?Kiss Manual Testing Goodbye—Ship 5x Faster (Sponsored)
Build features without the drag of multi-day QA Cycles. QA Wolf covers 80% of your web and mobile app with automated tests in just four months, then maintains and updates them 24/7.
Unlimited parallel test runs validate every change in minutes, not days.
The zero flakes guarantee cuts out false alarms and wasted engineering hours.
Salesloft saves $750k a year by running over 300 tests on each PR—a clear example of how QA Wolf transforms QA speed and efficiency.
Spend less time stressing over slow test suites and more time delivering what your customers need.
Take your releases from bottlenecked to blazing-fast!
Disclaimer: The details in this post have been derived from multiple AWS reInvent talks and articles by the Amazon engineering team. All credit for information about AWS Lambda’s internals goes to the presenters and authors. The link to these videos and articles is present in the references section at the end of the post. We’ve attempted to analyze the details and provide our input about them. If you find any inaccuracies or omissions, please leave a comment, and we will do our best to fix them.
AWS Lambda turned 10 recently.
Like with most innovations at Amazon, Lambda’s origin was rooted in the team’s observation of how customers used existing services.
The AWS engineering team noticed that many customers were maintaining entire fleets of EC2 instances to handle sporadic tasks such as writing data to a database, processing files, or performing other minor functions. These instances often sat idle but consumed resources both in terms of customer costs and AWS infrastructure.
This inefficiency signaled a gap in the AWS offerings. There was no service designed to handle short-lived, lightweight computational tasks without the need for constant resource provisioning.
AWS aimed to address this problem by creating a service that could:
Automatically and dynamically allocate compute resources as needed.
Allow developers to execute specific pieces of application logic (functions) without worrying about server provisioning, scaling, or maintenance.
Abstract away the "undifferentiated heavy lifting" of managing infrastructure, enabling developers to focus entirely on their core application logic.
The goal was to make it possible for developers to "just run some code" efficiently, securely, and cost-effectively, without the complexity of managing an EC2 fleet. This led to the birth of AWS Lambda at the end of 2014.
In this article, we’ll explore how the AWS engineering team approached the creation of AWS Lambda and the innovations they have made over the years to address customer needs.
The Concept of AWS Lambda
At Amazon, crafting internal documents, such as PR/FAQs (Press Release/Frequently Asked Questions), is a foundational practice for developing new ideas and products.
The process of creating these documents is designed to clearly articulate the product vision before working on it. Writing requires the authors to be explicit about the goals, capabilities, and limitations of the proposed product. These documents help anticipate customer and stakeholder concerns. Also, the FAQ section forces the teams to think through potential questions and challenges.
