
Over the course of the year, we’ve had the pleasure of working with many talented researchers from across the globe. As 2024 draws to a close, we take a look back at some of the excellent blog posts from our contributors.
Generating physically-consistent local-scale climate change projections
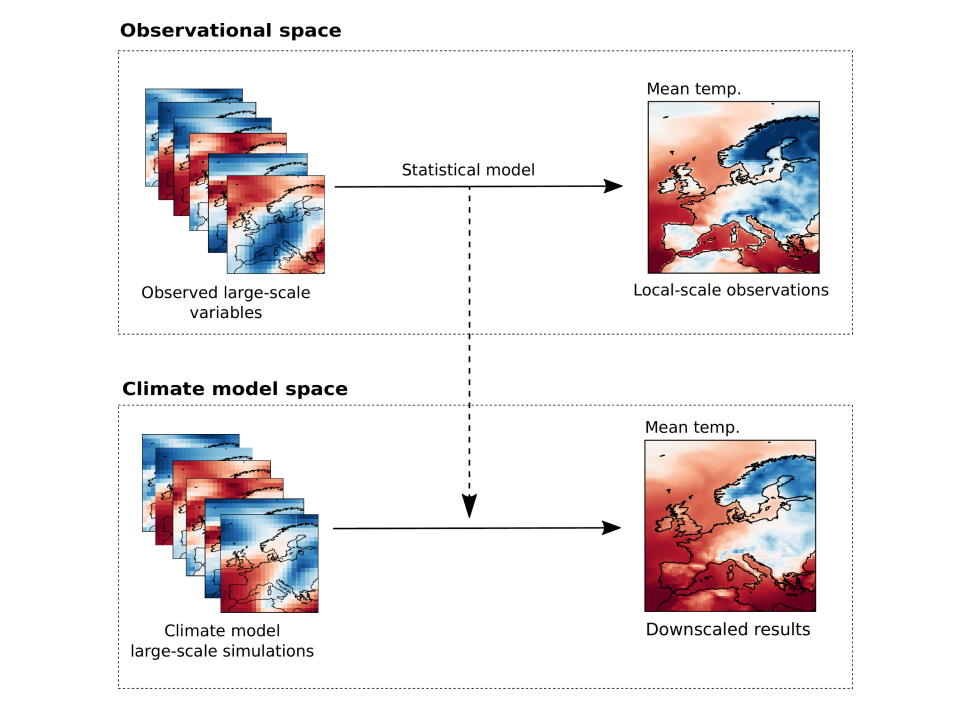
Jose González-Abad reports on work on statistical downscaling for climate models, and introduces a framework which encodes physical constraints to improve consistency and robustness.
Theoretical remarks on feudal hierarchies and reinforcement learning
