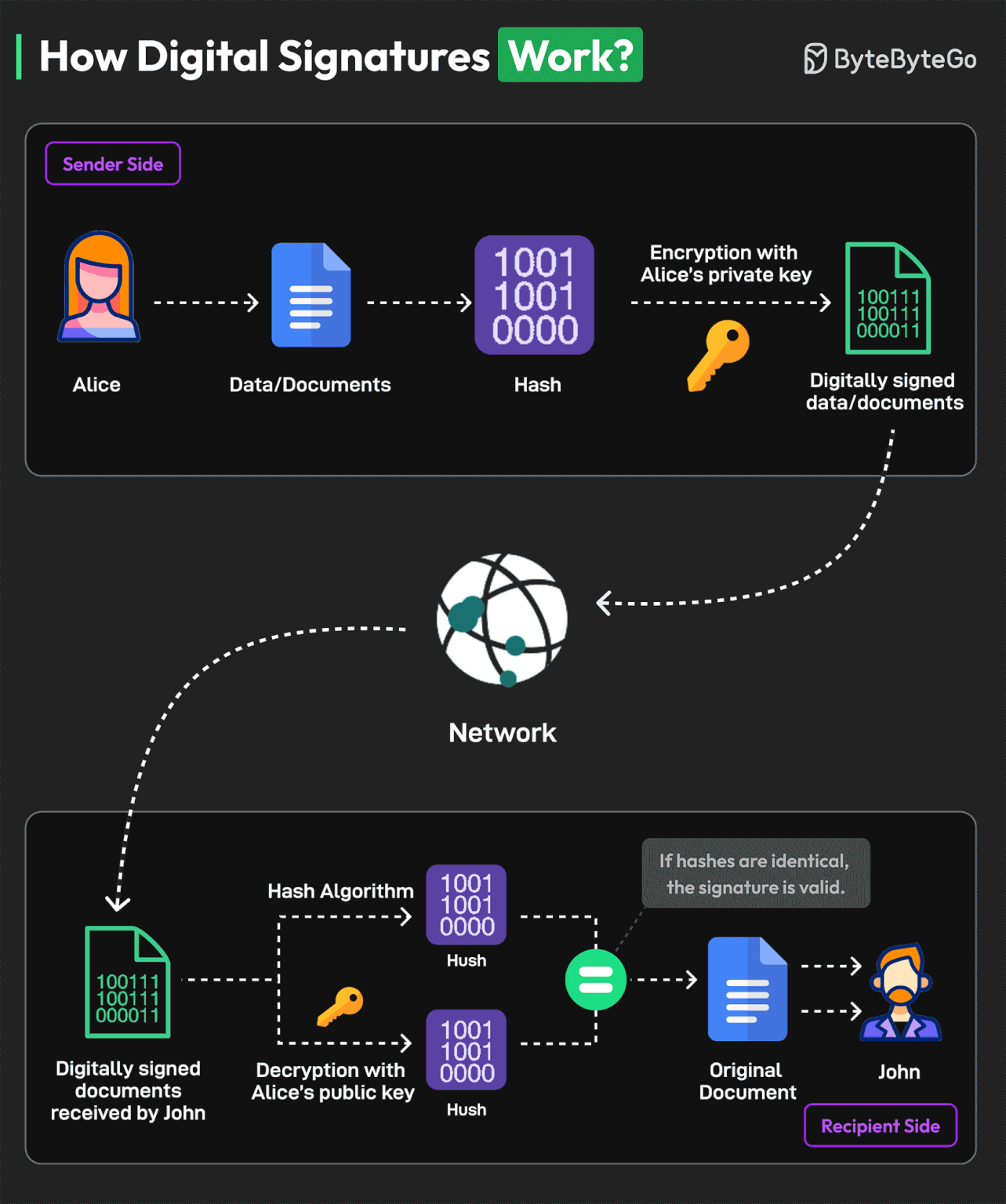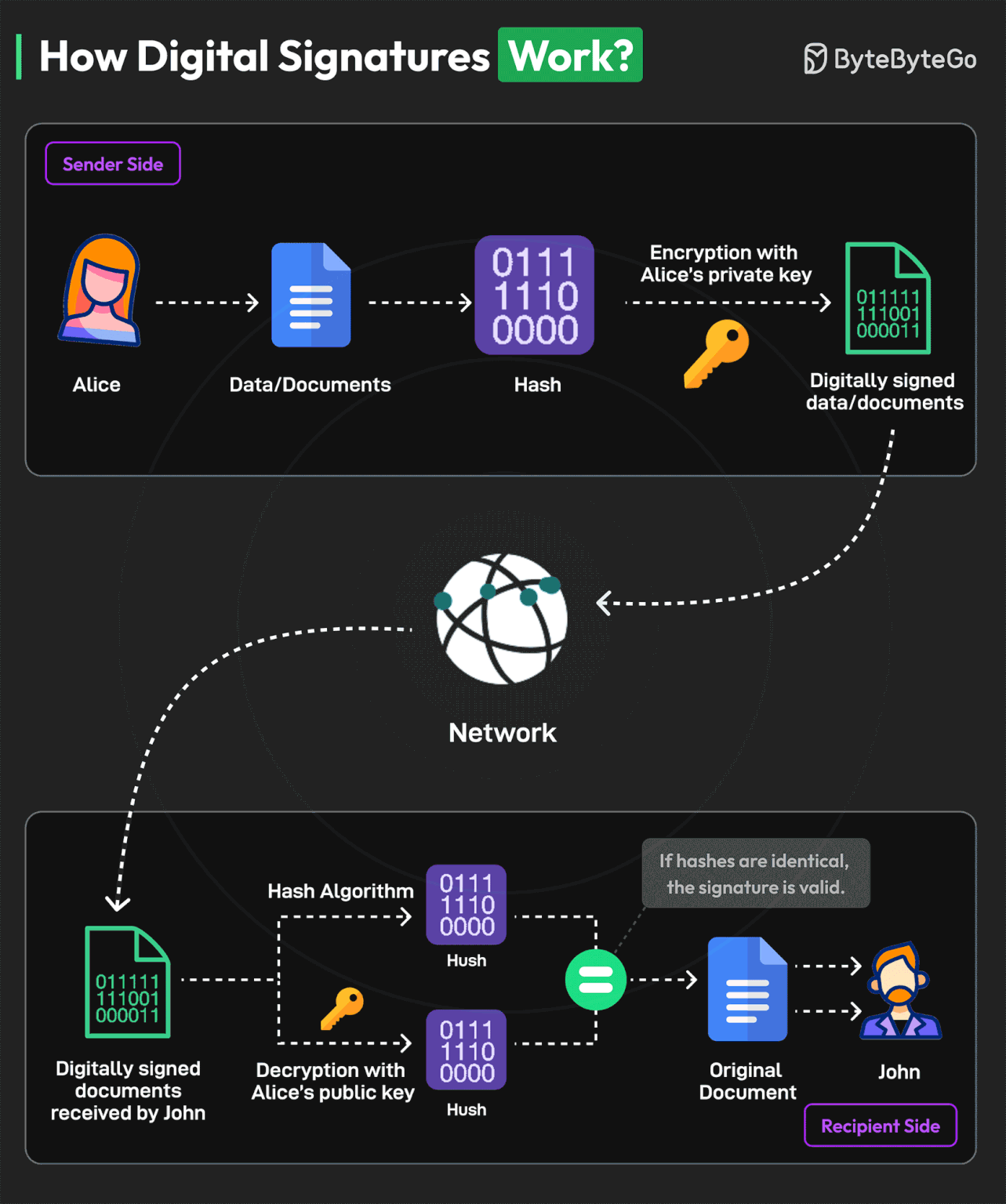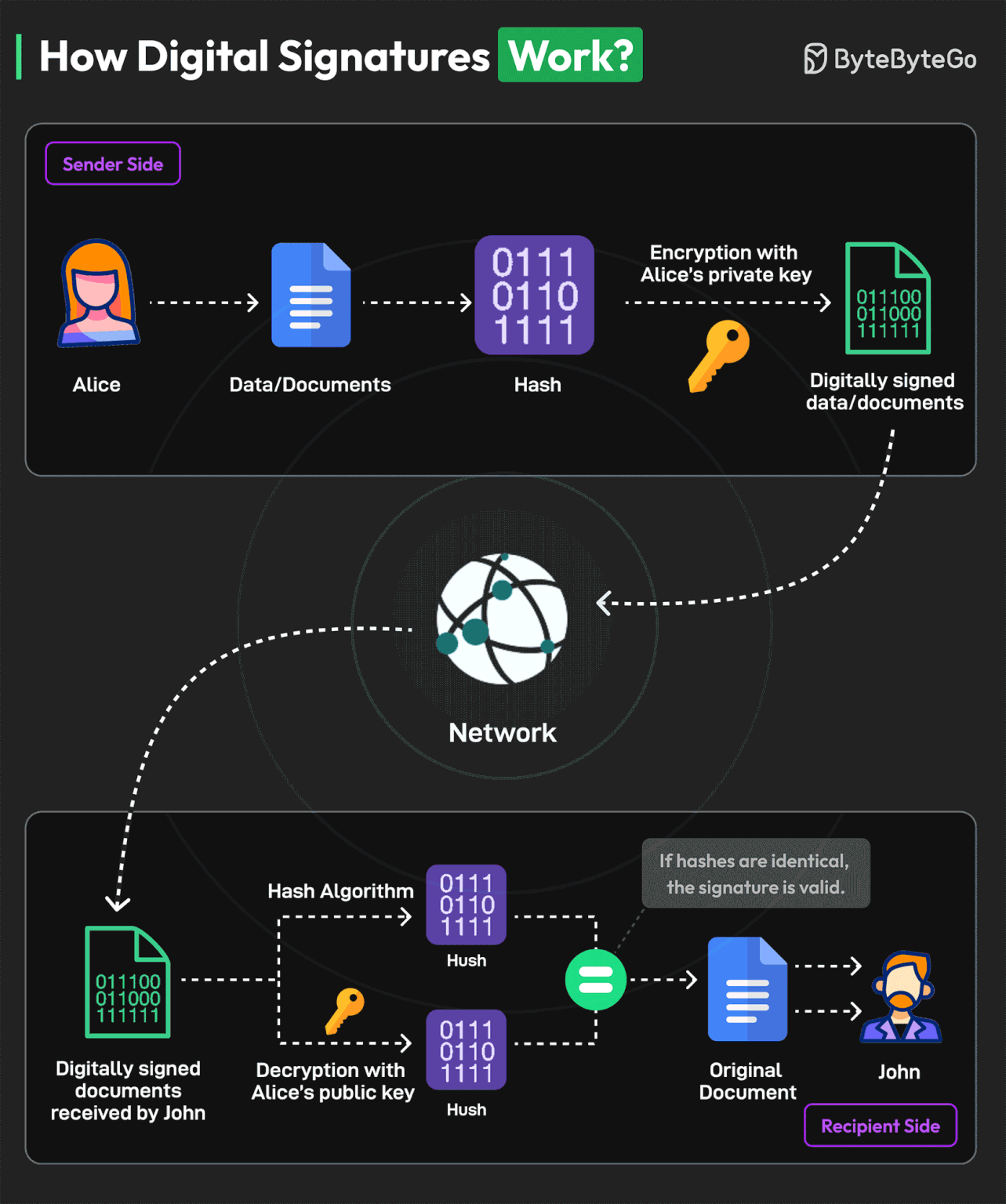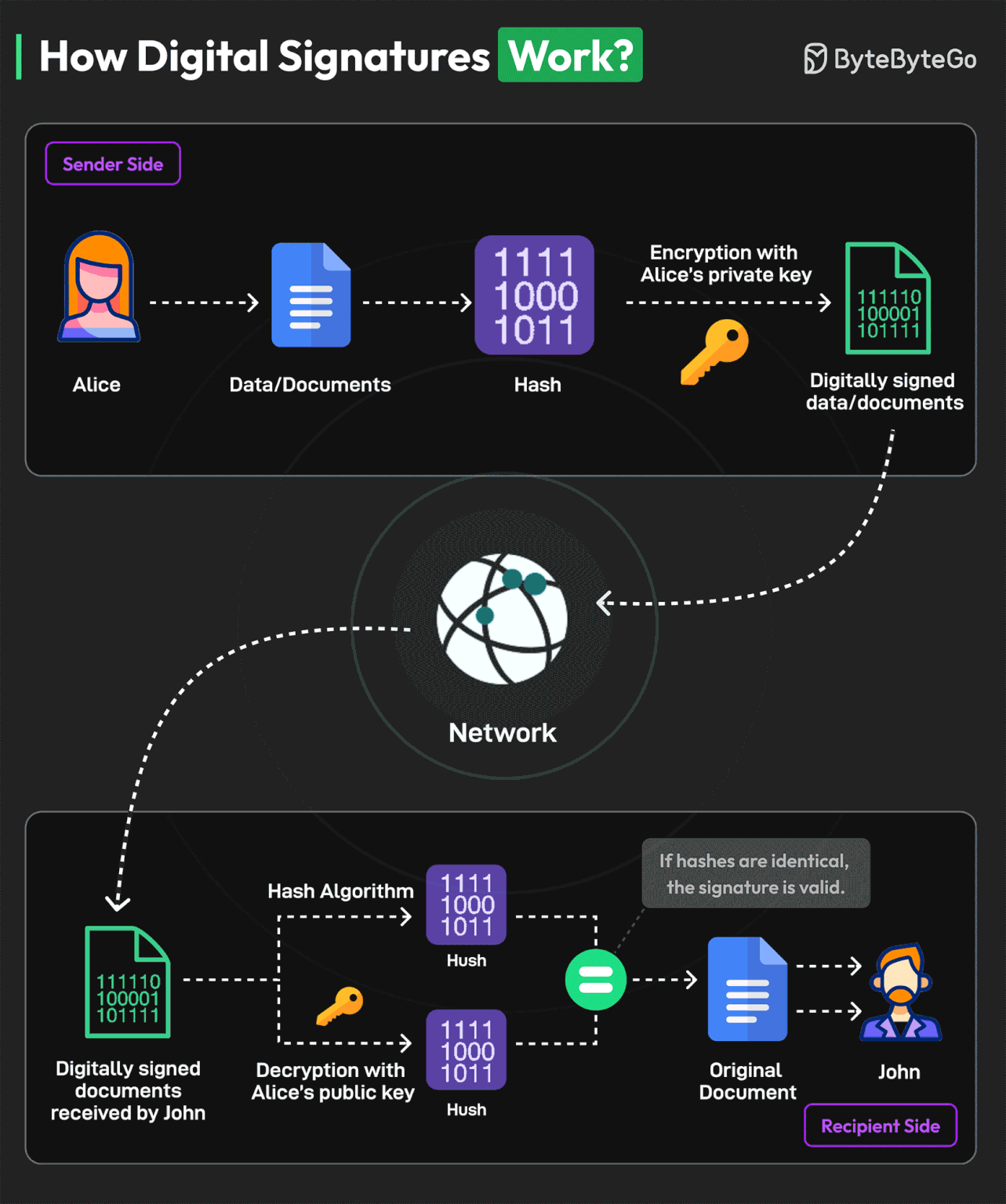
How Digital Signatures Work?
A digital signature is a specific kind of electronic signature to sign and secure electronically transmitted documents.
Digital signatures are similar to physical signatures since they are unique to every person. They identify the identity of the signer.
Here’s an example of the working process of a digital signature with Alice as the sender and John as the recipient:
Alice generates a cryptographic key pair consisting of a private key and a corresponding public key. The private key remains confidential and is known only to the signer, while the public key can be shared openly.
The signer (Alice) uses a hash function to create a unique fixed-length string of numbers and letters, called a hash, from the document. This hash value represents the contents of the document.
Alice uses their private key to encrypt the hash value of the message. This hash value is known as the digital signature.
The digital signature is attached to the original document, creating a digitally signed document. It is transmitted over the network to the recipient.
The recipient (John) extracts both the digital signature and the original hash value from the document.
The recipient uses Alice’s public key to decrypt the digital signature. This produces a hash value that was originally encrypted with the private key.
The recipient calculates a new hash value for the received message using the same hashing algorithm as the signer. They then compare this recalculated hash with the decrypted hash value obtained from the digital signature.
If the hash values are equal, the digital signature is valid, and it is determined that the document has not been tampered with or altered.
Over to you: Have you used digital signatures?