The initial draft is rarely perfect and goes through feedback and revision cycles. This ensures that ideas are refined and weaknesses are addressed.
The PR/FAQ for Lambda identified key customer problems, such as the need for cost-effective, scalable, and secure execution of short-lived tasks. It envisioned a serverless model that freed developers from managing servers, anticipated features like fine-grained billing and multi-language support, and laid the foundation for innovations like Firecracker and Lambda Layers.
Core Features at Launch
AWS Lambda introduced groundbreaking capabilities that transformed how developers approach application development and infrastructure management. Some key features were as follows:
Serverless Computing
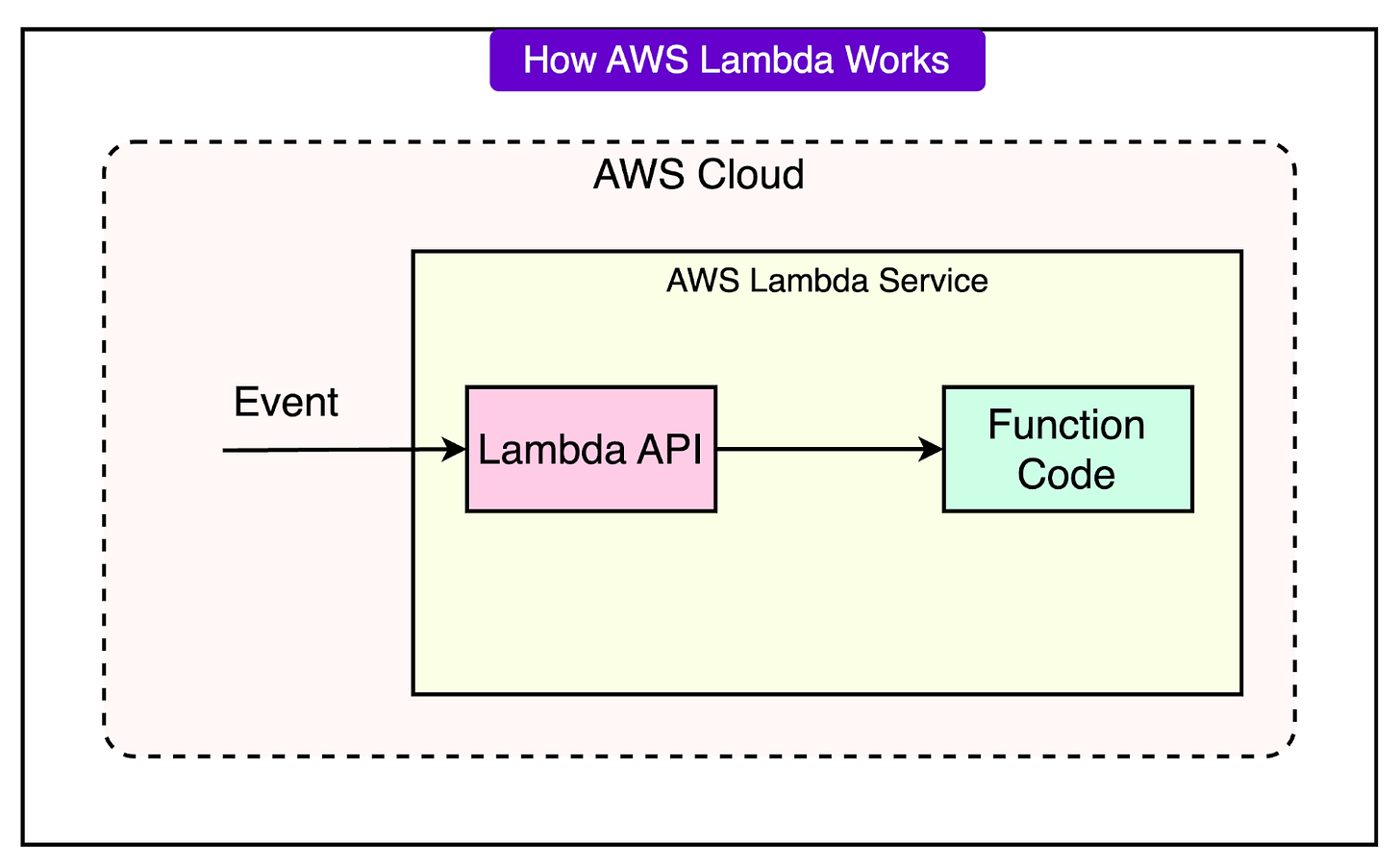
Lambda pioneered the serverless paradigm, allowing developers to run code without provisioning, managing, or scaling servers.
Here’s how it works in practice:
Developers provide their code and specify a handler function, which defines the entry point for Lambda to execute.
The platform automatically scales the number of instances based on incoming requests, handling spikes and periods of inactivity.
Stateless execution ensures that each invocation of a Lambda function is independent, meaning no data is carried over between executions unless explicitly managed using services like Amazon S3 or DynamoDB.
This approach eliminates the need for server capacity planning and lets the developers concentrate on their application rather than operational overhead.
How I use 20+ AI models in one app
(PRESENTED BY YOU.COM)
I routinely have ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini open side-by-side because each model excels at tasks that the others don't.
That’s why I like using You.com, the tool that combines the most popular AI models in one app:
Toggle 20+ AI models in the same chat thread
Compare answers to find the best one
Eliminates tab switching/prompt pasting
Ends soon: Access 12 months of Pro at no cost ($180 value). Just visit the offer page to redeem your special offer as a ByteByteGo newsletter subscriber.
Supported Languages and Deployment Options
Initially, Lambda only supported Node.js, a popular JavaScript runtime. Node.js was chosen for its lightweight nature and existing usage among AWS developers. To make it work, Lambda functions must adhere to specific runtime conventions (for example, the exports.handler function in Node.js).
Over time, support was expanded to languages like Python, Java, Ruby, Go, .NET, and custom runtimes.
Lambda supported deployment via ZIP files, allowing developers to bundle their code and dependencies for easy upload. Integration with Git repositories simplified workflows for developers who could link their source code repositories to deploy directly.
Cost Efficiency
Lambda introduced fine-grained billing, where customers paid only for the compute time consumed by their functions. It was a major shift from traditional EC2-based hosting models.