Diogo Carvalho writes about research on hierarchical reinforcement learning, work that won him and his colleagues a best paper award at ECAI 2023.
Crowdsourced clustering via active querying
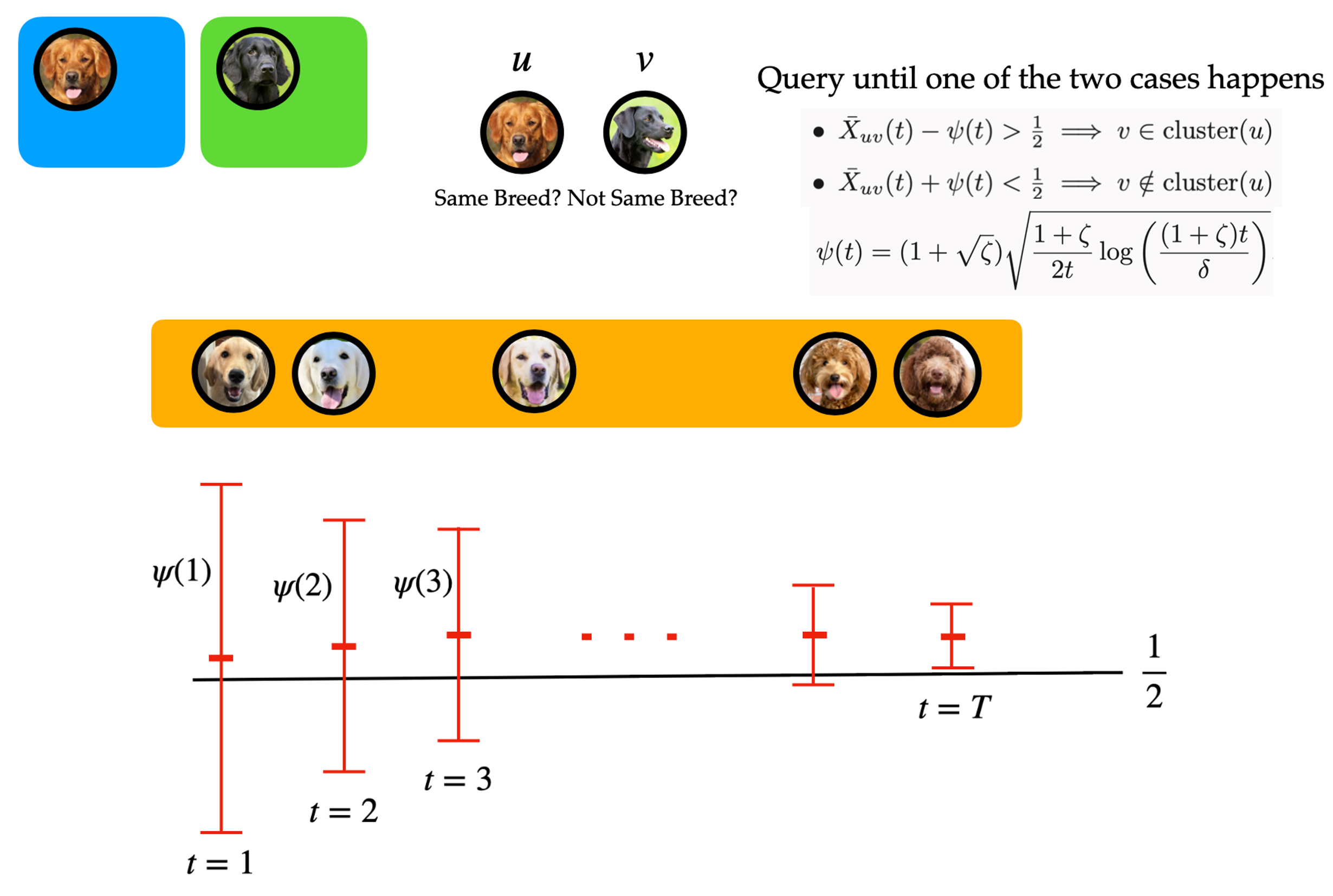
Yi Chen, Ramya Korlakai Vinayak and Babak Hassibi write about crowdsourced clustering: finding clusters in a dataset with unlabelled items by querying pairs of items for similarity.
The moderating effect of instant runoff voting
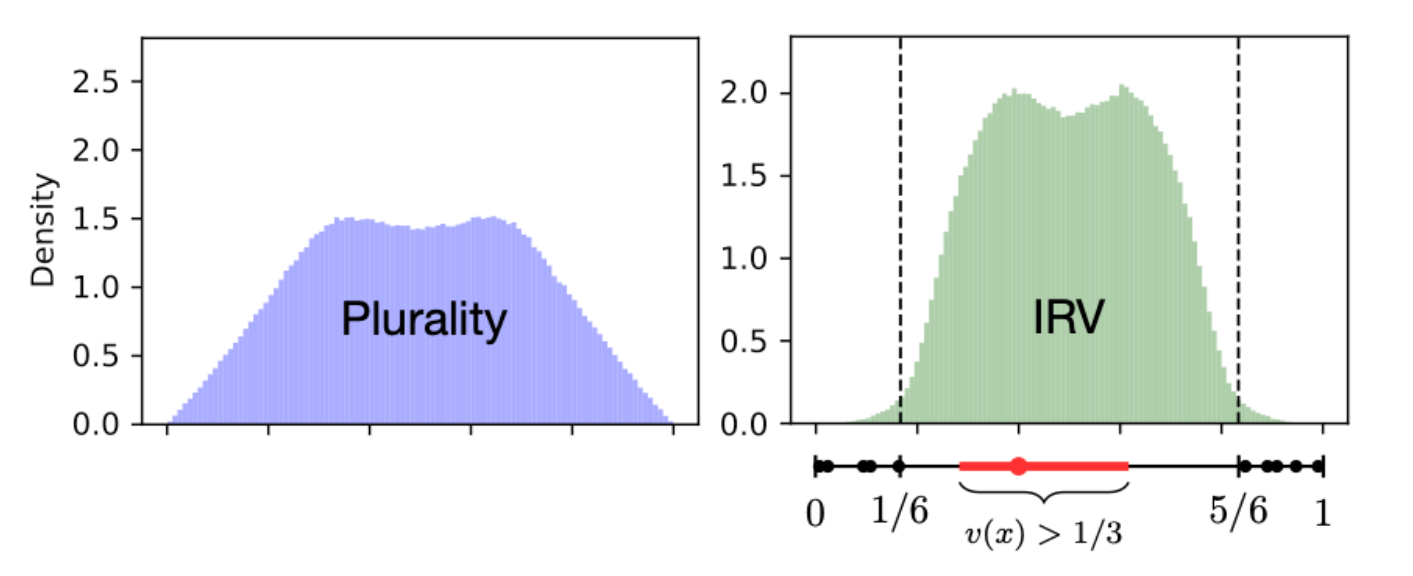
Kiran Tomlinson considers the instant runoff voting system and provide a mathematical backing for the argument that it favours moderate candidates in a way that plurality doesn’t.
