This week’s system design refresher:
Top 12 Tips for API Security
What happens when you type google .com into a browser?
A Cheatsheet on Infrastructure as Code Landscape
Why is Kafka fast?
A Crash Course on Architectural Scalability
SPONSOR US
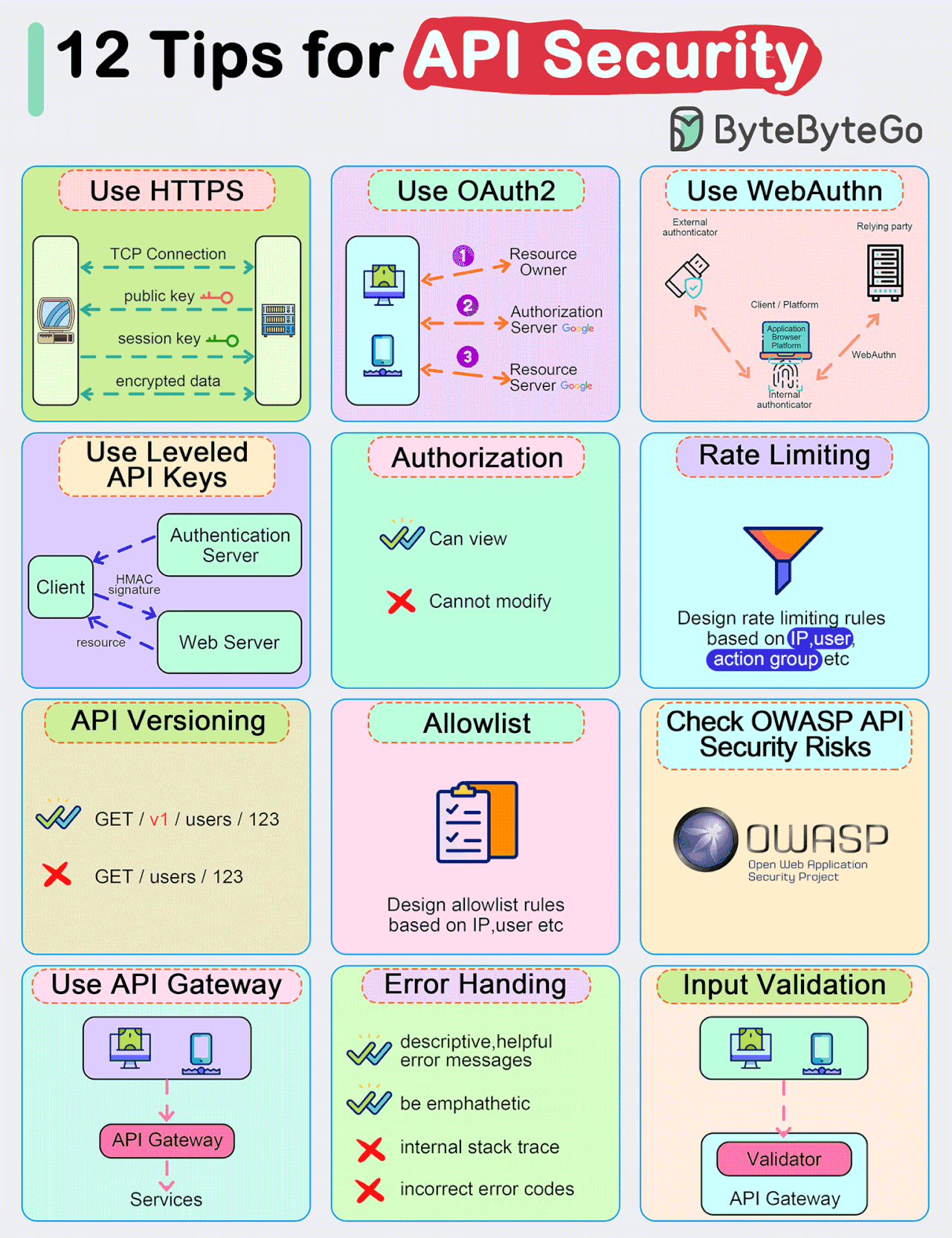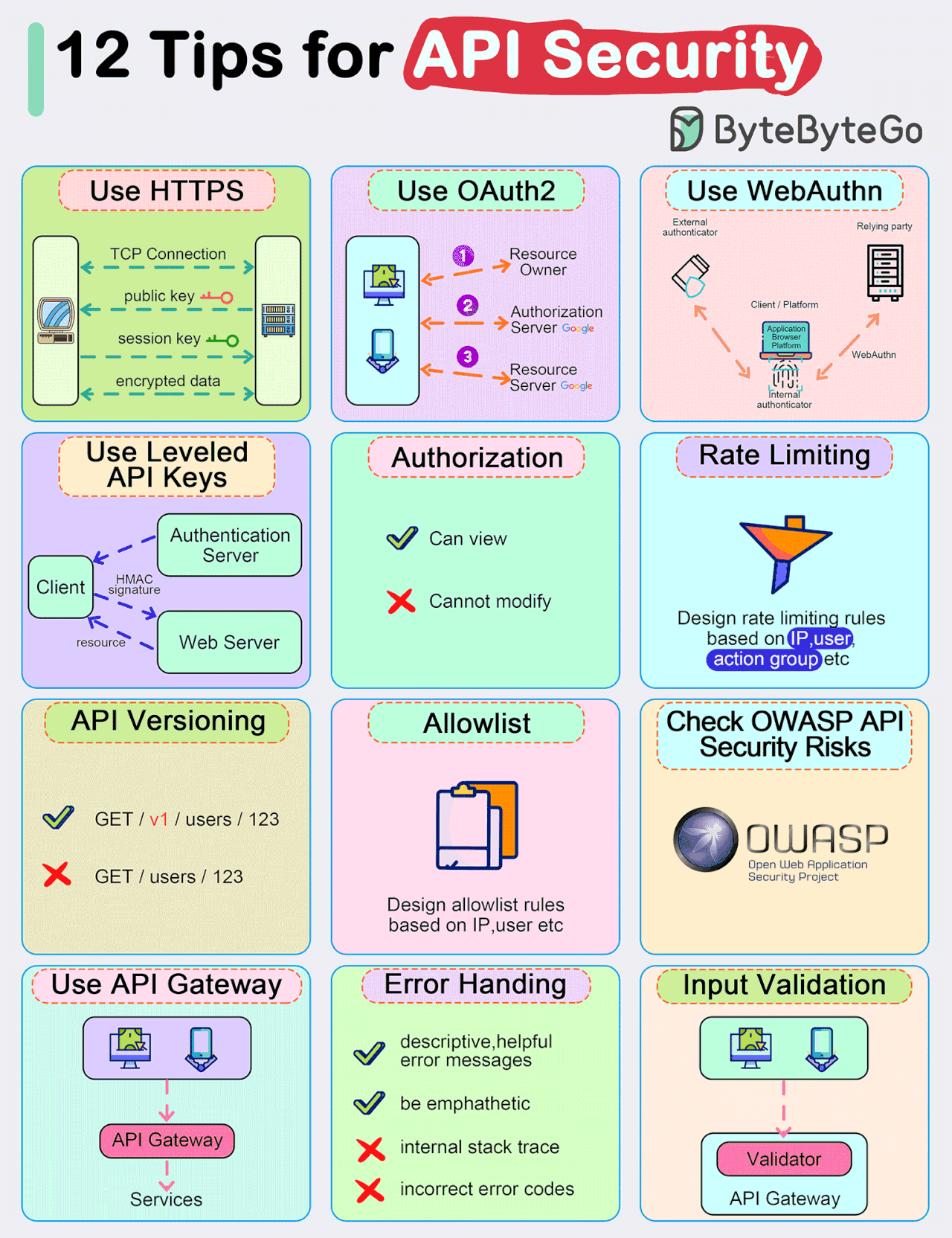