The time was rounded to the nearest 250ms at launch. However, it was later reduced to 1ms billing for even greater cost efficiency.
Also, AWS offered a generous free tier, which included a set number of invocations and execution times per month, encouraging developers to experiment with Lambda at no cost. Developers could choose memory allocation between 128 MB and 10 GB (as of 2023 updates), and Lambda would automatically allocate proportional CPU power.
Key Innovations Over the Decade
AWS Lambda has significantly evolved since its launch, incorporating new features and capabilities that have expanded its use cases and improved performance.
Support for Additional Runtimes
As mentioned earlier, Lambda supported only Node.js at launch. Over the years, AWS added support for popular languages to cater to a broader developer base. Here’s when different languages were added:
Java (2015)
Python (2015)
.NET Core (2016)
Go (2018)
Ruby (2018)
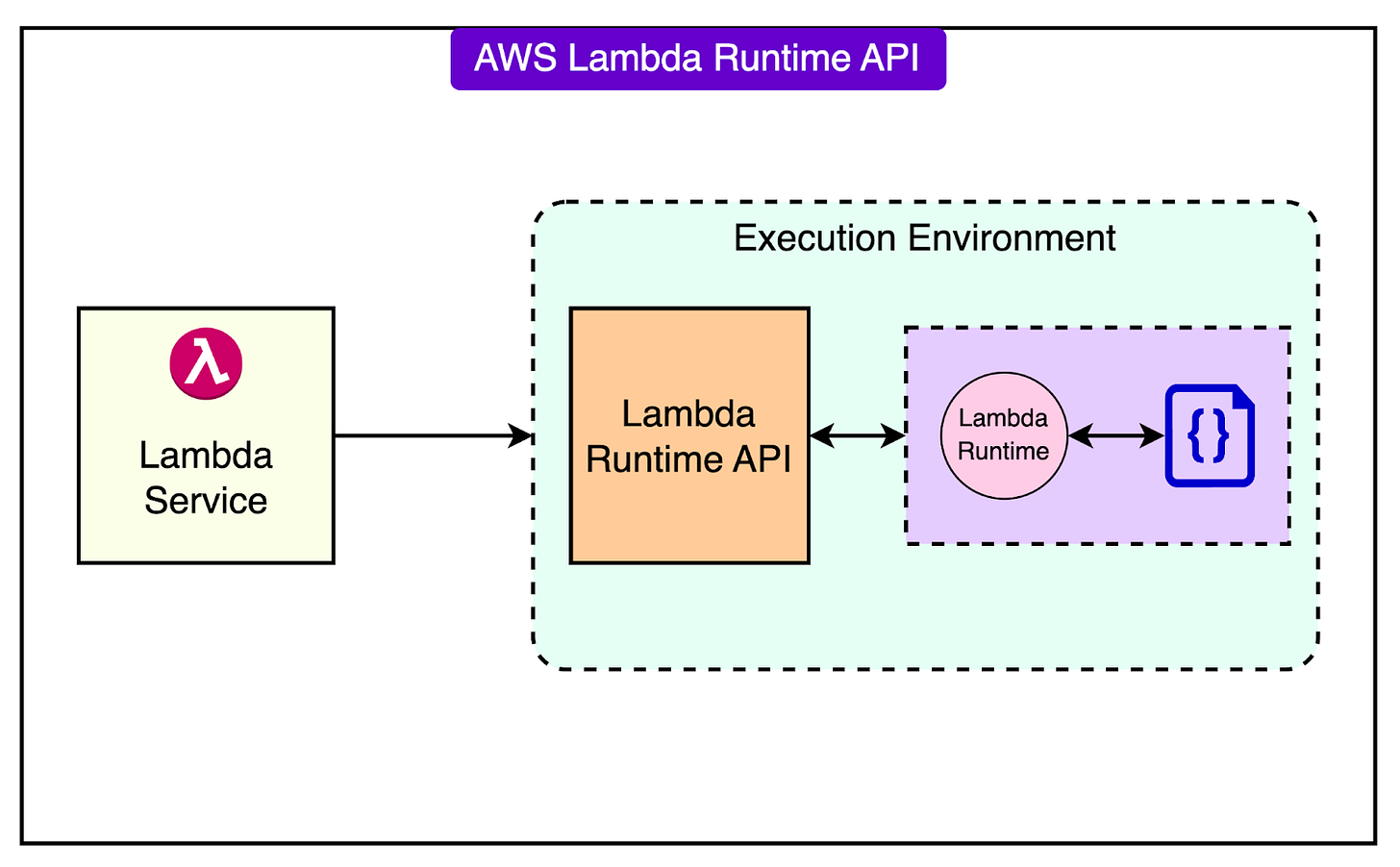
In 2018, they also introduced custom runtimes.