An iterative refinement model for PROTAC-induced structure prediction
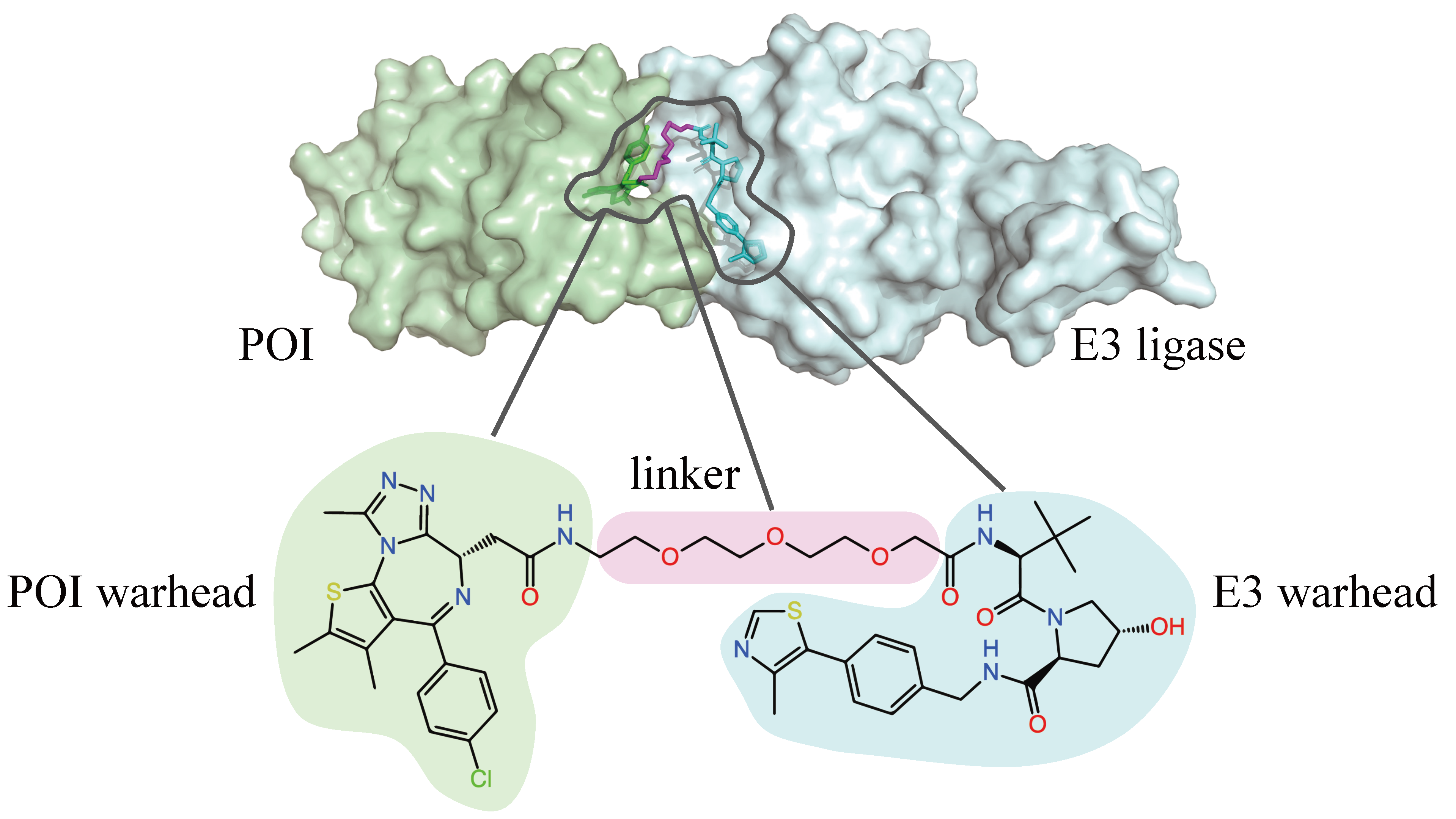
Proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) are small molecules that trigger the breakdown of traditionally “undruggable” proteins by binding simultaneously to their targets and degradation-associated proteins. Bo Qiang, Wenxian Shi, Yuxuan Song and Menghua Wu detail their work on PROTAC-induced structure prediction.