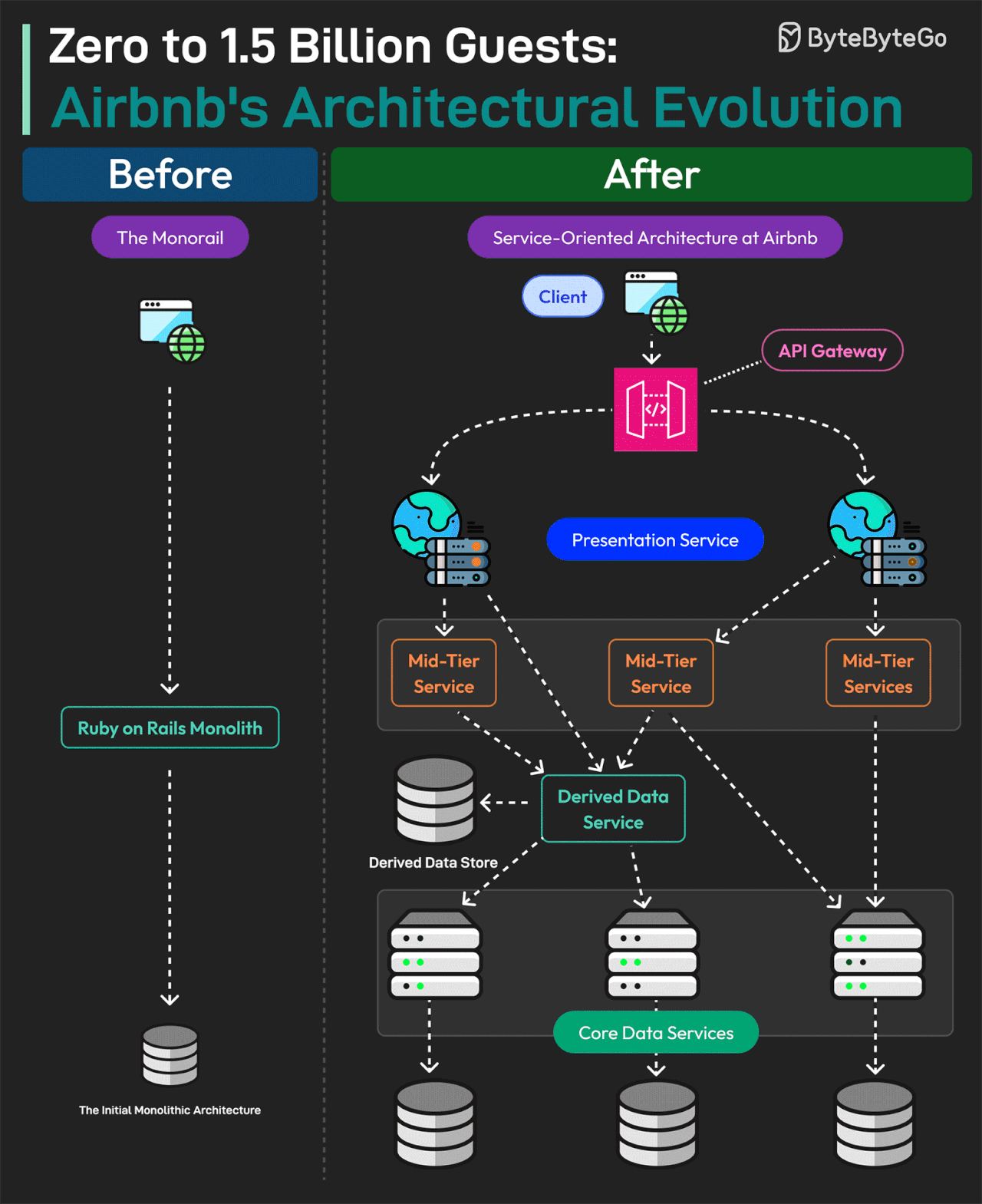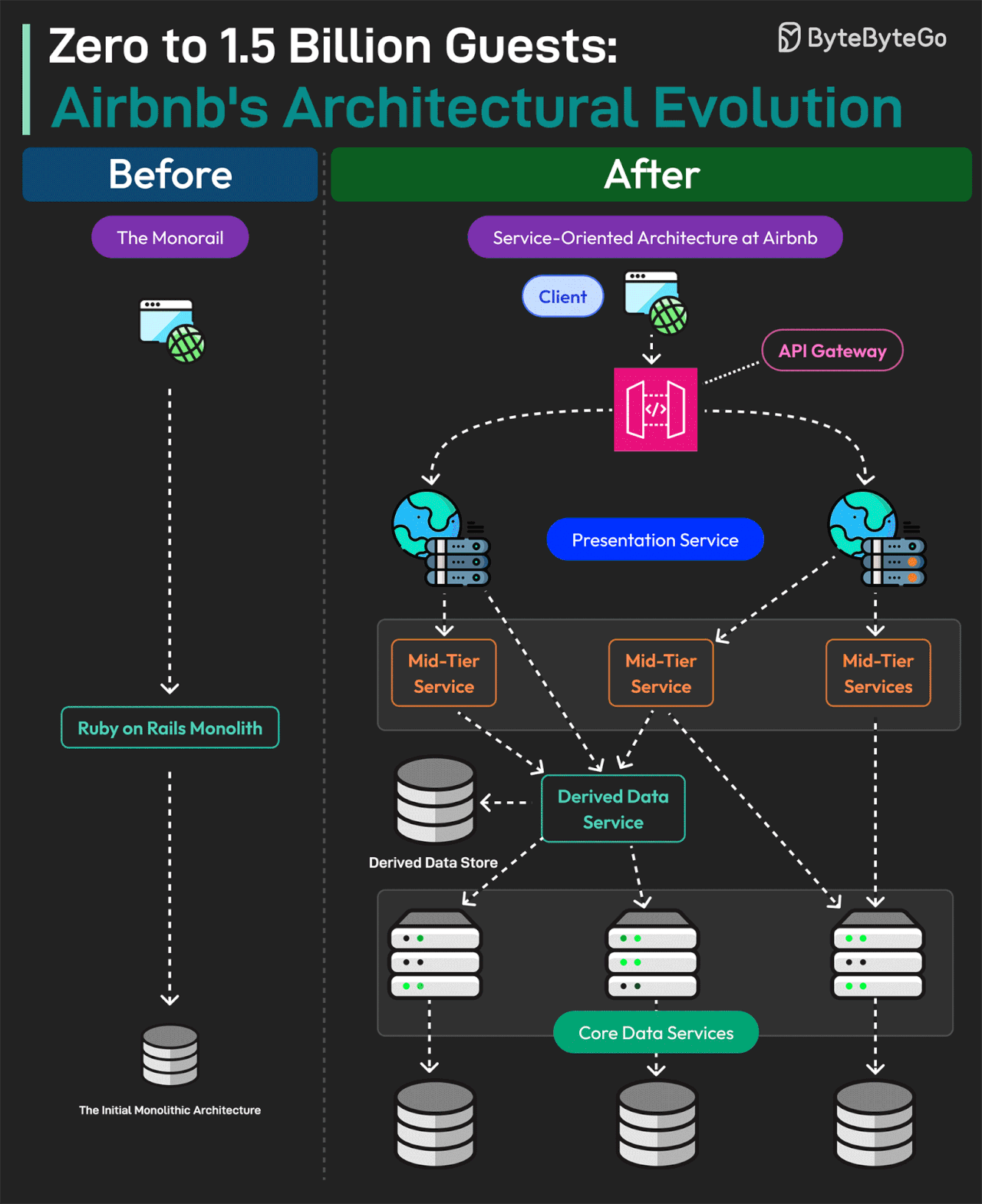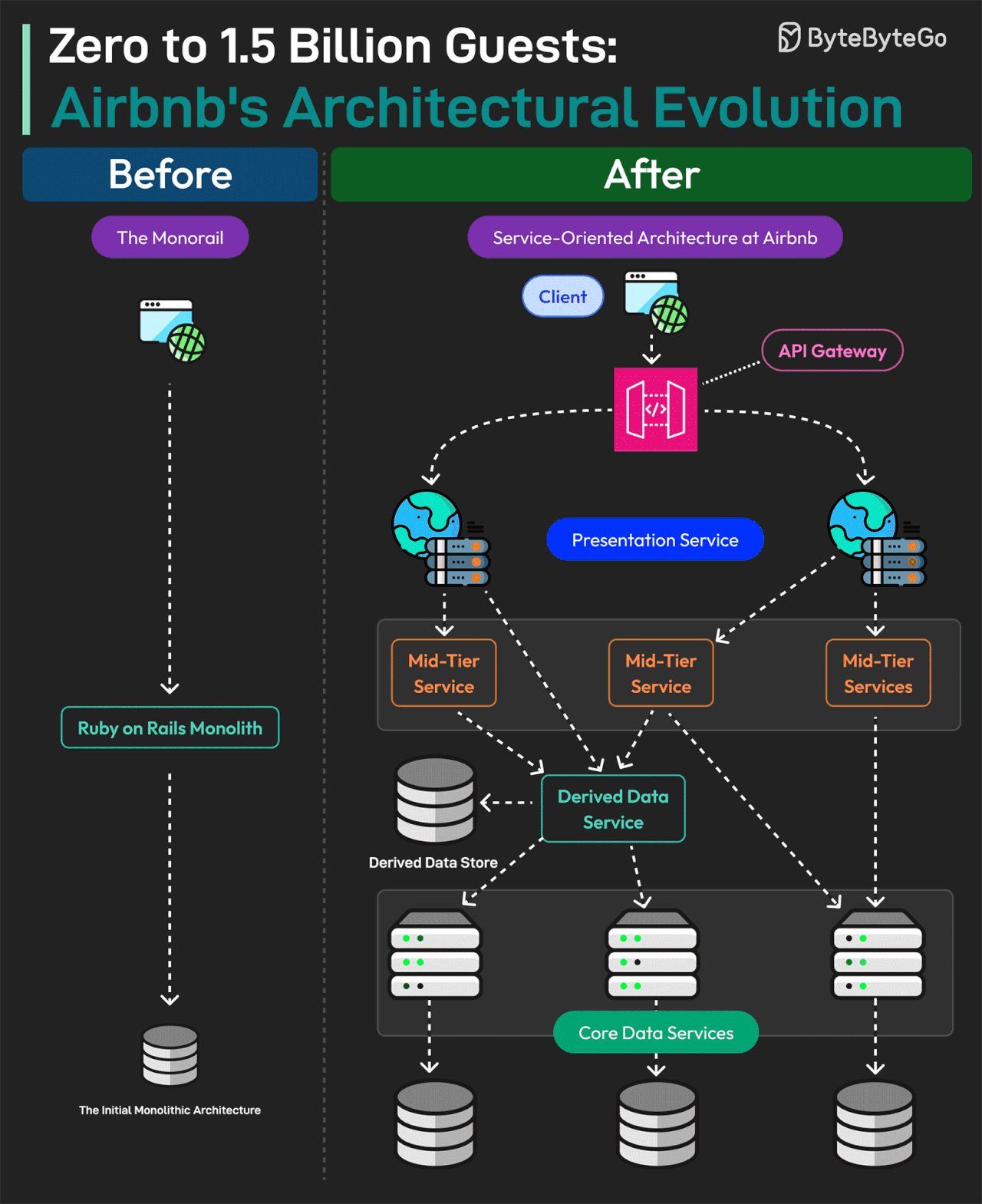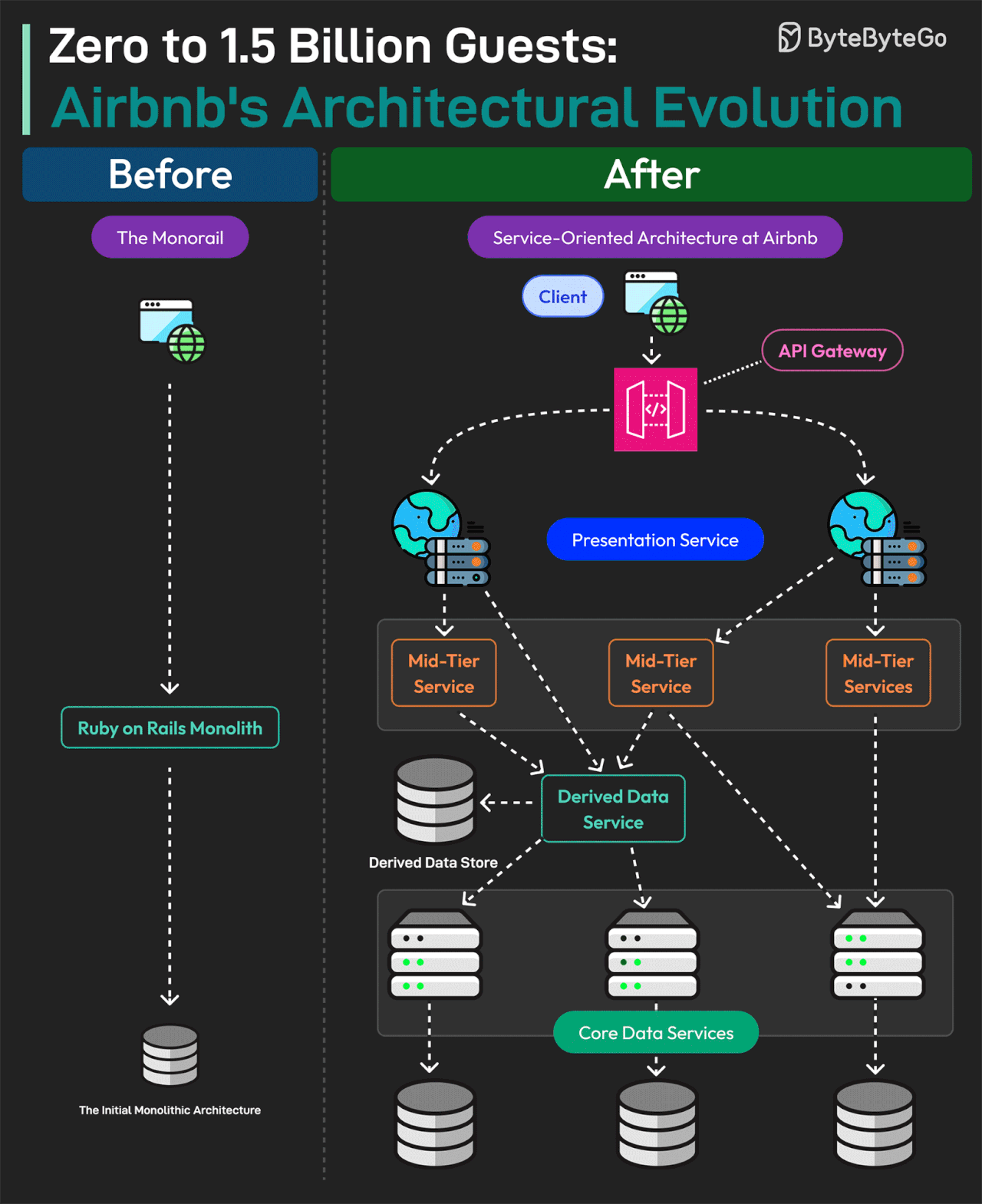
0 to 1.5 Billion Guests: Airbnb’s Architectural Evolution
Airbnb operates in 200+ countries and has helped 4 million hosts welcome over 1.5 billion guests across the world.
What powers Airbnb technically?
Airbnb started as a monolithic application. It was built using Ruby-on-Rails and was internally known as the Monorail.
The monolith was a single-tier unit responsible for both client and server-side functionality.
However, as Airbnb went into hypergrowth, the Monorail started facing issues. This is when they began a migration journey to move from monolithic to Service-Oriented Architecture.
For Airbnb, SOA is a network of loosely coupled services where clients make their requests to a gateway and the gateway routes these requests to multiple services and databases.
Various types of services were built such as:
Data Service: This is the bottom layer and acts as the entry point for all read and write operations on the data entities.
Derived Data Service: These services read from data services and apply basic business logic.
Middle Tier Service: They manage important business logic that doesn’t fit at the data service level or derived data service level.
Presentation Service: They aggregate data from all other services and also apply some frontend-specific business logic.
After the migration, the Monorail was eliminated and all reads/writes were migrated to the new services.
Reference: Airbnb at Scale: From Monolith to Microservices
SPONSOR US
Get your product in front of more than 1,000,000 tech professionals.
Our newsletter puts your products and services directly in front of an audience that matters - hundreds of thousands of engineering leaders and senior engineers - who have influence over significant tech decisions and big purchases.
Space Fills Up Fast - Reserve Today
Ad spots typically sell out about 4 weeks in advance. To ensure your ad reaches this influential audience, reserve your space now by emailing sponsorship@bytebytego.com.