Introduced with the Runtime API, this feature allowed developers to implement Lambda functions in virtually any language by packaging their runtime binaries.
See the diagram below:
Containerization Support
In 2020, Lambda began supporting container images, enabling developers to package their functions as Docker containers.
This was particularly useful for large dependencies exceeding the 250 MB limit of traditional ZIP-based deployments. By allowing containers up to 10 GB in size, Lambda could support complex workloads like machine learning inference and data-heavy applications.
A couple of technical benefits were as follows:
Reuse of existing CI/CD pipelines for building containerized applications.
Easier dependency management by letting developers include all necessary libraries in the container image.
Reducing Cold Start Latency
Cold starts occur when Lambda initializes a runtime environment for a function that hasn’t been invoked recently. This adds latency, especially for languages like Java that require significant initialization.
The AWS engineering team made a couple of enhancements to address this:
1 - Firecracker MicroVMs
Initially, AWS Lambda used EC2 instances to run functions, dedicating a T2 instance to each tenant. This was secure but inefficient, leading to high overhead due to the need to provision entire EC2 instances for each function.
In 2018, AWS introduced Firecracker.
Firecracker is a lightweight virtual machine manager (VMM) designed to run serverless workloads such as AWS Lambda and AWS Fargate. It creates and manages microVMs using Linux’s Kernel-based Virtual Machine.
MicroVMs are isolated, secure environments that are much faster to start than traditional virtual machines. They are designed to boot in milliseconds, significantly reducing the cold start latency for Lambda functions.
2 - SnapStart
When a Lambda function is invoked and there isn’t an already running execution environment, Lambda has to create a new one. This involves several steps:
Provisioning: Set up a new virtual machine
Downloading: Retrieve the function code from storage
Initializing: Start the runtime and initialize the function code.