Learning programs with numerical reasoning
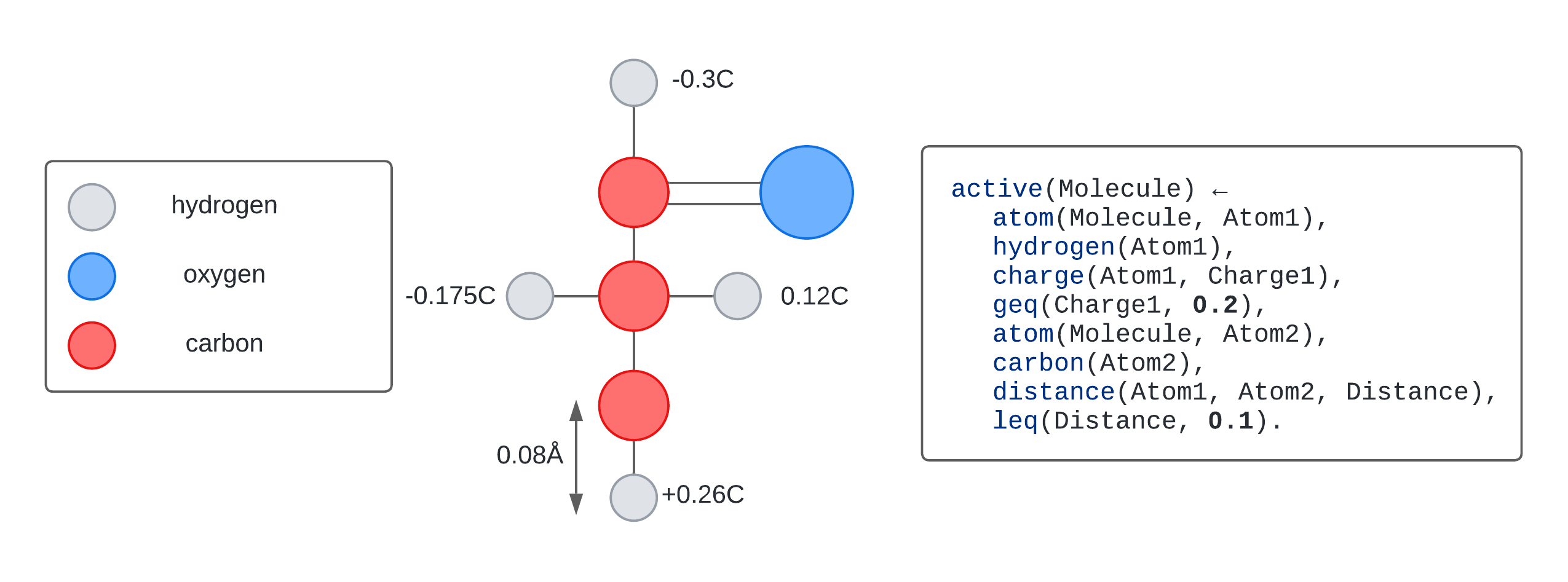
Inductive logic programming is a form of program synthesis that can learn explainable programs from small numbers of examples. Current approaches struggle to learn programs with numerical values. Céline Hocquette writes about work introducing a novel approach to dealing with these numerical values.
Are models biased on text without gender-related language?