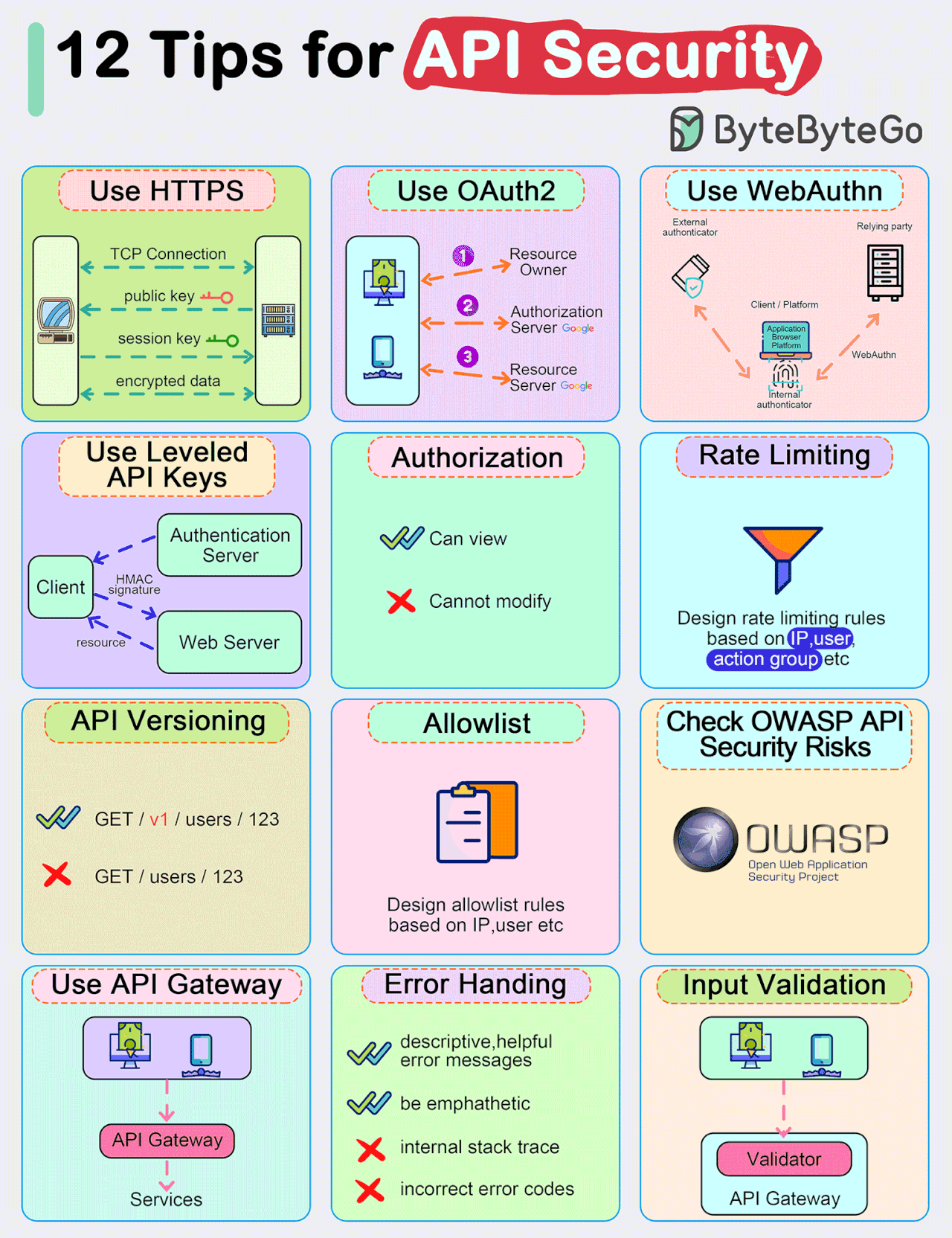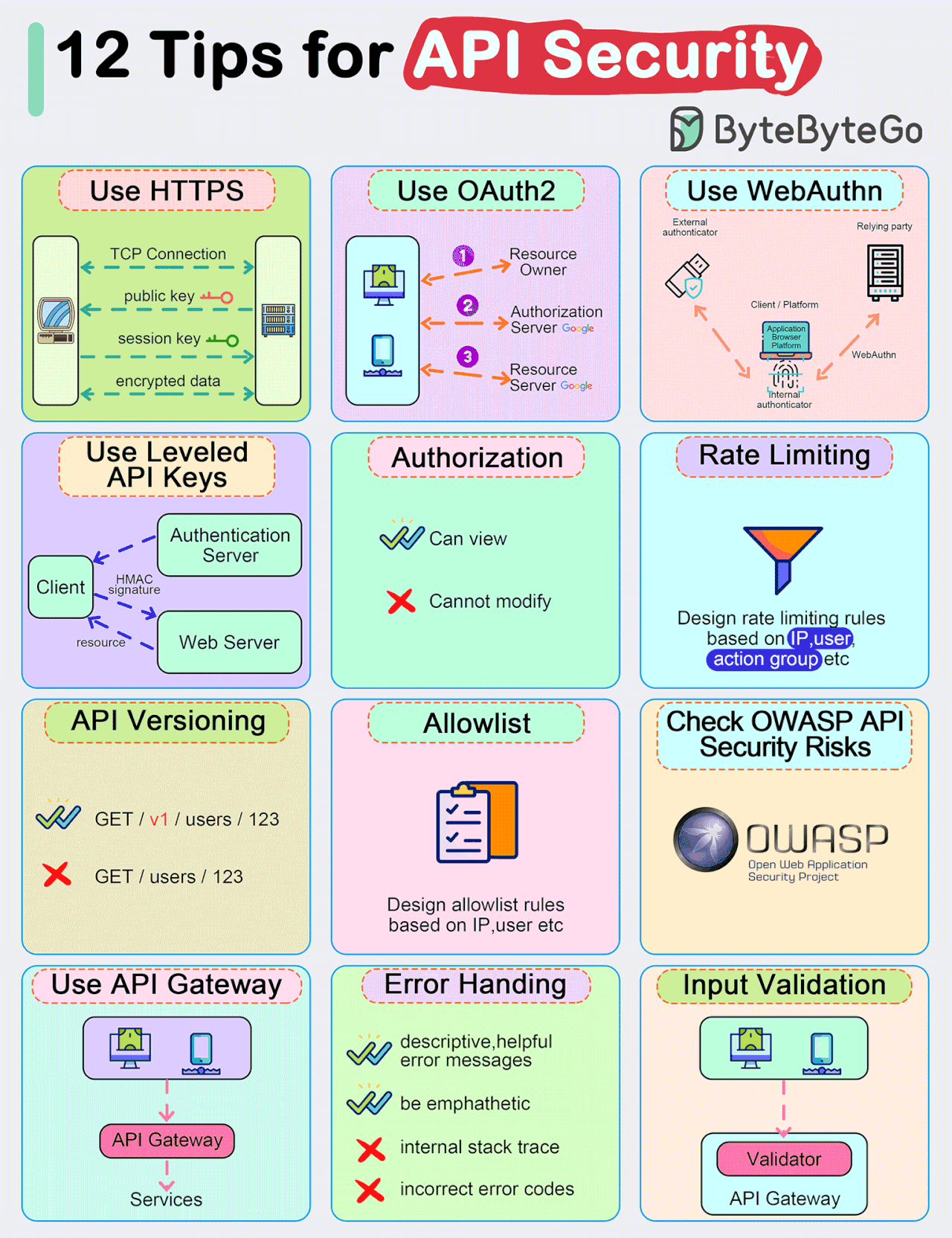
Top 12 Tips for API Security
Use HTTPS
Use OAuth2
Use WebAuthn
Use Leveled API Keys
Authorization
Rate Limiting
API Versioning
Whitelisting
Check OWASP API Security Risks
Use API Gateway
Error Handling
Input Validation
What happens when you type google .com into a browser?