These steps can take time, especially for complex functions or runtimes like Java, which have longer startup times.
SnapStart is a feature designed to reduce cold start latency by pre-initializing the execution environment and then using snapshots. It pre-warms function environments and captures a snapshot of the initialized runtime.
Lambda reuses this snapshot during subsequent invocations, bypassing the initialization process and significantly reducing startup time (up to 90%).
See the diagram below that shows how SnapStart works.
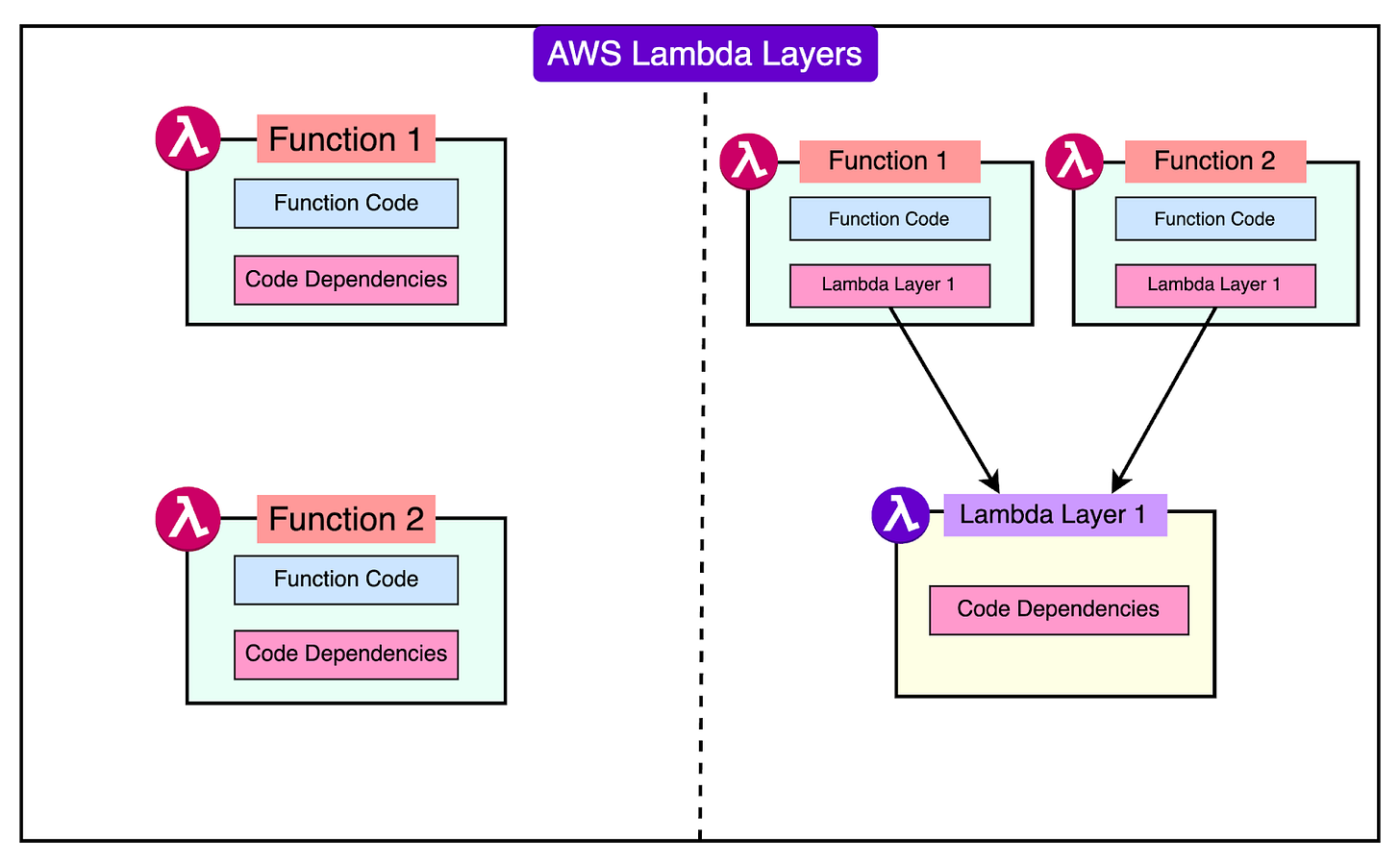
Lambda Layers
Introduced in 2018, Layers allow developers to share common dependencies (for example, libraries, binaries, and configuration files) across multiple functions.
Here’s how it works:
Developers create a Layer with the required dependencies and attach it to their Lambda functions.
Functions automatically load the Layer contents during execution, without requiring developers to repackage dependencies each time.
See the diagram below that shows the concept AWS Lambda Layers:
Lambda Layers help reduce deployment package size by separating common code from individual function code. This simplifies version management for shared dependencies.
Some common use cases for Lambda Layers are as follows:
Packaging libraries like TensorFlow for machine learning applications.
Sharing utility functions across a team or organization.
Using vendor-provided Layers for third-party integrations (for example, monitoring tools).
Ecosystem Improvement
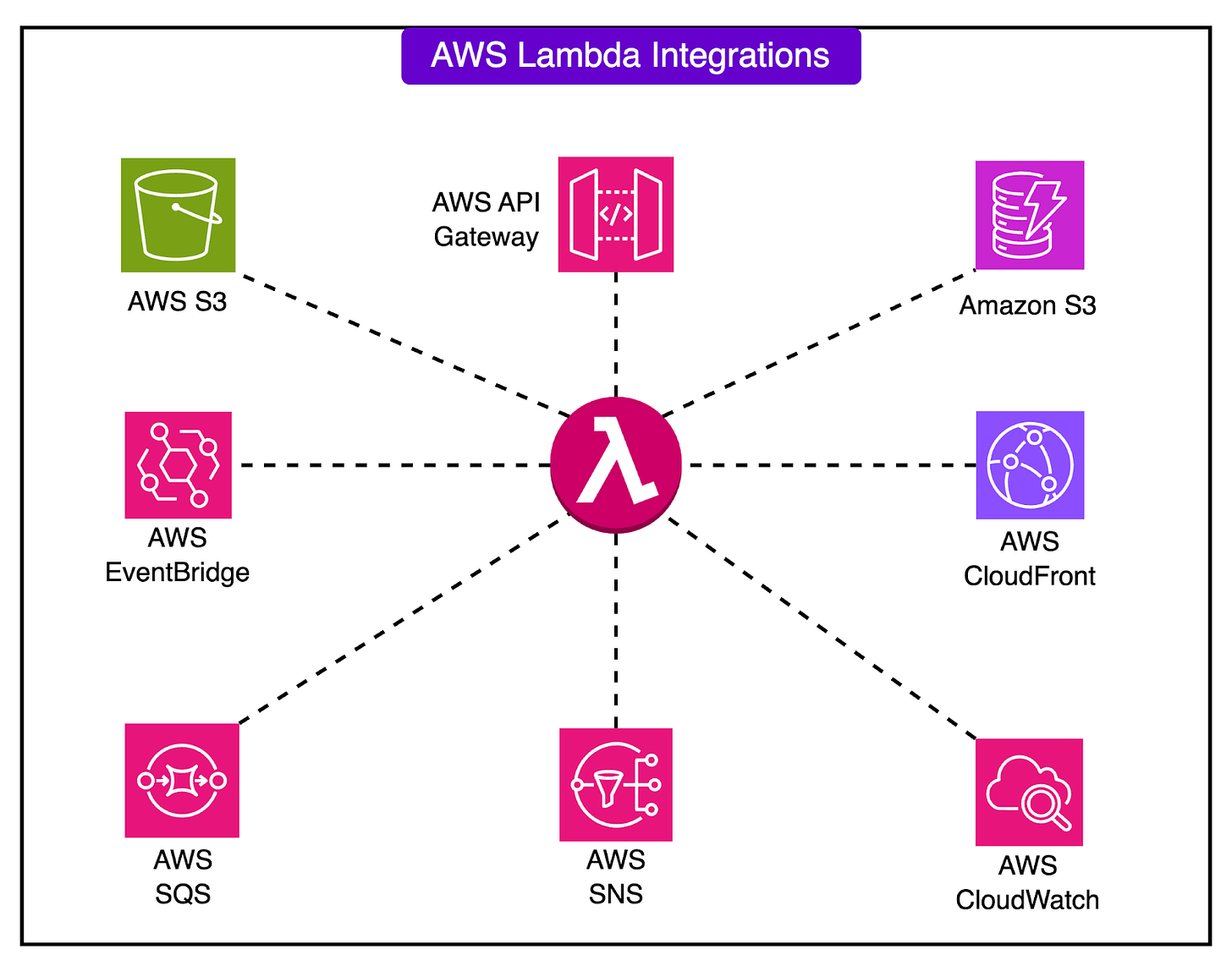
Over the years, the AWS engineering team has integrated Lambda with services like API Gateway, EventBridge, S3, DynamoDB, and SQS to build complex, event-driven architectures.
AWS improved provisioned concurrency, allowing developers to pre-warm environments for latency-sensitive applications. The AWS Serverless Application Model (SAM) and AWS CDK also simplified the development and deployment of serverless applications.
Operational Excellence in AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda was designed to simplify cloud application development while prioritizing key operational goals: security, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Here’s how these goals help different stakeholders.