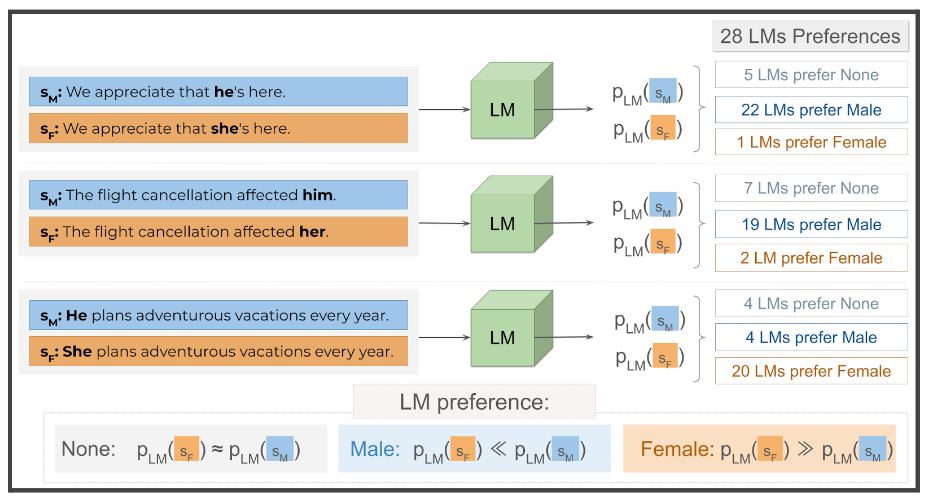
Catarina G Belém and colleagues audited 28 popular language models to find out whether such models display gender biases in stereotype-free contexts. They found that, contrary to prior assumptions, gender bias does not solely stem from the presence of gender-related words in sentences.
Bridging the gap between user expectations and AI capabilities: Introducing the AI-DEC design tool
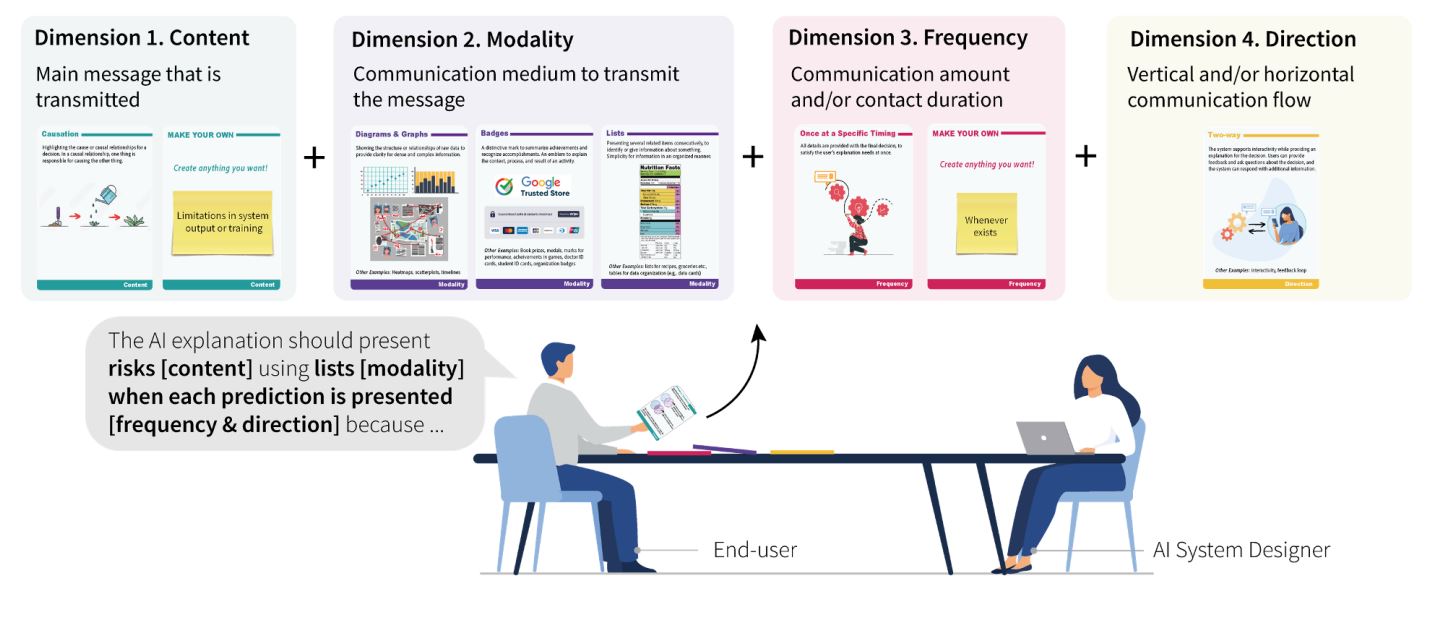
Christine Lee presents AI-DEC, a participatory design tool that enables users and AI systems to communicate their perspectives and collaboratively build AI explanations.