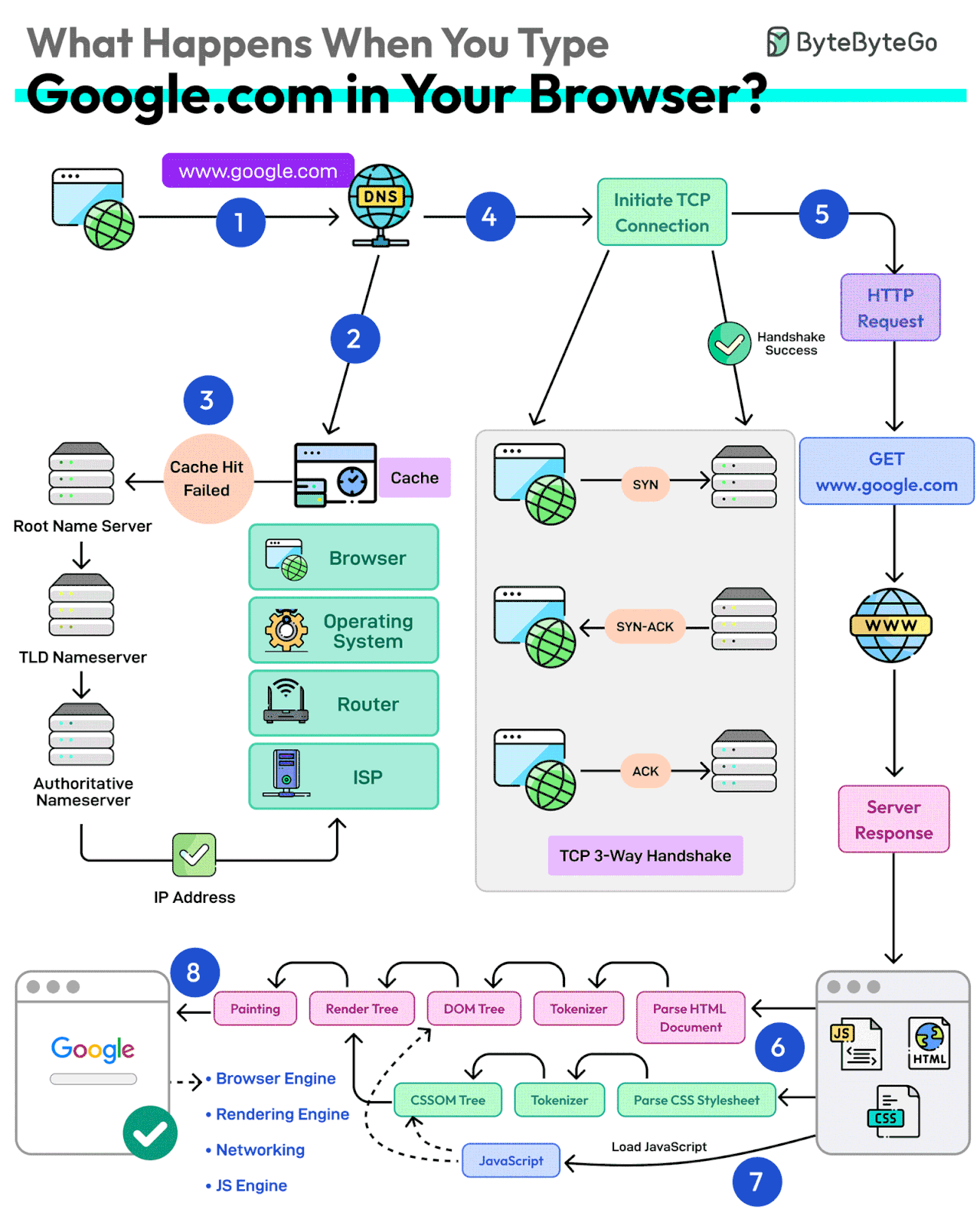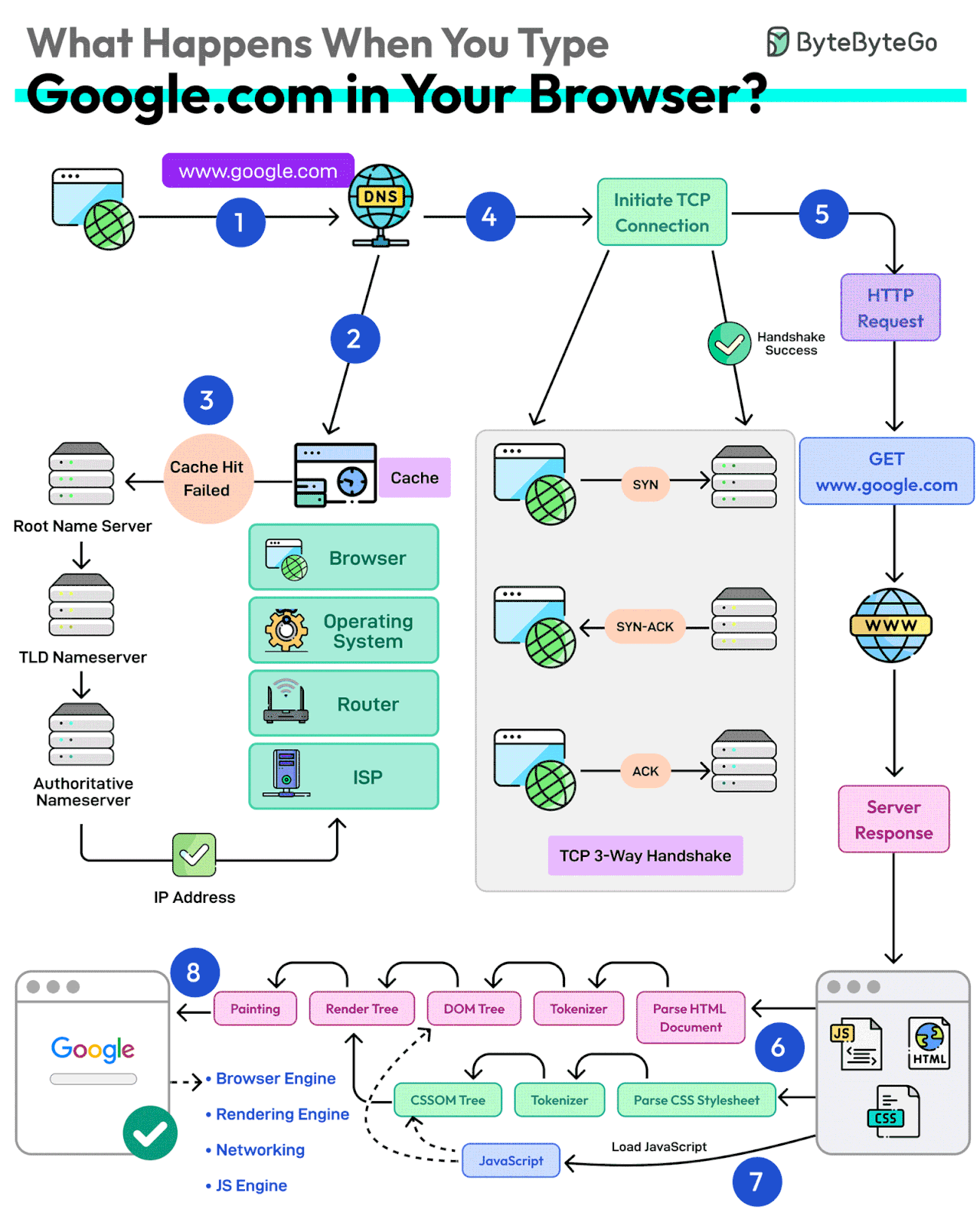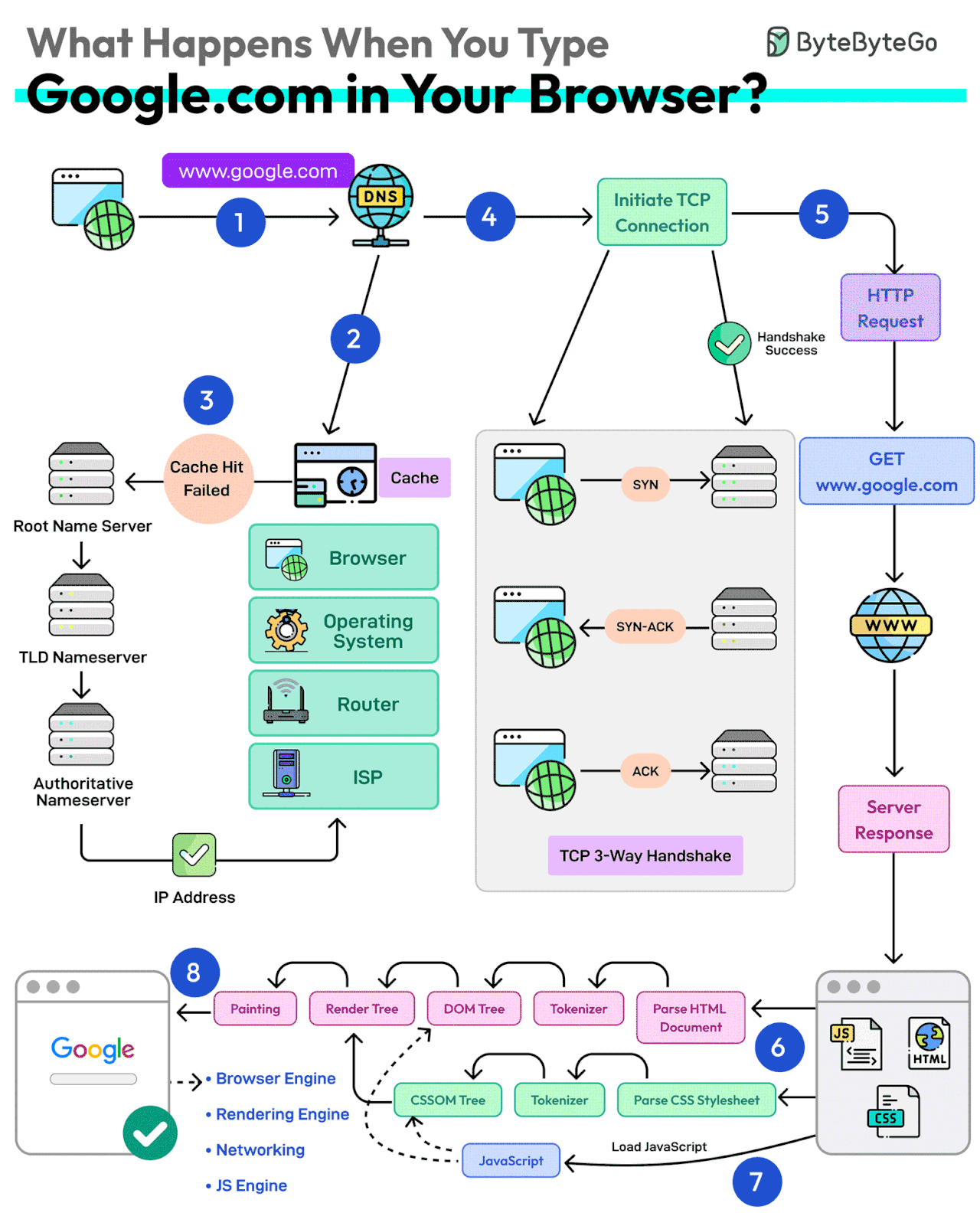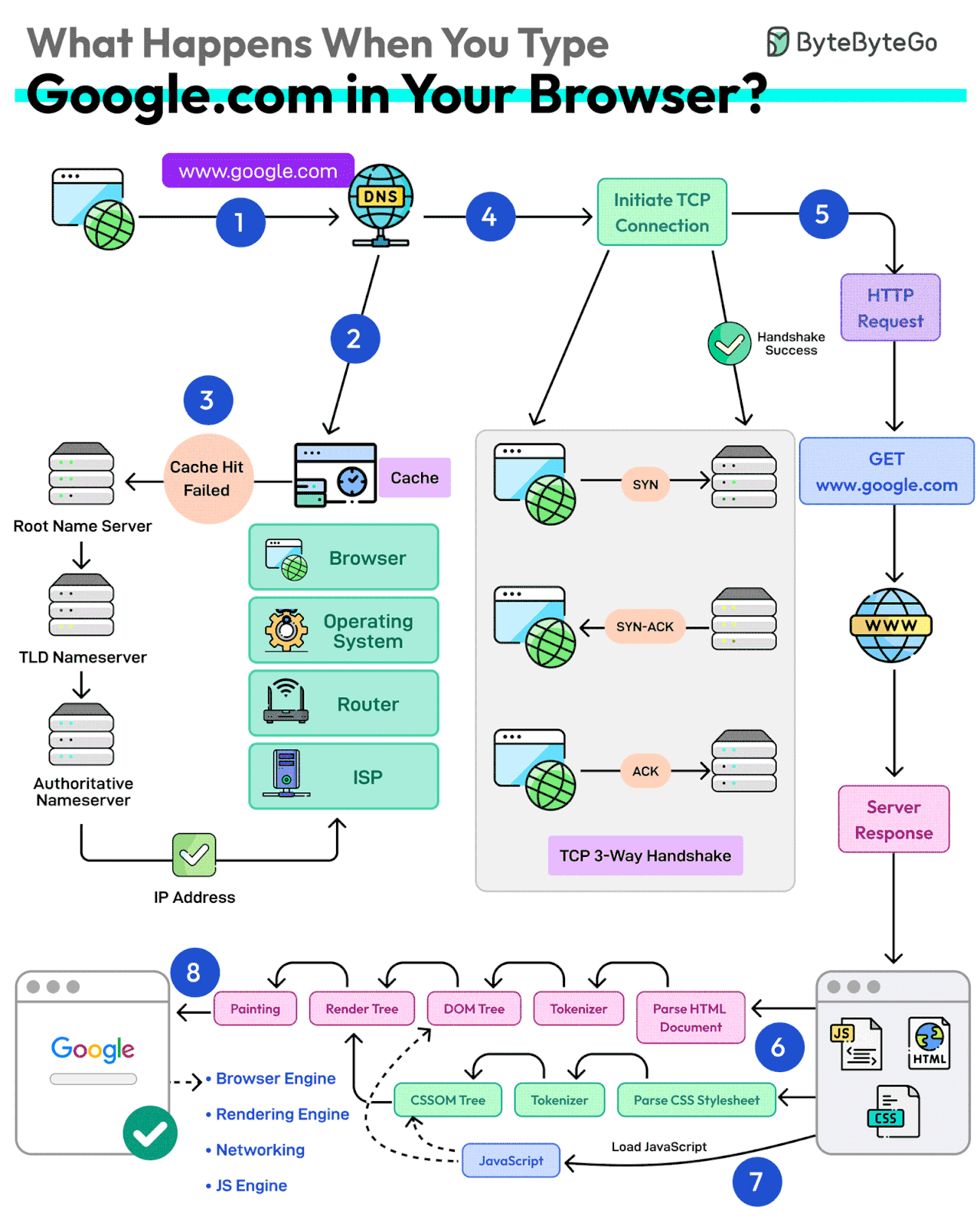
First up, you type the website address in the browser’s address bar.
The browser checks its cache first. If there’s a cache miss, it must find the IP address.
DNS lookup begins (think of it as looking up a phone number). The request goes through different DNS servers (root, TLD, and authoritative). Finally, the IP address is retrieved.
Next, your browser initiates a TCP connection like a handshake. For example, in the case of HTTP 1.1, the client and server perform a TCP three-way handshake with SYN, SYN-ACK, and ACK messages.