For Developers: Lambda eliminates the complexity of infrastructure management, enabling developers to focus purely on application logic. Local testing tools reduce iteration time and increase confidence in deployments.
For Businesses: The “scale-to-zero” model and usage-based billing make Lambda cost-effective for small-scale projects while being robust enough for enterprise applications.
For AWS: By automating critical aspects like scaling, patching, and resource management, AWS Lambda showcases the potential of serverless computing to simplify cloud operations and increase developer productivity.
Conclusion
Lambda introduced the world to serverless computing where developers focus entirely on code and application logic, leaving infrastructure management to the cloud provider.
Organizations across industries, from startups to large enterprises, leverage Lambda to build scalable, cost-effective, and event-driven applications.
Over its first decade, Lambda has evolved through a relentless focus on customer needs. Customers often use services like Lambda in ways the creators didn’t anticipate, driving the need for continuous innovation and feature expansion. Therefore, customer feedback has been instrumental in shaping Lambda’s capabilities.
Looking ahead, AWS aims to further optimize cold starts and runtime performance, particularly for latency-sensitive applications. Greater integration with AWS and non-AWS services is expected, enabling Lambda to support a wider range of architectures and technologies.
References:
SPONSOR US
Get your product in front of more than 1,000,000 tech professionals.
Our newsletter puts your products and services directly in front of an audience that matters - hundreds of thousands of engineering leaders and senior engineers - who have influence over significant tech decisions and big purchases.
Space Fills Up Fast - Reserve Today
Ad spots typically sell out about 4 weeks in advance. To ensure your ad reaches this influential audience, reserve your space now by emailing sponsorship@bytebytego.com.