Proportional aggregation of preferences for sequential decision making
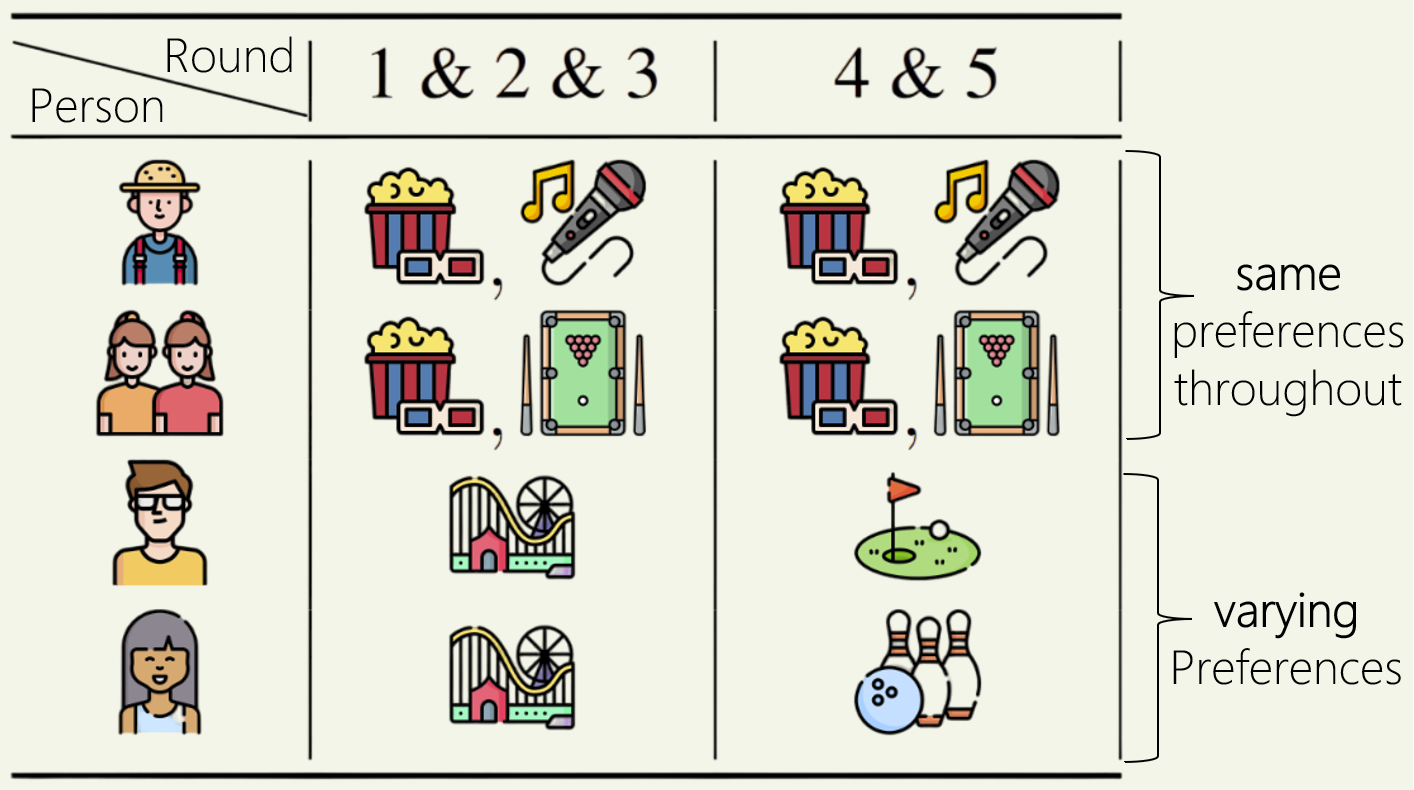
Nikhil Chandak and Shashwat Goel address the challenge of ensuring fairness in sequential decision making, leveraging proportionality concepts from social choice theory.