Once the handshake is successful, the browser makes an HTTP request to the server and the server responds with HTML, CSS, and JS files.
Finally, the browser processes everything. It parses the HTML document and creates DOM and CSSOM trees.
The browser executes the JavaScript and renders the page through various steps (tokenizer, parser, render tree, layout, and painting).
Finally, the webpage appears on your screen.
Over to you: Which other step will you add to the overall process?
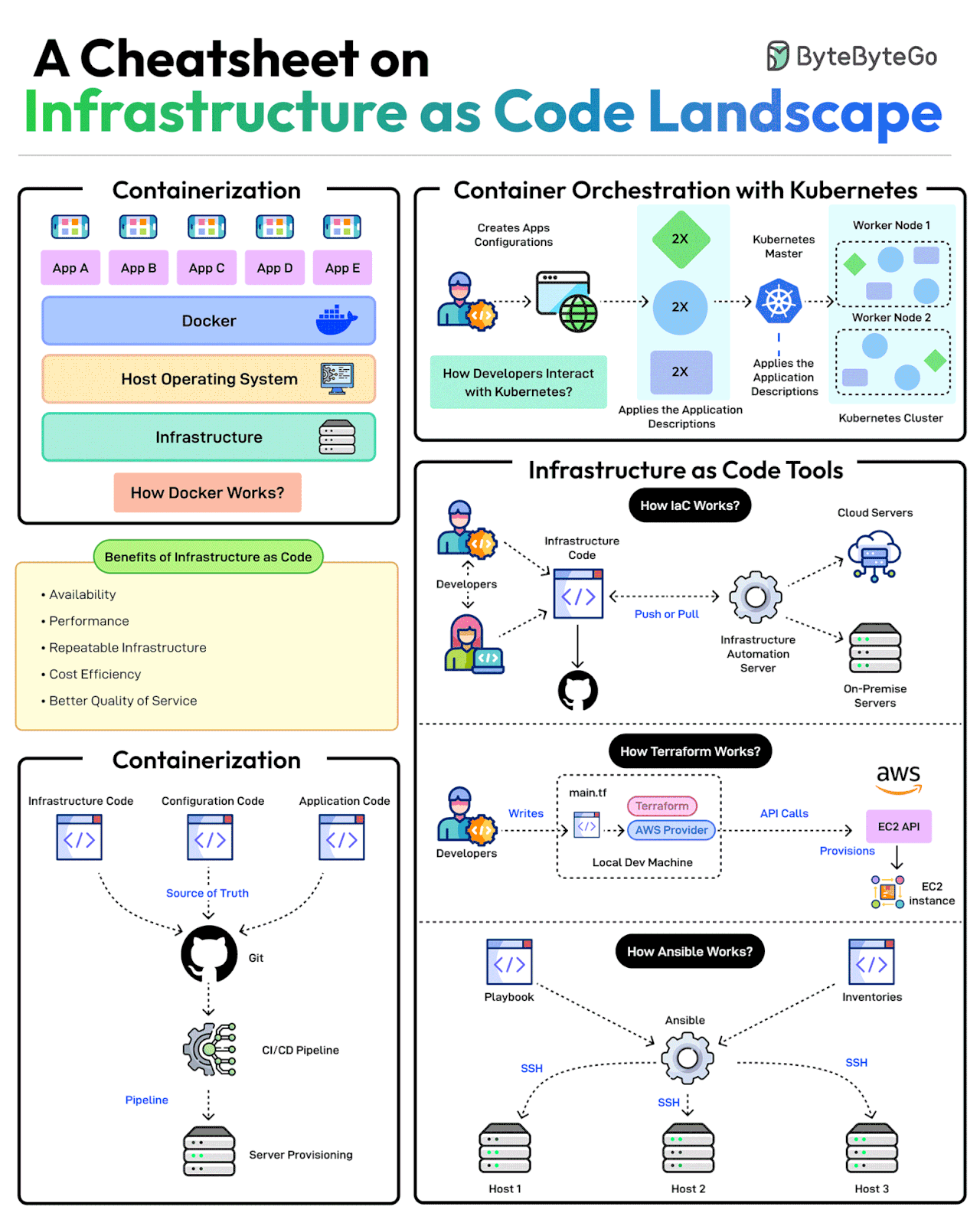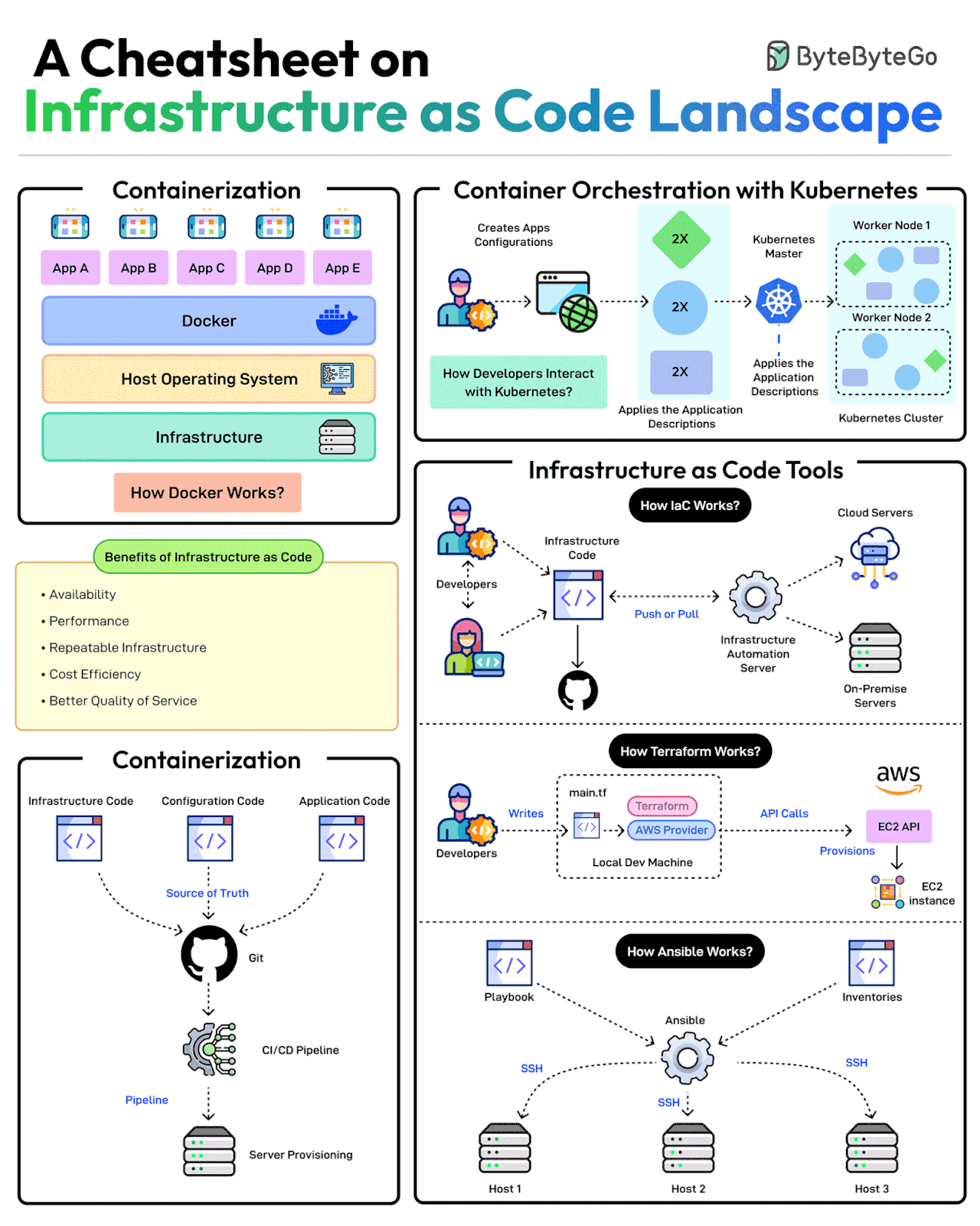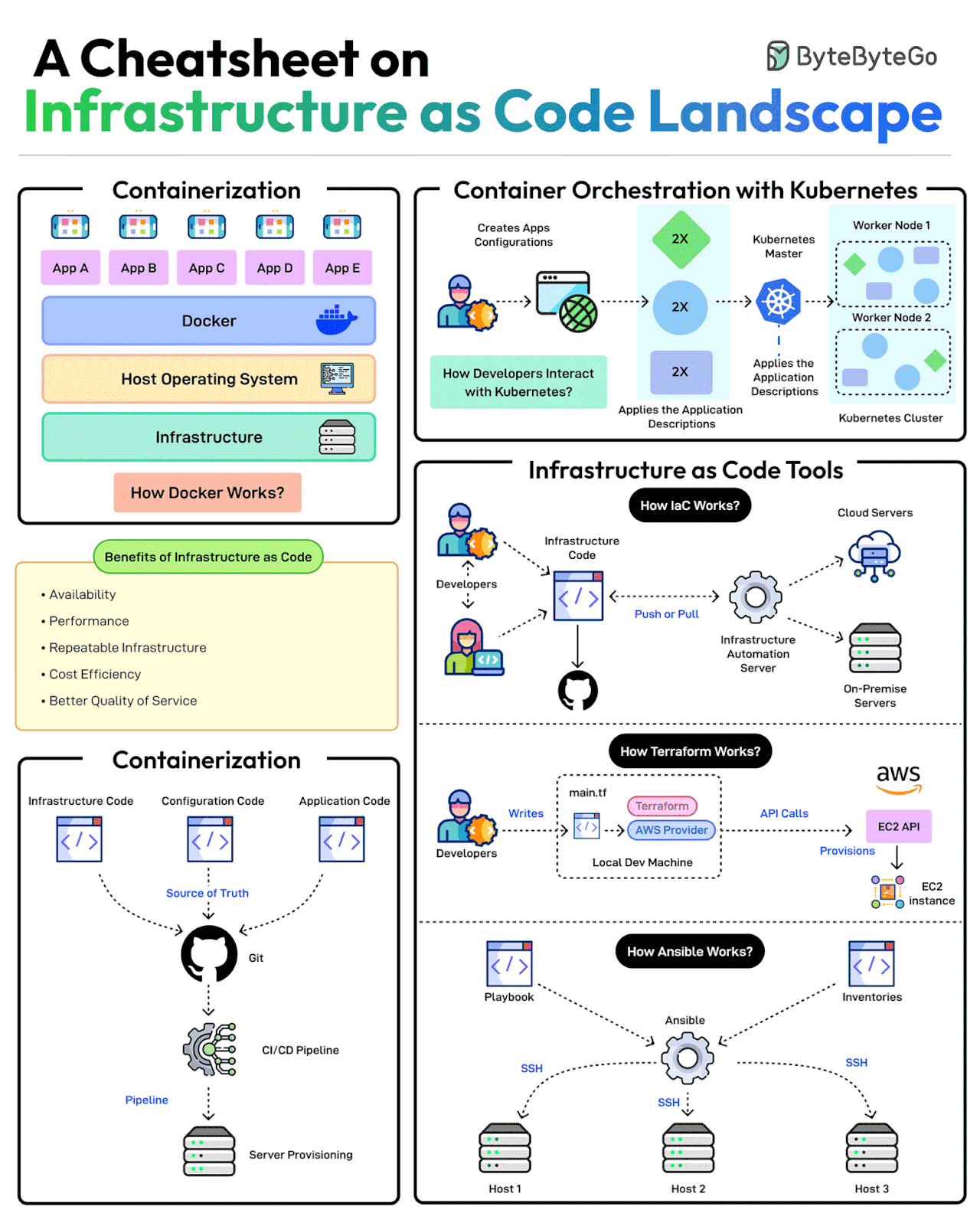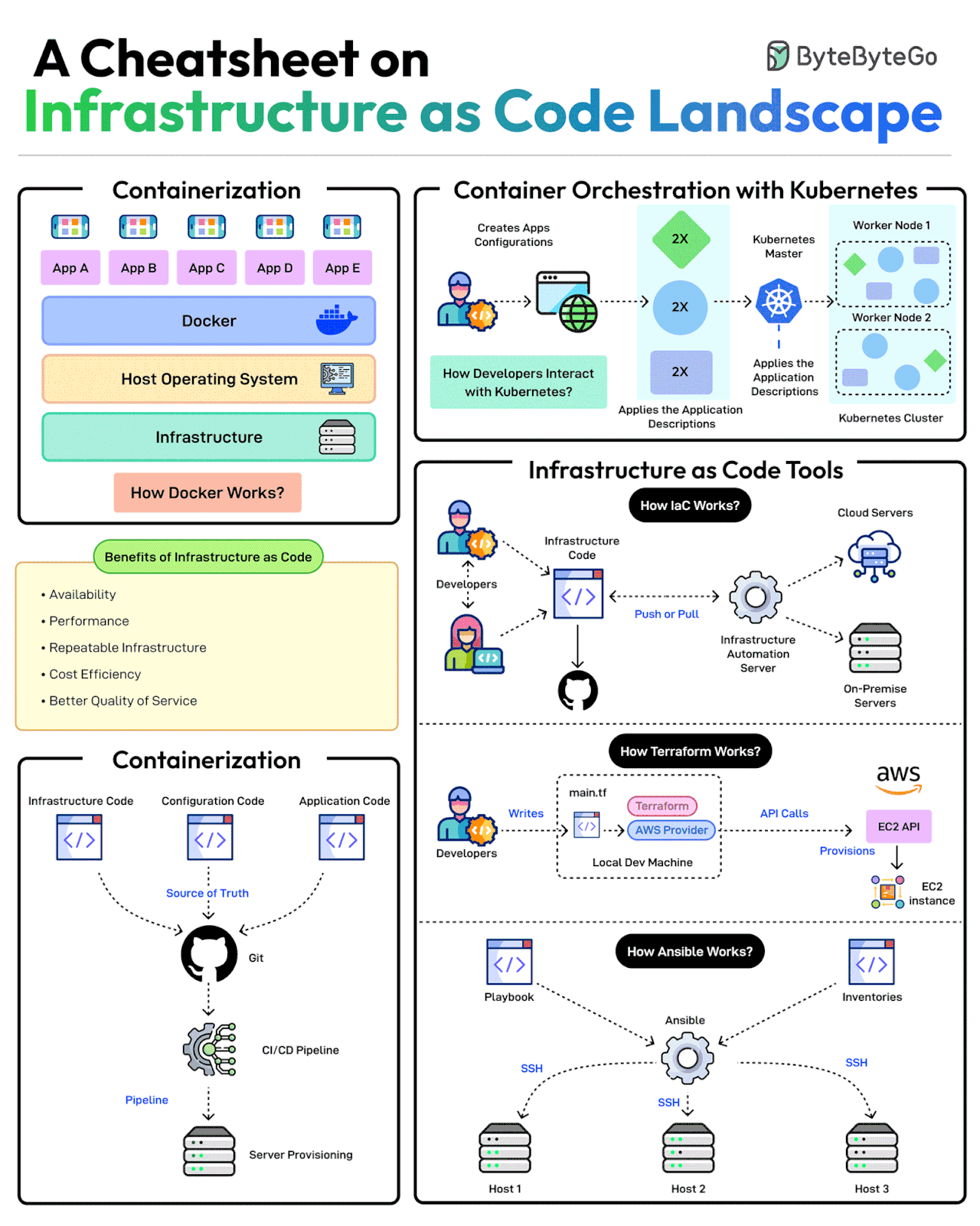
A Cheatsheet on Infrastructure as Code Landscape
Scalable infrastructure provisioning provides several benefits related to availability, scalability, repeatability, and cost-effectiveness.