Building trust in AI: Transparent models for better decisions
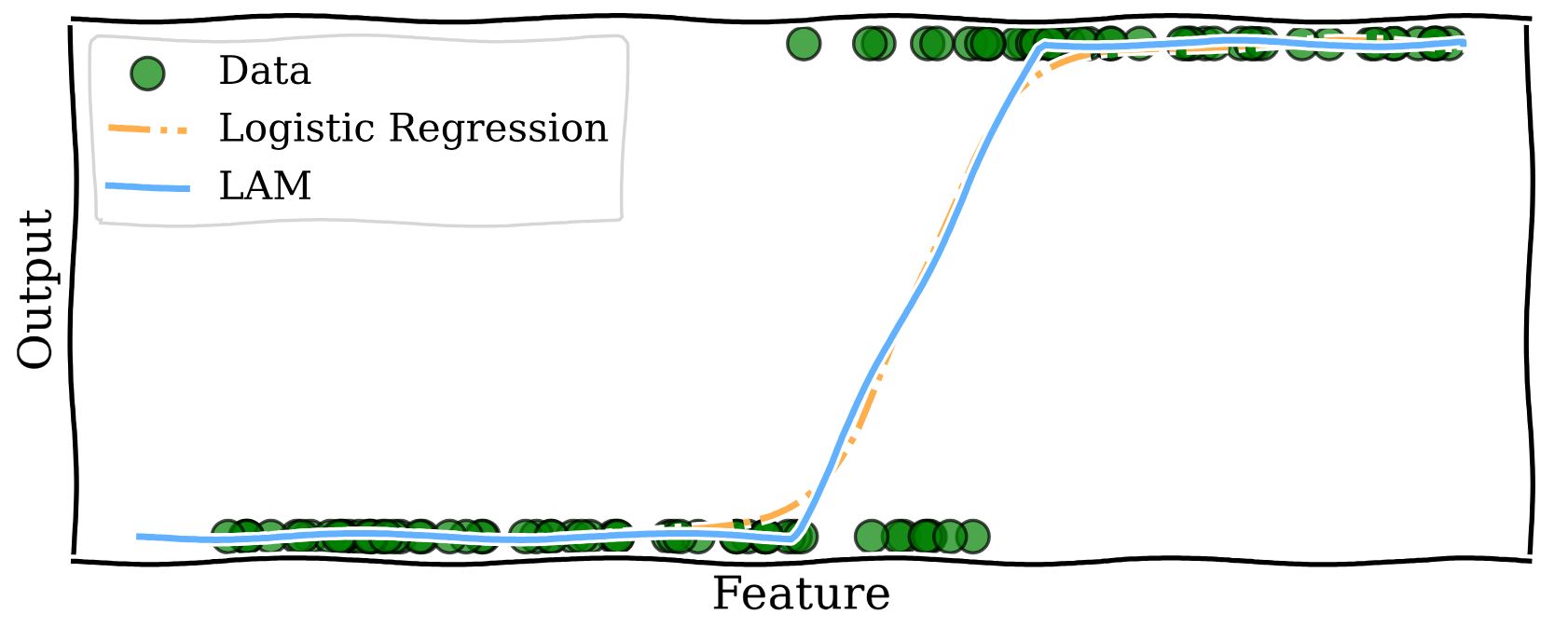
Danial Dervovic is working on improving the interpretability of logistic regression models, proposing an augmentation to such models, which makes decisions made by them more understandable.
Enhancing controlled query evaluation through epistemic policies
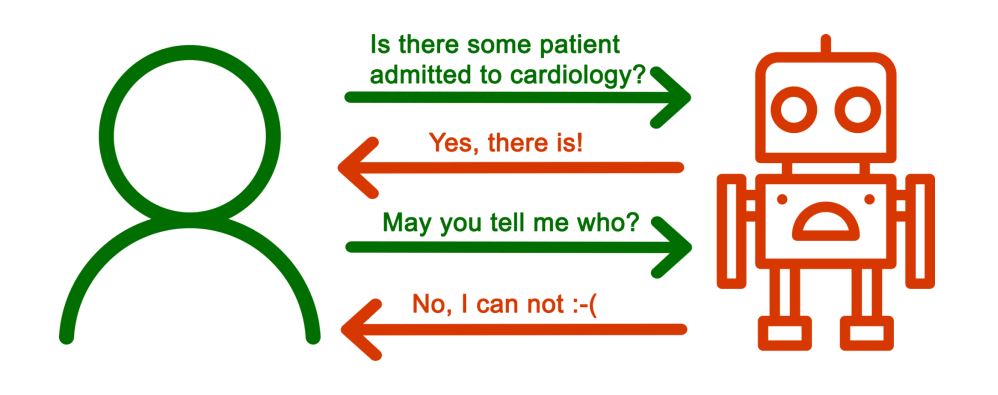
A significant data challenge concerns the sharing of information without compromising sensitive details. Gianluca Cima, Domenico Lembo, Lorenzo Marconi, Riccardo Rosati and Domenico Fabio Savo present the controlled query evaluation framework – an approach that safeguards confidentiality whilst still providing answers to queries.
Dynamic faceted search: from haystack to highlight
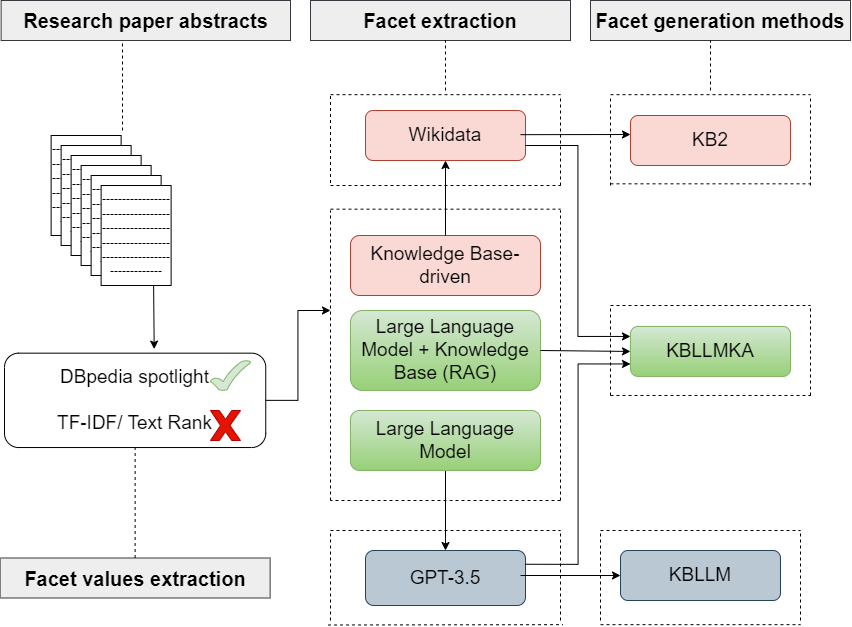
The number of scholarly articles is growing rapidly, and finding the most relevant information from this vast collection of data can be daunting. Mutahira Khalid, Sören Auer and Markus Stocker utilise facet generation, an advanced search method that allows users to filter and refine search results.
Improving calibration by relating focal loss, temperature scaling, and properness
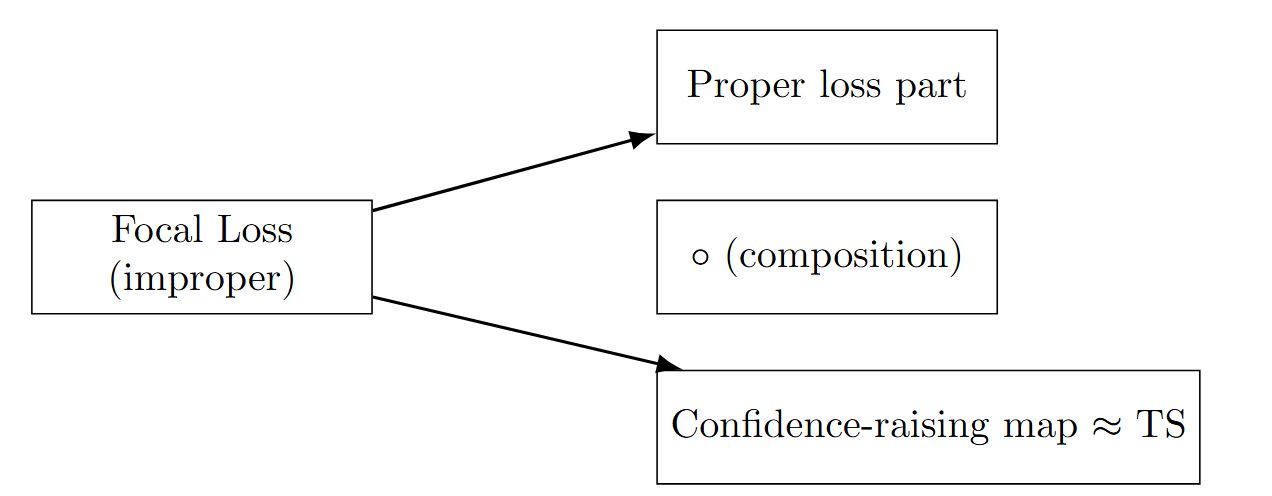
A key factor influencing both the accuracy and calibration of a model is the choice of the loss function during training. Viacheslav Komisarenko explores how to choose a loss function to achieve good calibration.
Multi-agent path finding in continuous environments

How can a group of agents minimise their journey length whilst avoiding collisions? Kristýna Janovská and Pavel Surynek explain all.