But how do you achieve this?
Provisioning infrastructure using code is the key to scalable infra management.
There are multiple strategies that can help:
Containerization is one of the first strategies to make application deployments based on code. Docker is one of the most popular ways to containerize the application.
Next, container orchestration becomes a necessity when dealing with multiple containers in an application. This is where container orchestration tools like Kubernetes become important.
IaC treats infrastructure provisioning and configuration as code, allowing developers to define the application infrastructure in files that can be versioned, tested, and reused. Popular tools such as Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, and Ansible can be used. Ansible is more of a configuration tool.
GitOps leverages a Git workflow combined with CI/CD to automate infrastructure and configuration updates.
Over to you: Have you used Infrastructure as Code for your projects?
Why is Kafka fast?
There are many design decisions that contributed to Kafka’s performance. In this post, we’ll focus on two. We think these two carried the most weight.
The first one is Kafka’s reliance on Sequential I/O.
The second design choice that gives Kafka its performance advantage is its focus on efficiency: zero copy principle.
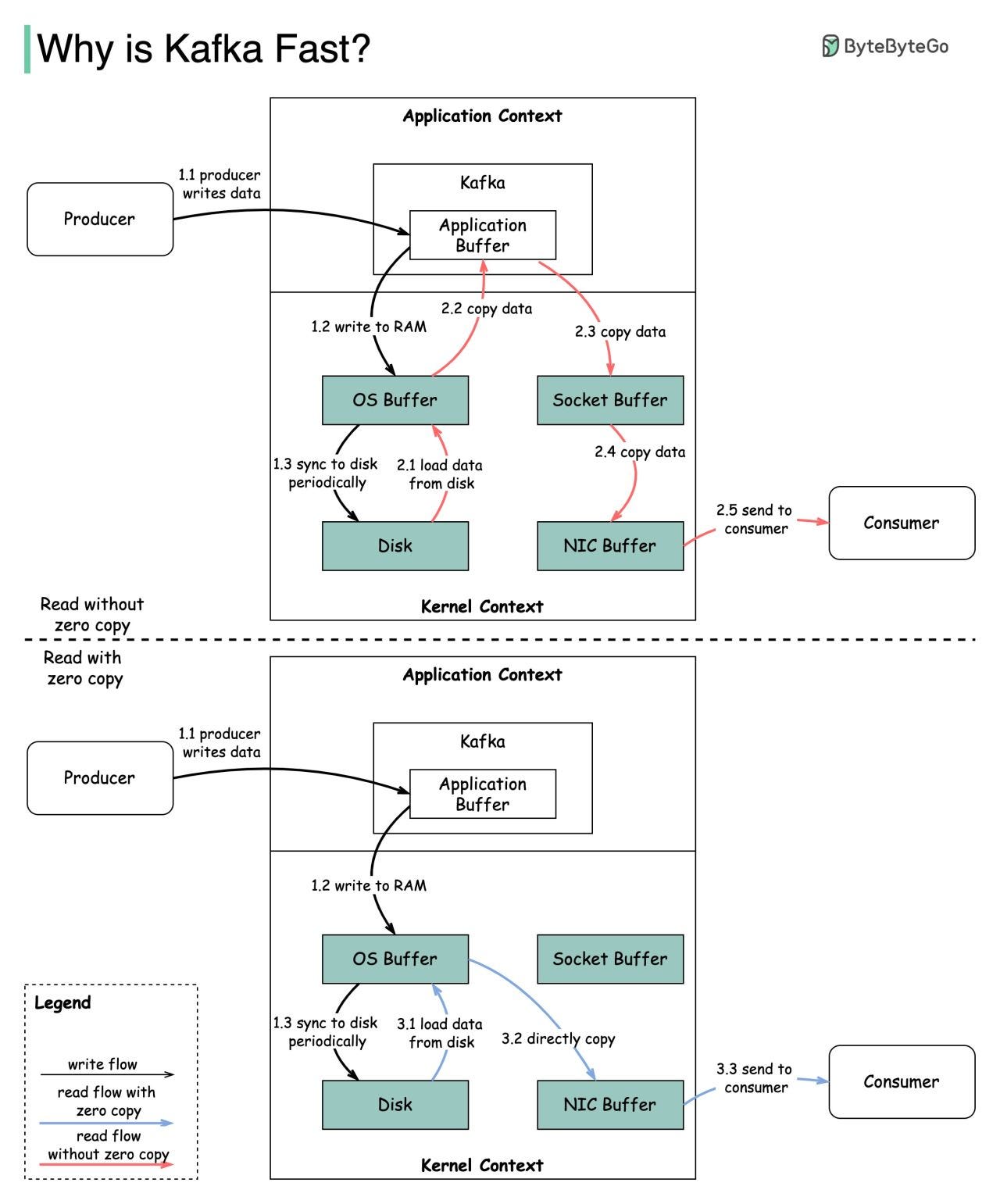
The diagram below illustrates how the data is transmitted between producer and consumer, and what zero-copy means.
Step 1.1 - 1.3: Producer writes data to the disk
Step 2: Consumer reads data without zero-copy
2.1: The data is loaded from disk to OS cache
2.2 The data is copied from OS cache to Kafka application
2.3 Kafka application copies the data into the socket buffer
2.4 The data is copied from socket buffer to network card
2.5 The network card sends data out to the consumer
Step 3: Consumer reads data with zero-copy
3.1: The data is loaded from disk to OS cache
3.2 OS cache directly copies the data to the network card via sendfile() command
3.3 The network card sends data out to the consumer
Zero copy is a shortcut to save multiple data copies between the application context and kernel context.
A Crash Course on Architectural Scalability
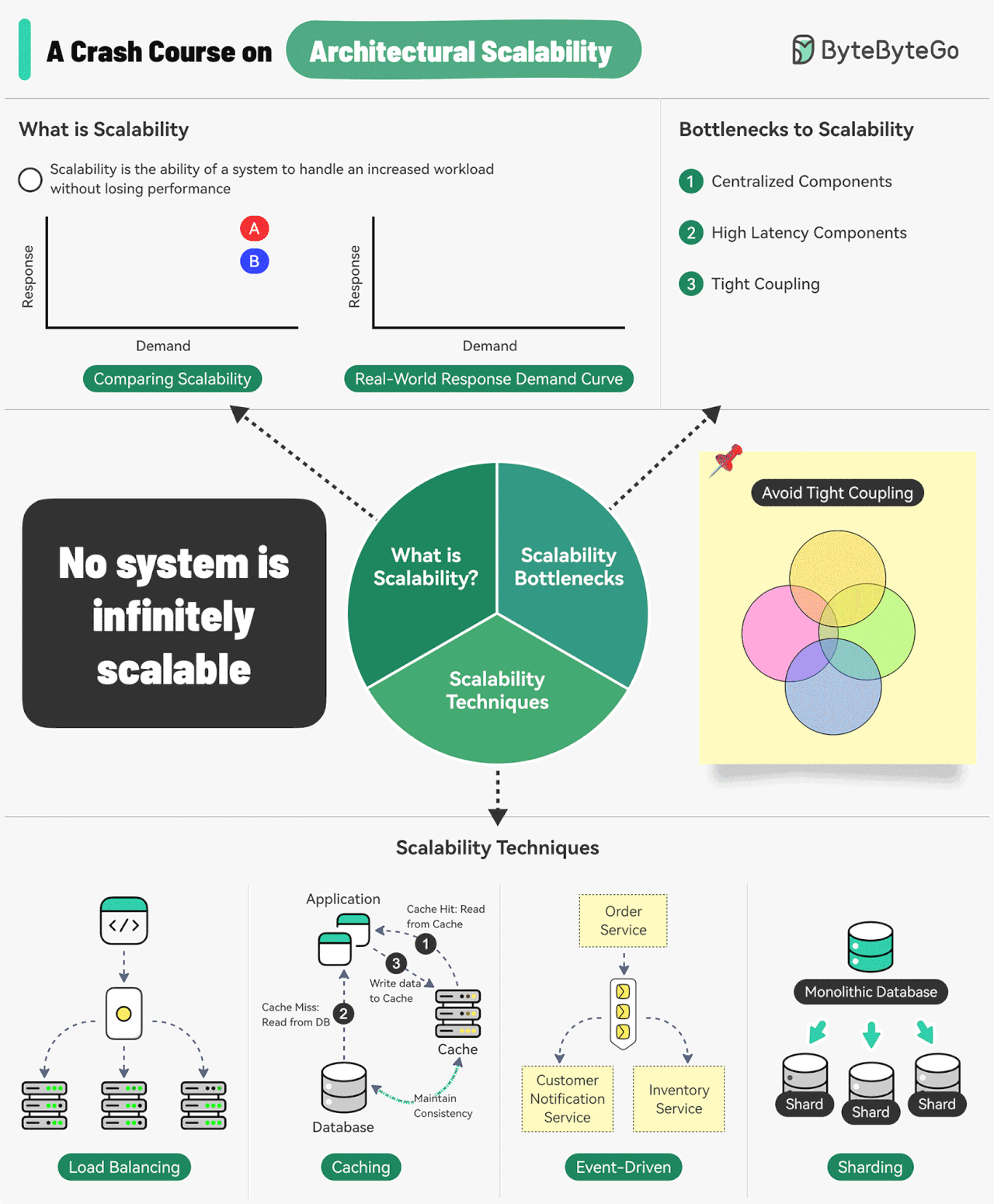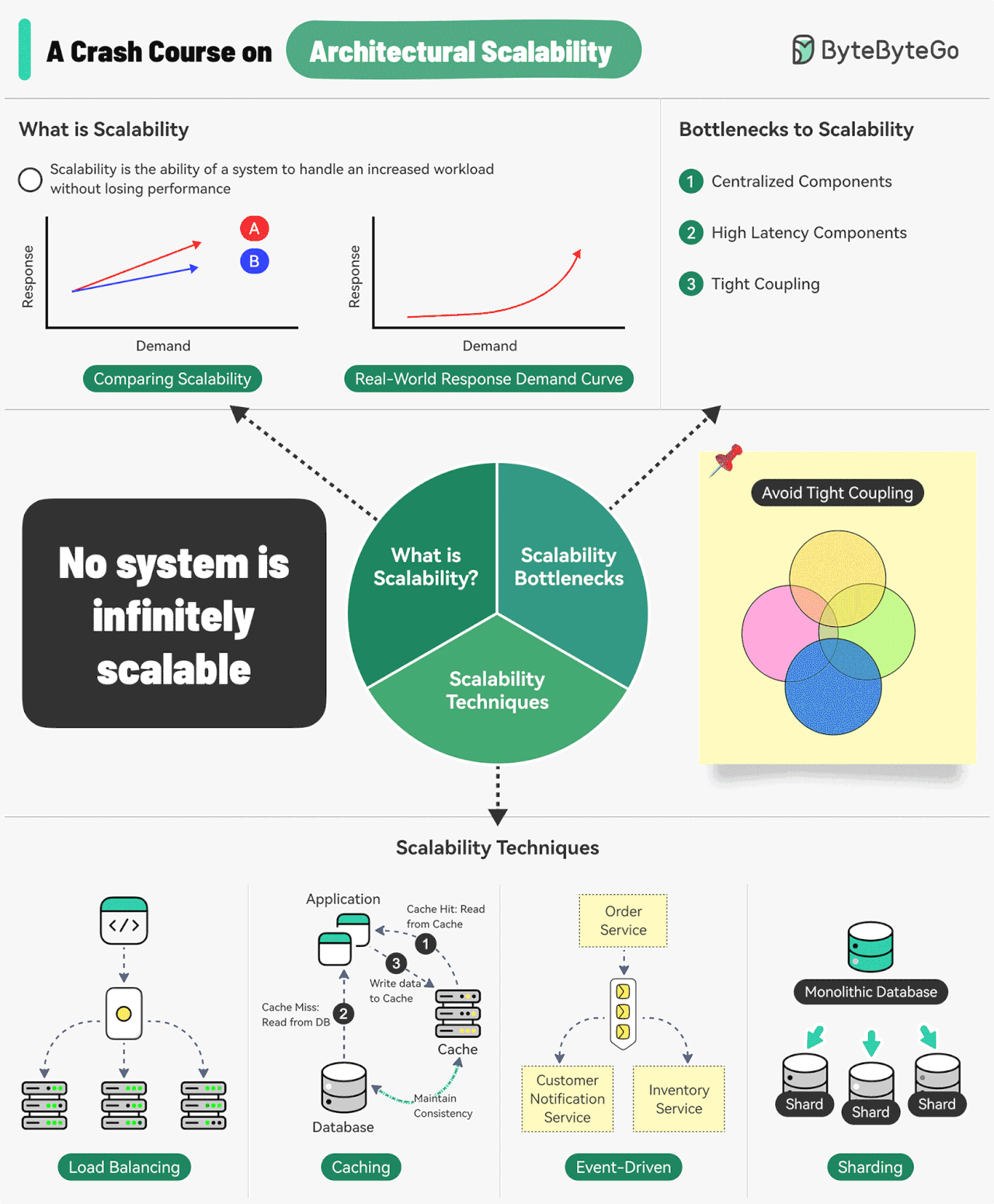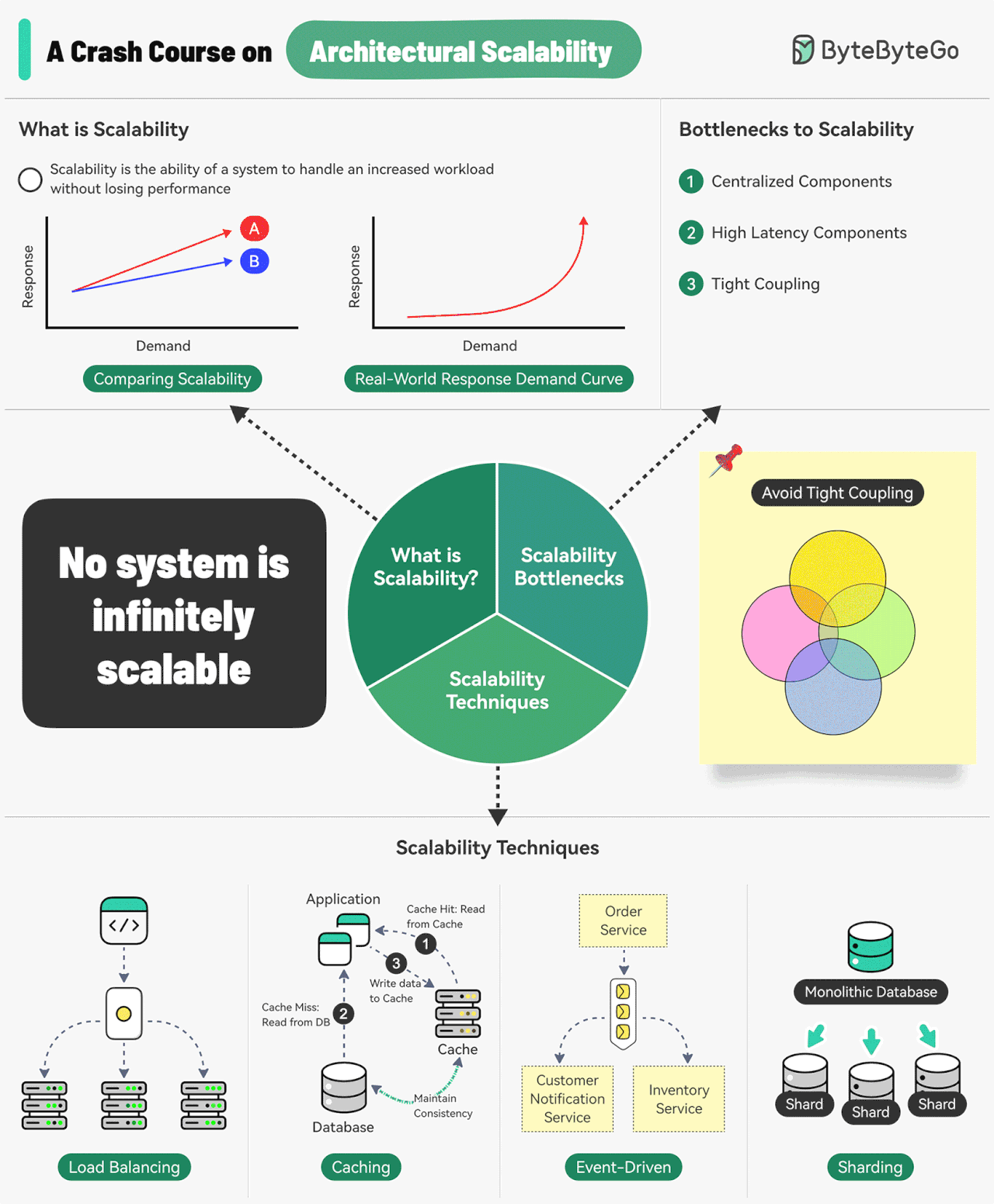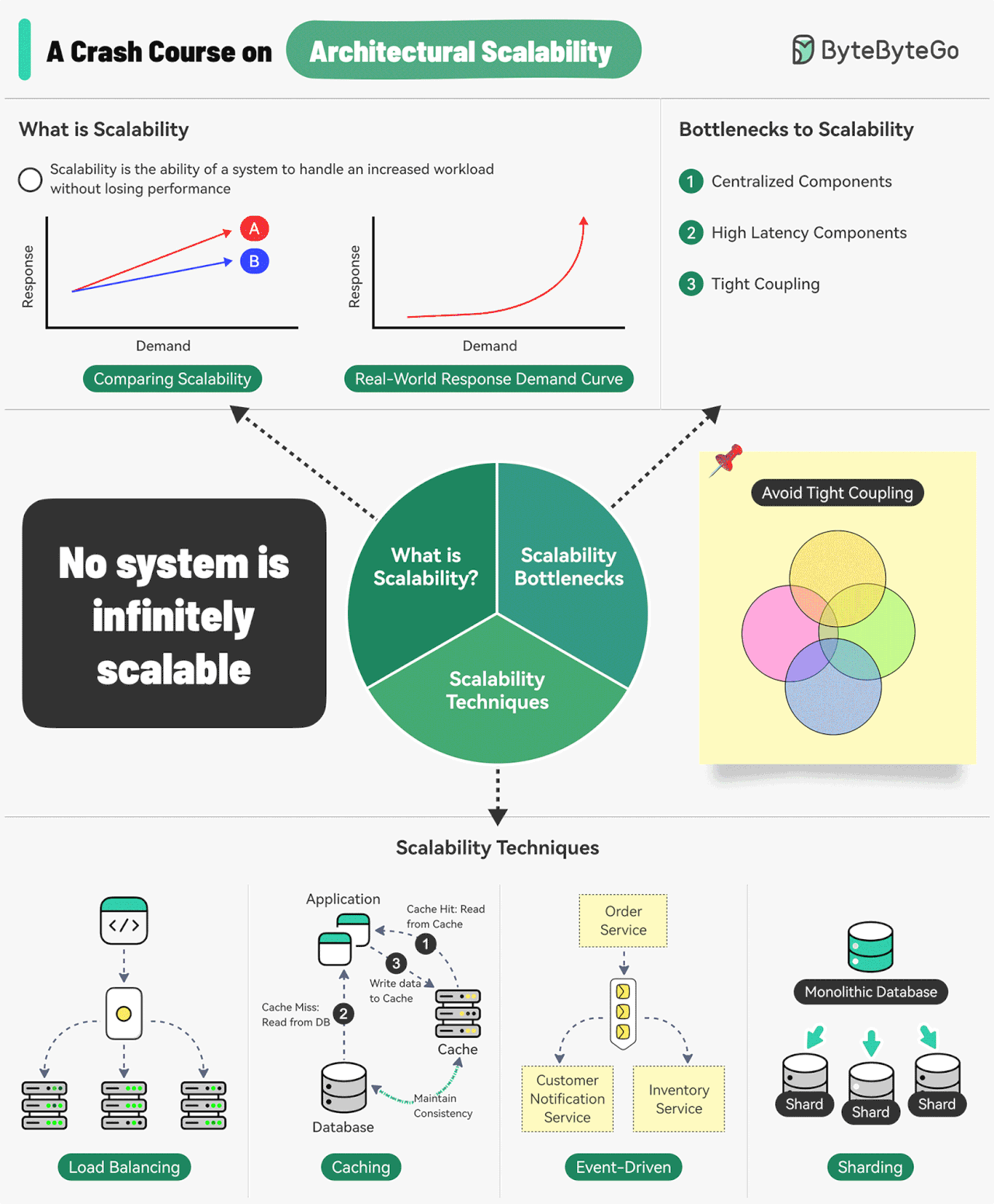
Scalability is the ability of a system to handle an increased workload without losing performance.
However, we can also look at scalability in terms of the scaling strategy.
Scalability is the system’s ability to handle an increased workload by repeatedly applying a cost-effective strategy. This means it can be difficult to scale a system beyond a certain point if the scaling strategy is not financially viable.
Three main bottlenecks to scalability are:
Centralized components: This can become a single point of failure
High Latency Components: These are components that perform time-consuming operations.
Tight Coupling: Makes the components difficult to scale
Therefore, to build a scalable system, we should follow the principles of statelessness, loose coupling, and asynchronous processing.
Some common techniques for improving scalability are as follows:
Load Balancing: Spread requests across multiple servers to prevent a single server from becoming a bottleneck.
Caching: Store the most commonly request information in memory.
Event-Driven Processing: Use an async processing approach to process long-running tasks.
Sharding: Split a large dataset into smaller subsets called shards for horizontal scalability.
Over to you: How do you improve a system’s scalability?
SPONSOR US
Get your product in front of more than 1,000,000 tech professionals.
Our newsletter puts your products and services directly in front of an audience that matters - hundreds of thousands of engineering leaders and senior engineers - who have influence over significant tech decisions and big purchases.
Space Fills Up Fast - Reserve Today
Ad spots typically sell out about 4 weeks in advance. To ensure your ad reaches this influential audience, reserve your space now by emailing sponsorship@bytebytego.com.